Go 語言廣度優先搜尋圖
圖是一種資料結構,它由邊或節點和頂點組成。頂點是節點之間的連線。為了遍歷所有這些節點,我們有不同的遍歷演算法。在本文中,我們將討論廣度優先搜尋,或者我們可以稱之為 BFS。在廣度優先搜尋中,我們首先從一個節點開始,然後移動到另一個節點,直到到達死衚衕。
示例
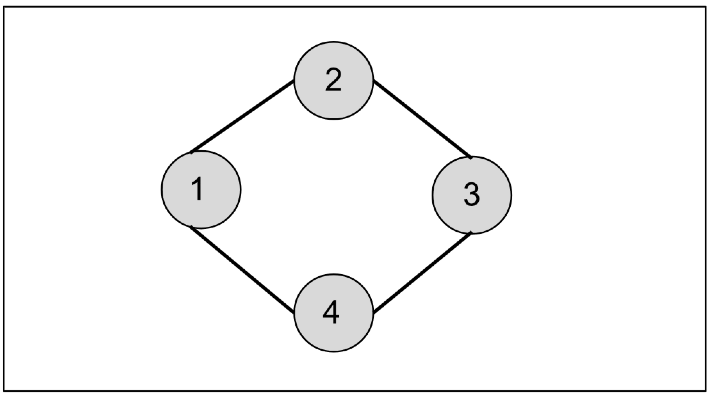
如果我們從節點 1 開始,它將首先訪問節點 2 和節點 4。然後從節點 2,我們將訪問節點 3。這樣,廣度優先搜尋遍歷將是 1、2、4 和 3。
演算法
步驟 1:使用 import 關鍵字在頂部匯入所需的包。
步驟 2:然後 main 函式將首先執行。
首先,我們宣告並初始化圖。
然後我們呼叫 BFS() 函式,並將圖和節點作為引數。
步驟 3:在 BFS() 函式中,以下步驟將在每次函式呼叫時執行。
isvisited := make(map[int]bool)
建立一個 map,用於儲存有關節點是否被訪問的資訊。
var bfsQueue Queue
為佇列資料結構建立一個引數。
isvisited[node] = true, bfsQueue.Enqueue(node)
將傳入的節點標記為已訪問,並將該節點新增到佇列中。
對所有連線的節點執行 for 迴圈,並將其新增到佇列中。
示例 1
在本例中,我們以矩陣的形式表示圖,並在矩陣上應用廣度優先搜尋。這種方法的複雜度將為 O(e*e),其中 e 是邊的數量,空間複雜度為 O(e*e),即矩陣的大小。
package main
import "fmt"
type Queue struct {
List []int
}
// function to add element in queue
func (q *Queue) Enqueue(element int) {
q.List = append(q.List, element)
}
// function to delete element in the queue
func (q *Queue) Dequeue() int {
if q.isEmpty() {
fmt.Println("Queue is empty.")
return 0
}
element := q.List[0]
q.List = q.List[1:]
return element
}
// function check that queue is empty or not
func (q *Queue) isEmpty() bool {
return len(q.List) == 0
}
// BFS() is a function with matrix and int value as parameter
func BFS(graph [][]int, node int) {
// initializing the map that will keep
// the track is the node is visited or not
isvisited := make(map[int]bool)
// creating a Queue variable
// in which we will add an element at the same level
// of that node
var bfsQueue Queue
// marking current node as visited
isvisited[node] = true
// adding a current node in the queue
bfsQueue.Enqueue(node)
// running a for loop until the queue becomes empty
for !bfsQueue.isEmpty() {
currNode := bfsQueue.List[0]
fmt.Print(currNode, " ")
// adding all the connected node in queue if not visted
for nodes := 0; nodes < len(graph[currNode]); nodes++ {
if graph[currNode][nodes] == 1 && !isvisited[nodes] {
bfsQueue.Enqueue(nodes)
isvisited[nodes] = true
}
}
// removing the current node from queue
// after visiting
bfsQueue.Dequeue()
}
}
func main() {
// matrix representation of the undirected connected graph
// where if the value is 1 the node i is connected
// with node j
graph := [][]int{{0, 1, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 1, 0}}
fmt.Println("Golang program to do Breath first search of an undirected connected graph represented in the form of a matrix.")
// calling BFS() function for the breadth-first search
// traversal of a graph
BFS(graph, 0)
fmt.Println()
}
輸出
Golang program to do Breath first search of an undirected connected graph represented in the form of a matrix. 0 1 3 2
示例 2
在本例中,我們以鄰接表的形式表示圖,並相應地應用廣度優先搜尋。這種方法的複雜度將為 O(e*v),其中 e 是邊的數量,v 是頂點的數量。空間複雜度為 O(e*v),即鄰接表的大小。
package main
import "fmt"
type Queue struct {
List []int
}
// function to add an element in the queue
func (q *Queue) Enqueue(element int) {
q.List = append(q.List, element)
}
// function to delete elements in the queue
func (q *Queue) Dequeue() int {
if q.isEmpty() {
fmt.Println("Queue is empty.")
return 0
}
element := q.List[0]
q.List = q.List[1:]
return element
}
// function checks whether the queue is empty or not
func (q *Queue) isEmpty() bool {
return len(q.List) == 0
}
// BFS() is a function with matrix and int value as parameter
func BFS(graph [4][]int, node int) {
//Initializing the map that will keep
// the track is the node is visited or not
isvisited := make(map[int]bool)
// creating a Queue variable
// in which we will add elements at the same level
// of that node
var bfsQueue Queue
// marking current node as visited
isvisited[node] = true
// adding the current node in the queue
bfsQueue.Enqueue(node)
// running a for loop until the queue becomes empty
for !bfsQueue.isEmpty() {
currNode := bfsQueue.List[0]
fmt.Print(currNode, " ")
// adding all the connected nodes in the queue if not visited
for _, nodes := range graph[currNode] {
if !isvisited[nodes] {
bfsQueue.Enqueue(nodes)
isvisited[nodes] = true
}
}
// removing the current node from queue
// after visiting
bfsQueue.Dequeue()
}
}
func main() {
//adjacency list representation of the undirected connected graph
// where if the value is 1 the node i is connected
// with node j
var graph [4][]int
// initializing each list of the array
graph[0] = []int{1, 3}
graph[1] = []int{0, 2}
graph[2] = []int{1, 3}
graph[3] = []int{0, 2}
fmt.Println("Golang program to do Breath first search of an undirected connected graph represented in the form of an adjacency list.")
// calling BFS() function for the breadth-first search
// traversal of a graph
BFS(graph, 0)
fmt.Println()
}
輸出
Golang program to do Breath first search of an undirected connected graph represented in the form of an adjacency list. 0 1 3 2
結論
這兩種表示圖資料結構和執行廣度優先搜尋演算法的不同方法。第二種方法,我們建立鄰接表,在時間和空間上都更有效,因為我們將那些與節點連線的節點號新增到陣列中。要了解更多關於 Go 語言的資訊,您可以瀏覽這些 教程。

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係型資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 語言程式設計
C 語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP