JavaScript中的廣度優先搜尋遍歷
BFS在訪問子節點之前先訪問相鄰節點,並且在搜尋過程中使用佇列。以下是BFS的工作原理:
- 訪問相鄰的未訪問節點。將其標記為已訪問。顯示它。將其插入佇列。
- 如果未找到相鄰節點,則從佇列中移除第一個節點。
- 重複規則1和規則2,直到佇列為空。
讓我們來看一個BFS遍歷如何工作的示例
步驟 | 遍歷 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
1 | 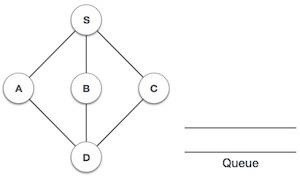 | 初始化佇列。 |
2 | 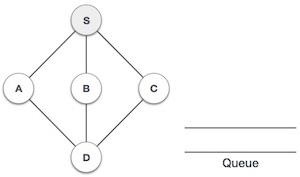 | 我們首先訪問S(起始節點)並將其標記為已訪問。 |
3 | 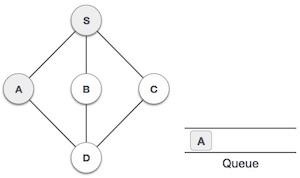 | 然後我們從S檢視未訪問的相鄰節點。在這個例子中,我們有三個節點,但按字母順序我們選擇A,將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
4 | 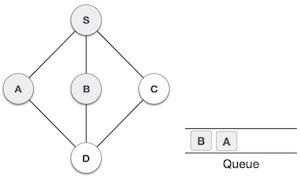 | 接下來,來自S的未訪問相鄰節點是B。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
5 | 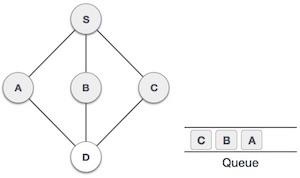 | 接下來,來自S的未訪問相鄰節點是C。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
6 | 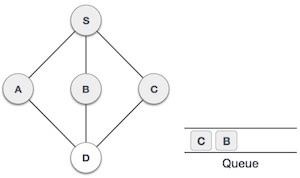 | 現在,S沒有未訪問的相鄰節點了。因此,我們出隊並找到A。 |
7 | 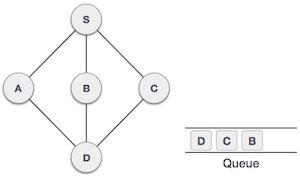 | 從A,我們有D作為未訪問的相鄰節點。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
在這個階段,我們沒有未標記(未訪問)的節點了。但根據演算法,我們繼續出隊以獲取所有未訪問的節點。當佇列清空時,程式結束。
讓我們看看如何在JavaScript中實現它。
示例
BFS(node) {
// Create a Queue and add our initial node in it
let q = new Queue(this.nodes.length);
let explored = new Set();
q.enqueue(node);
// Mark the first node as explored explored.
add(node);
// We'll continue till our queue gets empty
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
let t = q.dequeue();
// Log every element that comes out of the Queue
console.log(t);
// 1. In the edges object, we search for nodes this node is directly connected to.
// 2. We filter out the nodes that have already been explored.
// 3. Then we mark each unexplored node as explored and add it to the queue.
this.edges[t]
.filter(n => !explored.has(n))
.forEach(n => {
explored.add(n);
q.enqueue(n);
});
}
}您可以使用以下方法測試此函式:
示例
let g = new Graph();
g.addNode("A");
g.addNode("B");
g.addNode("C");
g.addNode("D");
g.addNode("E");
g.addNode("F");
g.addNode("G");
g.addEdge("A", "C");
g.addEdge("A", "B");
g.addEdge("A", "D");
g.addEdge("D", "E");
g.addEdge("E", "F");
g.addEdge("B", "G");
g.BFS("A");輸出
這將給出以下輸出:
A C B D G E F

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP