深度優先搜尋(DFS)演算法
深度優先搜尋(DFS)是一種圖遍歷演算法。在此演算法中,給出一個起始頂點,當找到一個鄰接頂點時,它首先移動到該鄰接頂點,並嘗試以相同的方式遍歷。
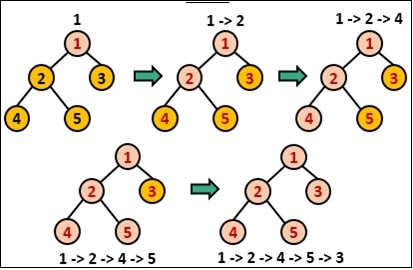
它遍歷整個深度,儘可能深入,之後它回溯到先前的頂點以找到新的路徑。
要以迭代方式實現 DFS,我們需要使用堆疊資料結構。如果想以遞迴方式進行,則不需要外部堆疊,可以使用內部堆疊進行遞迴呼叫。
輸入和輸出
Input: The Adjacency matrix of a graph. A B C D E F A 0 1 1 1 0 0 B 1 0 0 1 1 0 C 1 0 0 1 1 0 D 1 1 1 0 1 1 E 0 1 0 1 0 1 F 0 0 1 1 1 0 Output: DFS Traversal: C F E B D A
演算法
dfs(vertices, start)
輸入:所有頂點的列表和起始節點。
輸出:遍歷圖中的所有節點。
Begin initially make the state to unvisited for all nodes push start into the stack while stack is not empty, do pop element from stack and set to u display the node u if u is not visited, then mark u as visited for all nodes i connected to u, do if ith vertex is unvisited, then push ith vertex into the stack mark ith vertex as visited done done End
示例
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
#define NODE 6
typedef struct node {
int val;
int state; //status
}node;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0}
};
void dfs(node *vertex, node start) {
node u;
stack<node> myStack;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vertex[i].state = 0; //not visited
}
myStack.push(start);
while(!myStack.empty()) {
//pop and print node
u = myStack.top();
myStack.pop();
cout << char(u.val+'A') << " ";
if(u.state != 1) {
//update vertex status to visited
u.state = 1;
vertex[u.val].state = 1;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(graph[i][u.val]) {
if(vertex[i].state == 0) {
myStack.push(vertex[i]);
vertex[i].state = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
node vertices[NODE];
node start;
char s;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vertices[i].val = i;
}
s = 'C'; //starting vertex C
start.val = s-'A';
cout << "DFS Traversal: ";
dfs(vertices, start);
cout << endl;
}輸出
DFS Traversal: C F E B D A

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP