- LightGBM 教程
- LightGBM - 首頁
- LightGBM - 概述
- LightGBM - 架構
- LightGBM - 安裝
- LightGBM - 核心引數
- LightGBM - Boosting演算法
- LightGBM - 樹增長策略
- LightGBM - 資料集結構
- LightGBM - 二元分類
- LightGBM - 迴歸
- LightGBM - 排序
- LightGBM - Python 實現
- LightGBM - 引數調整
- LightGBM - 繪圖功能
- LightGBM - 早停訓練
- LightGBM - 特徵互動約束
- LightGBM 與其他 Boosting 演算法的比較
- LightGBM 有用資源
- LightGBM - 有用資源
- LightGBM - 討論
LightGBM - 迴歸
流行的機器學習方法 LightGBM(輕量級梯度提升機)用於迴歸和分類應用。當用於迴歸時,它會建立一系列決策樹,每棵樹都試圖透過減少前一棵樹的誤差來最小化損失函式(例如均方誤差)。
LightGBM 如何用於迴歸?
LightGBM 的基礎,梯度提升,按順序依次建立多個決策樹。每棵樹都努力糾正前一棵樹所犯的錯誤。
與其他按層增長樹的提升演算法不同,LightGBM 按葉節點增長樹。這意味著在擴充套件模型時,它會最佳化損失減少(即,最能改進模型的葉子節點)。這會產生更深、更準確的樹,但需要仔細調整以避免過擬合。
為了減少預期結果和實際結果之間的差異,LightGBM 使用兩種型別的迴歸任務損失函式——均方誤差 (MSE) 和平均絕對誤差 (MAE)。
何時使用 LightGBM 迴歸
以下是一些可以使用 LightGBM 進行迴歸的情況:
當給定大型資料集時。
當需要快速高效的模型時。
當您的資料包含大量特徵(列)或缺失值時。
使用 LightGBM 進行迴歸的示例
現在讓我們看看如何建立一個 LightGBM 迴歸模型。這些步驟將幫助您瞭解該過程的每個步驟是如何工作的。
步驟 1 - 安裝所需的庫
在開始之前,請確保您已安裝必要的庫。Scikit-learn 用於資料處理,lightgbm 用於 LightGBM 模型。
pip install pandas scikit-learn lightgbm
步驟 2 - 載入資料
首先,使用 pandas 載入資料集。此資料集包含與健康相關的資料,包括年齡、性別、BMI、子女數量、居住地、吸菸狀況和醫療費用。
import pandas as pd
# Load the dataset from your local file path
data = pd.read_csv('/My Docs/Python/medical_cost.csv')
# Display the first few rows of the dataset
print(data.head())
輸出
這將產生以下結果:
age sex bmi children smoker region charges 0 19 female 27.900 0 yes southwest 16884.92400 1 18 male 33.770 1 no southeast 1725.55230 2 28 male 33.000 3 no southeast 4449.46200 3 33 male 22.705 0 no northwest 21984.47061 4 32 male 28.880 0 no northwest 3866.85520
步驟 3 - 分離特徵和目標變數
現在正在分離目標變數 (y) 和特徵 (X)。在本例中,我們希望使用其他特徵來預測“費用”列。
# 'charges' is the target column that we want to predict
# All columns except 'charges' are features
X = data.drop('charges', axis=1)
# The 'charges' column is the target variable
y = data['charges']
步驟 4 - 處理分類資料
資料集中的分類特徵(性別、吸菸者和地區)需要轉換為數值格式,因為 LightGBM 使用數值資料。獨熱編碼用於將這些類別列轉換為二進位制格式(0 和 1)。
# Convert categorical variables to numerical X = pd.get_dummies(X, drop_first=True)
這裡:
pd.get_dummies() 用於為每個類別生成額外的二進位制列。
drop_first=True 透過消除每個分類變數的第一個類別來避免多重共線性。
步驟 5 - 分割資料
為了瞭解模型的效能,我們將資料分成兩組——訓練集(佔資料的 80%)和測試集(佔資料的 20%)。
train_test_split() 用於隨機分割資料,同時保持給定的比例 (test_size=0.2)。
使用 random_state = 42 可以確保分割結果可重現。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # Split the data into training and test sets X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
步驟 6:初始化 LightGBM 迴歸器
現在我們將為迴歸初始化 LightGBM 模型。LGBMRegressor 是 LightGBM 的實現,專門用於迴歸任務。LGBMRegressor 模型非常高效和靈活,可以有效地處理大型資料集。
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor # Initialize the LightGBM regressor model model = LGBMRegressor()
步驟 7:訓練模型
接下來,我們將使用訓練資料 (X_train 和 y_train) 來訓練模型。這裡使用 fit() 方法透過查詢訓練資料中的模式並預測目標變數(費用)來訓練模型。
# Train the model on the training data model.fit(X_train, y_train)
輸出
執行上述程式碼後,我們將得到以下結果:
[LightGBM] [Info] Auto-choosing col-wise multi-threading, the overhead of testing was 0.001000 seconds. You can set `force_col_wise=true` to remove the overhead. [LightGBM] [Info] Total Bins 319 [LightGBM] [Info] Number of data points in the train set: 1070, number of used features: 8 [LightGBM] [Info] Start training from score 13346.089733 LGBMRegressori LGBMRegressor()
步驟 8:進行預測
訓練後,我們使用模型對測試集 (X_test) 進行預測。model.predict(X_test) 根據從訓練資料中學習到的模式生成測試集的預測值。
# Predict on the test set y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
步驟 9:評估模型
我們將使用均方誤差 (MSE) 來衡量模型的效能,這是一個常用的迴歸指標。均方誤差或 MSE 計算的是預期值和實際值之間的差異的平方平均值。較低的 MSE 值表示更好的效能。
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# Calculate the MSE
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print(f'Mean Squared Error: {mse}')
輸出
這將生成以下輸出:
Mean Squared Error: 20557383.0620152
分析 MSE 值以瞭解模型預測目標變數的準確程度。如果 MSE 值很高,請考慮透過調整超引數或收集新資料來更新模型。
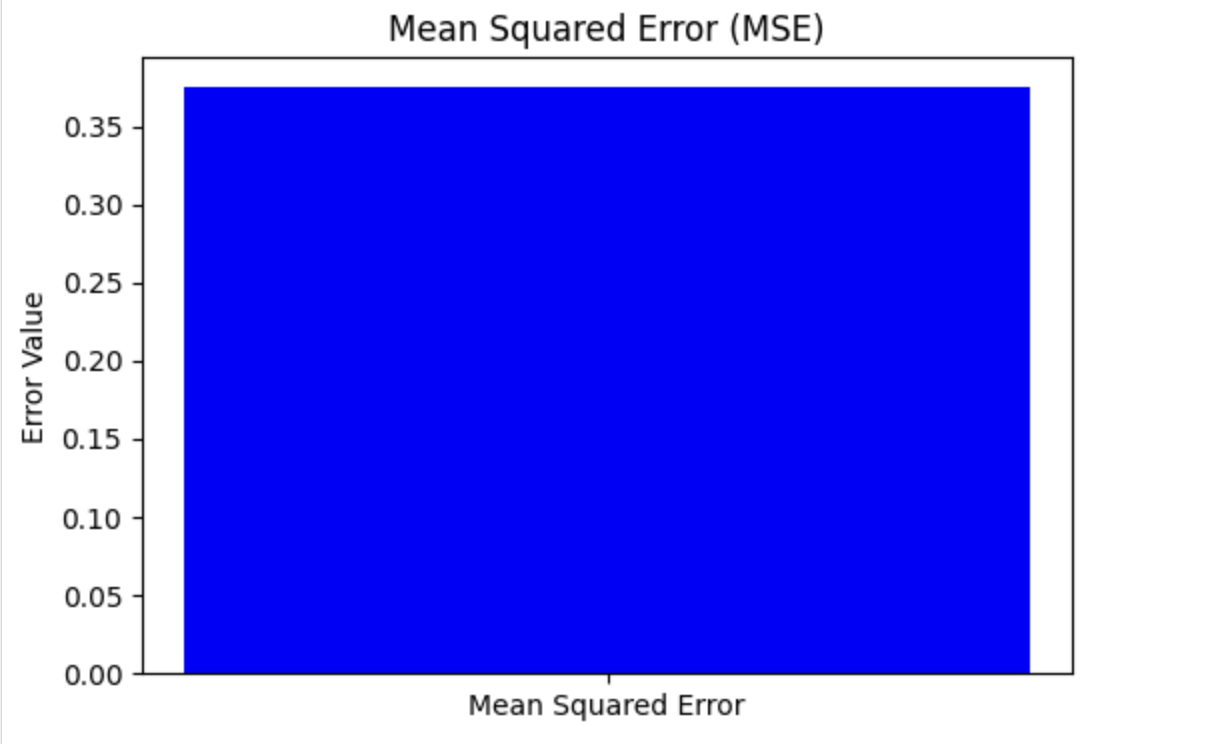
視覺化均方誤差 (MSE)
要檢視均方誤差,請使用 MSE 值建立一個條形圖。這提供了對問題嚴重程度的清晰直觀的表示。
這裡,您可以看到如何使用 matplotlib(一個流行的用於繪圖的 Python 庫)來繪製它:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# Example data (replace these with your actual values)
# Actual values
y_test = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
# Predicted values
y_pred = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
# Calculate the MSE
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
# Plotting the Mean Squared Error
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.bar(['Mean Squared Error'], [mse], color='blue')
plt.ylabel('Error Value')
plt.title('Mean Squared Error (MSE)')
plt.show()
輸出
以下是上述程式碼的結果: