給定無環圖中每層最小元素之和
不包含任何迴圈或迴路的圖稱為無環圖。樹是一種無環圖,其中每個節點都連線到另一個唯一的節點。無環圖也稱為無環圖。
環圖和無環圖的區別 -
環圖 |
無環圖 |
|---|---|
圖形成閉環。 |
圖不形成閉環。 |
圖不包含深度迴圈 |
圖包含每個深度。 |
示例 1
讓我們舉一個環圖的例子 -
當存在閉環時,就會形成環圖。
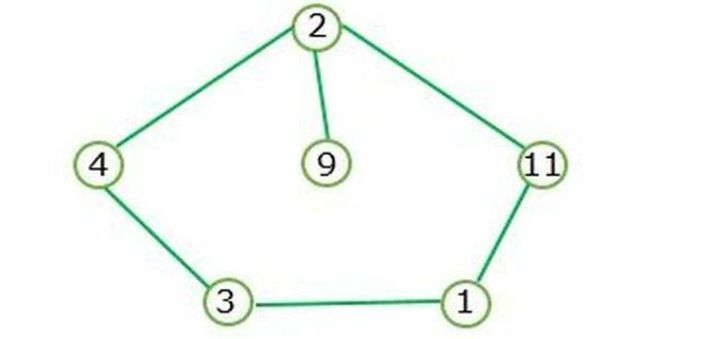
圖 I 表示環圖,不包含深度節點。
示例 2
讓我們舉一個無環圖的例子 -
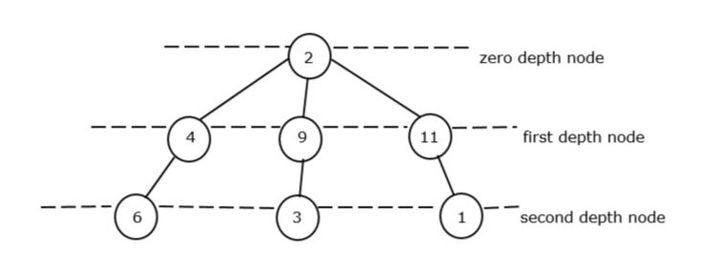
樹的根節點稱為零深度節點。在圖 II 中,在零深度處只有一個根,即2。因此,它被認為是零的最小深度節點。
在第一個深度節點中,我們有 3 個節點元素,如 4、9 和 1,但最小元素是4。
在第二個深度節點中,我們再次有 3 個節點元素,如 6、3 和 1,但最小元素是1。
我們將瞭解如何推匯出總深度節點,
總深度節點 = 零深度節點的最小值 + 第一深度節點的最小值 + 零深度節點的最小值
總深度節點 = 2 + 4 + 3 = 9。因此,9 是無環圖的最小總和。
語法
The following syntax used in the program:
struct name_of_structure{
data_type var_name;
// data member or field of the structure.
}
struct - 此關鍵字用於表示結構資料型別。
name_of_structure - 我們為結構提供任何名稱。
結構是在一個地方收集各種相關變數。
Queue < pair < datatype, datatype> > queue_of_pair
make_pair()
引數
C++ 中的配對佇列 -
這是配對佇列的一般 STL 模板,用於組合兩種不同的資料型別,並且佇列對屬於實用程式標頭檔案。
Queue_of_pair - 我們為對賦予任何名稱。
make_pair() - 用於構造具有兩個元素的對物件。
name_of_queue.push()
引數
name_of_queue - 我們為佇列命名。
push() - 這是佇列標頭檔案下提供的一種預定義方法,push 方法的作用是插入元素或值。
name_of_queue.pop()
引數
name_of_queue - 我們為佇列命名。
pop() - 這是佇列標頭檔案下提供的一種預定義方法,pop 方法的作用是刪除所有元素或值。
演算法
我們將從名為'iostream'、'climits'、'utility'和'queue'的程式標頭檔案開始。
我們正在建立具有整數值'val'的結構'tree_node'以獲取節點值。然後我們使用給定的資料建立tree_node 指標以初始化左子節點和右子節點以儲存值。接下來,我們建立一個tree_node函式,其中 int x 作為引數傳遞並驗證它是否等於'val'整數並將左子節點和右子節點分配為 null。
現在我們將定義一個函式minimum_sum_at_each_depth(),它接受一個整數值作為引數以查詢每層的最小和。使用 if 語句,它檢查樹的根值是否為 null,如果是則返回 0。
我們正在建立 STL(標準模板庫)的配對佇列以組合兩個值。
我們建立了一個名為 q 的配對佇列變數,它將執行兩種方法,即push()和make_pair()。使用這兩種方法,我們正在插入值並構造物件的兩個對。
我們正在初始化三個變數,即'present_depth'、'present_sum'和'totalSum',它們將用於進一步查詢當前和以及查詢最小總和。
初始化變數後,我們建立一個 while 迴圈來檢查條件,如果配對佇列不為空,則節點的計數將從開頭開始。接下來,我們使用'pop()'方法刪除現有節點,因為它將移動到樹的下一層以計算最小和。
現在我們將建立三個 if 語句以返回最小總和。
之後,我們將開始主函式並分別使用根指標、左子節點和右子節點構造輸入模式的樹格式,並透過新的'tree_node'傳遞節點值。
最後,我們呼叫'minimum_sum_at_each_depth(root)'函式並將引數 root 傳遞給它以處理每層的最小和。接下來,列印語句“無環圖每層的總和”並獲取結果。
請記住,配對佇列是一個包含佇列元素對的容器。
示例
在此程式中,我們將計算每層所有最小節點的總和。
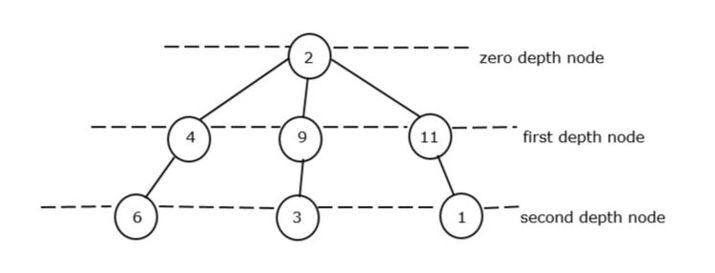
在此圖 II 中,總深度的最小和為 15+8+4+1 = 13。
現在我們將把這個圖作為輸入傳遞給此程式。
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
// required for FIFO operation
#include <utility>
// required for queue pair
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
// create the structure definition for a binary tree node of non-cycle graph
struct tree_node {
int val;
tree_node *left;
tree_node *right;
tree_node(int x) {
val = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
// This function is used to find the minimum sum at each depth
int minimum_sum_at_each_depth(tree_node* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
queue<pair<tree_node*, int>> q;
// create a queue to store node and depth and include pair to combine two together values.
q.push(make_pair(root, 0));
// construct a pair object with two element
int present_depth = -1;
// present depth
int present_sum = 0;
// present sum for present depth
int totalSum = 0;
// Total sum for all depths
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<tree_node*, int> present = q.front();
// assign queue pair - present
q.pop();
// delete an existing element from the beginning
if (present.second != present_depth) {
// We are moving to a new depth, so update the total sum and reset the present sum
present_depth = present.second;
totalSum += present_sum;
present_sum = INT_MAX;
}
// Update the present sum with the value of the present node
present_sum = min(present_sum, present.first->val);
//We are adding left and right children to the queue for updating the new depth.
if (present.first->left) {
q.push(make_pair(present.first->left, present.second + 1));
}
if (present.first->right) {
q.push(make_pair(present.first->right, present.second + 1));
}
}
// We are adding the present sum of last depth to the total sum
totalSum += present_sum;
return totalSum;
}
// start the main function
int main() {
tree_node *root = new tree_node(15);
root->left = new tree_node(14);
root->left->left = new tree_node(11);
root->left->right = new tree_node(4);
root->right = new tree_node(8);
root->right->left = new tree_node(13);
root->right->right = new tree_node(16);
root->left->left->left = new tree_node(1);
root->left->right->left = new tree_node(6);
root->right->right->right = new tree_node(2);
root->right->left->right = new tree_node(7);
cout << "Total sum at each depth of non cycle graph: " << minimum_sum_at_each_depth(root) << endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
Total sum at each depth of non cycle graph: 28
結論
我們探討了給定無環圖中每層元素最小和的概念。我們瞭解了箭頭運算子如何連線節點並構建樹形結構,並使用它計算每層的最小和。該應用程式使用無環圖,例如城市規劃、網路拓撲、谷歌地圖等。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 語言程式設計
C 語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP