
- LightGBM 教程
- LightGBM - 首頁
- LightGBM - 概述
- LightGBM - 架構
- LightGBM - 安裝
- LightGBM - 核心引數
- LightGBM - Boosting演算法
- LightGBM - 樹生長策略
- LightGBM - 資料集結構
- LightGBM - 二元分類
- LightGBM - 迴歸
- LightGBM - 排序
- LightGBM - Python實現
- LightGBM - 引數調優
- LightGBM - 繪圖功能
- LightGBM - 早停訓練
- LightGBM - 特徵互動約束
- LightGBM 與其他Boosting演算法的比較
- LightGBM 有用資源
- LightGBM - 有用資源
- LightGBM - 討論
LightGBM - Python實現
本章將介紹使用Python開發LightGBM模型的步驟。我們將使用Scikit-learn的load_breast_cancer資料集構建一個二元分類模型。步驟如下:載入資料,準備LightGBM所需的資料,設定引數,訓練模型,進行預測,並評估結果。
LightGBM的實現
讓我們使用Python建立一個基本模型:
1. 載入資料集
首先,我們使用Scikit-learn的load_breast_cancer方法載入資料集。此資料集包含乳腺癌分類的特徵和標籤。
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer # Load dataset data = load_breast_cancer() X = data.data y = data.target
2. 分割資料
使用Scikit-learn的train_test_split方法將資料集分割成訓練集和測試集。這允許我們在一個數據集上訓練模型,然後在另一個數據集上評估其效能。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # Split the data X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
3. 準備LightGBM所需的資料
將訓練資料和測試資料轉換為LightGBM資料集格式。此步驟優化了LightGBM訓練演算法的資料格式。
import lightgbm as lgb # Convert the data to LightGBM dataset format train_data = lgb.Dataset(X_train, label=y_train) test_data = lgb.Dataset(X_test, label=y_test, reference=train_data)
4. 定義引數
設定LightGBM模型的引數。這包括目標函式、評估指標、學習率、葉子節點數量和最大樹深度。
params = {
'objective': 'binary',
'metric': 'binary_logloss',
'boosting_type': 'gbdt',
'learning_rate': 0.1,
# Increased from 31
'num_leaves': 63,
# Set to a positive value to limit depth
'max_depth': 10
}
5. 訓練模型
使用訓練資料訓練LightGBM模型。為了防止過擬合,我們使用早停機制,這意味著當驗證集上沒有進展時訓練結束。
# Train the model with early stopping
lgb_model = lgb.train(
params,
train_data,
num_boost_round=100,
valid_sets=[test_data],
# Use callback for early stopping
callbacks=[lgb.early_stopping(stopping_rounds=10)]
)
輸出
以下是上述步驟的結果:
[LightGBM] [Info] Number of positive: 286, number of negative: 169 [LightGBM] [Info] Auto-choosing col-wise multi-threading, the overhead of testing was 0.000734 seconds. You can set `force_col_wise=true` to remove the overhead. [LightGBM] [Info] Total Bins 4548 [LightGBM] [Info] Number of data points in the train set: 455, number of used features: 30 [LightGBM] [Info] [binary:BoostFromScore]: pavg=0.628571 -> initscore=0.526093 [LightGBM] [Info] Start training from score 0.526093 [LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf [LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
6. 進行預測
使用訓練好的模型預測測試資料。我們將機率轉換為二元結果。
# Predict on the test set y_pred = lgb_model.predict(X_test) y_pred_binary = [1 if x > 0.5 else 0 for x in y_pred]
7. 評估模型
計算測試集的準確率分數以評估模型的效能。這使我們能夠了解模型對以前未見過的資料的效能。
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Evaluate the model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_binary)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}")
輸出
以下是上述模型的準確率:
Accuracy: 0.96
LightGBM模型的探索性資料分析 (EDA)
在訓練和測試LightGBM模型之前,必須進行探索性資料分析 (EDA),以瞭解資料集,識別模式並準備建模。EDA包括檢查資料集的結構、分佈、相關性和潛在問題。
以下是使用EDA處理load_breast_cancer資料集的步驟:
1. 載入和檢查資料集
首先,我們必須載入資料集並檢查其基本結構,例如樣本數量、特徵和目標變數。
import pandas as pd from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer # Load dataset data = load_breast_cancer() df = pd.DataFrame(data.data, columns=data.feature_names) df['target'] = data.target # Inspect the dataset print(df.head()) print(df.info()) print(df.describe())
輸出
這將產生以下結果:
mean radius mean texture mean perimeter mean area mean smoothness \ 0 17.99 10.38 122.80 1001.0 0.11840 1 20.57 17.77 132.90 1326.0 0.08474 2 19.69 21.25 130.00 1203.0 0.10960 3 11.42 20.38 77.58 386.1 0.14250 4 20.29 14.34 135.10 1297.0 0.10030 mean compactness mean concavity mean concave points mean symmetry \ 0 0.27760 0.3001 0.14710 0.2419 1 0.07864 0.0869 0.07017 0.1812 2 0.15990 0.1974 0.12790 0.2069 3 0.28390 0.2414 0.10520 0.2597 4 0.13280 0.1980 0.10430 0.1809 mean fractal dimension ... worst texture worst perimeter worst area \ 0 0.07871 ... 17.33 184.60 2019.0 1 0.05667 ... 23.41 158.80 1956.0 2 0.05999 ... 25.53 152.50 1709.0 3 0.09744 ... 26.50 98.87 567.7 4 0.05883 ... 16.67 152.20 1575.0 worst smoothness worst compactness worst concavity worst concave points \ 0 0.1622 0.6656 0.7119 0.2654 1 0.1238 0.1866 0.2416 0.1860 2 0.1444 0.4245 0.4504 0.2430 3 0.2098 0.8663 0.6869 0.2575 4 0.1374 0.2050 0.4000 0.1625 worst symmetry worst fractal dimension target 0 0.4601 0.11890 0 1 0.2750 0.08902 0 2 0.3613 0.08758 0 3 0.6638 0.17300 0 4 0.2364 0.07678 0
2. 檢查缺失值
現在讓我們看看資料集中是否存在任何缺失值。
# Check for missing values print(df.isnull().sum())
輸出
這將生成以下結果:
mean radius 0 mean texture 0 mean perimeter 0 mean area 0 mean smoothness 0 mean compactness 0 mean concavity 0 mean concave points 0 mean symmetry 0 mean fractal dimension 0 radius error 0 texture error 0 perimeter error 0 area error 0 smoothness error 0 compactness error 0 concavity error 0 concave points error 0 symmetry error 0 fractal dimension error 0 worst radius 0 worst texture 0 worst perimeter 0 worst area 0 worst smoothness 0 worst compactness 0 worst concavity 0 worst concave points 0 worst symmetry 0 worst fractal dimension 0 target 0 dtype: int64
3. 特徵分佈
確定每個特徵的分佈。為了更多地瞭解特徵值的範圍和分佈,可以使用直方圖、箱線圖或其他視覺化方法。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns # Plot histograms for each feature df.iloc[:, :-1].hist(bins=30, figsize=(20, 15)) plt.show() # Box plot for a selected feature sns.boxplot(x='target', y='mean radius', data=df) plt.show()
輸出
這將建立以下結果:
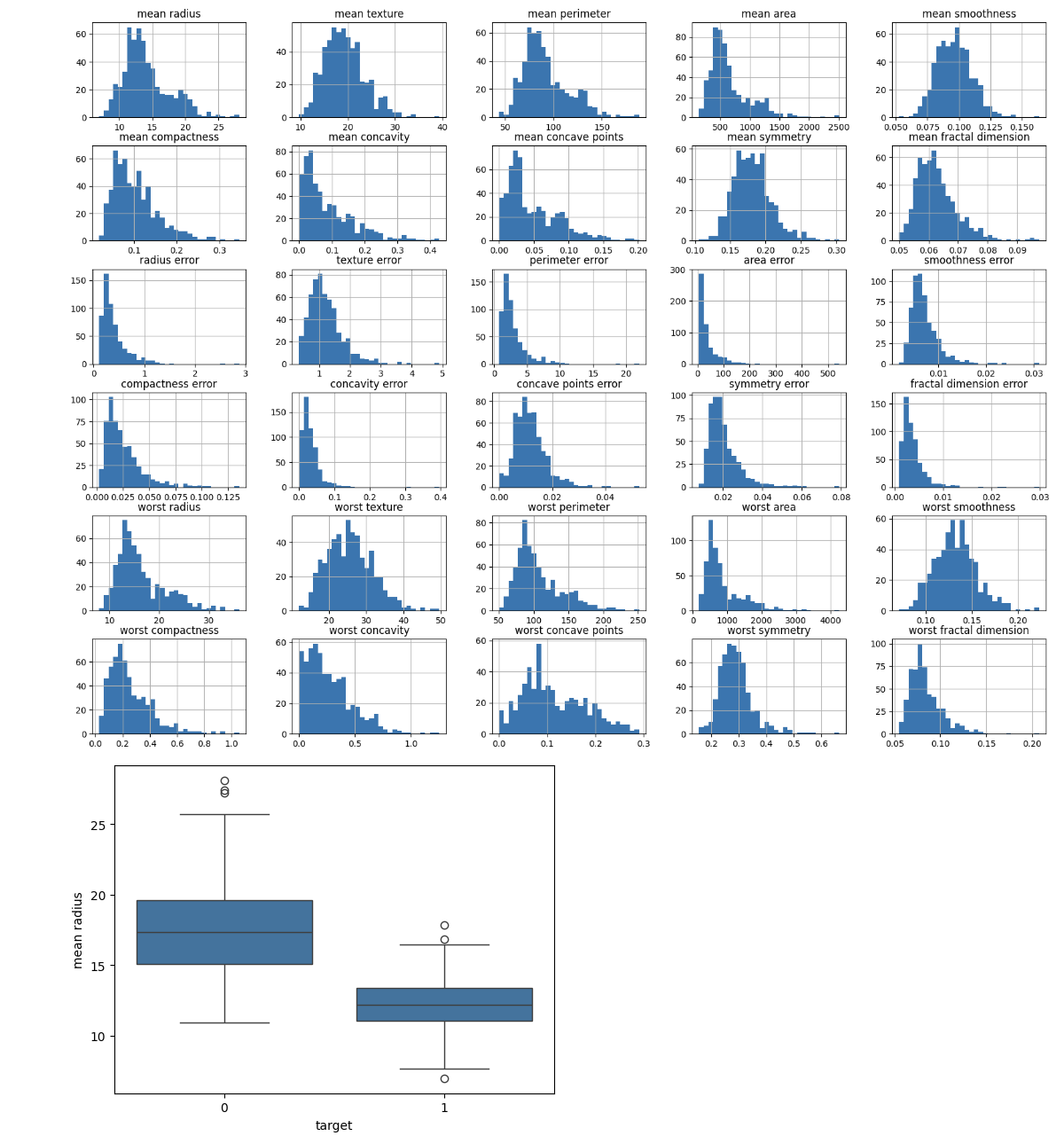
4. 分析類別分佈
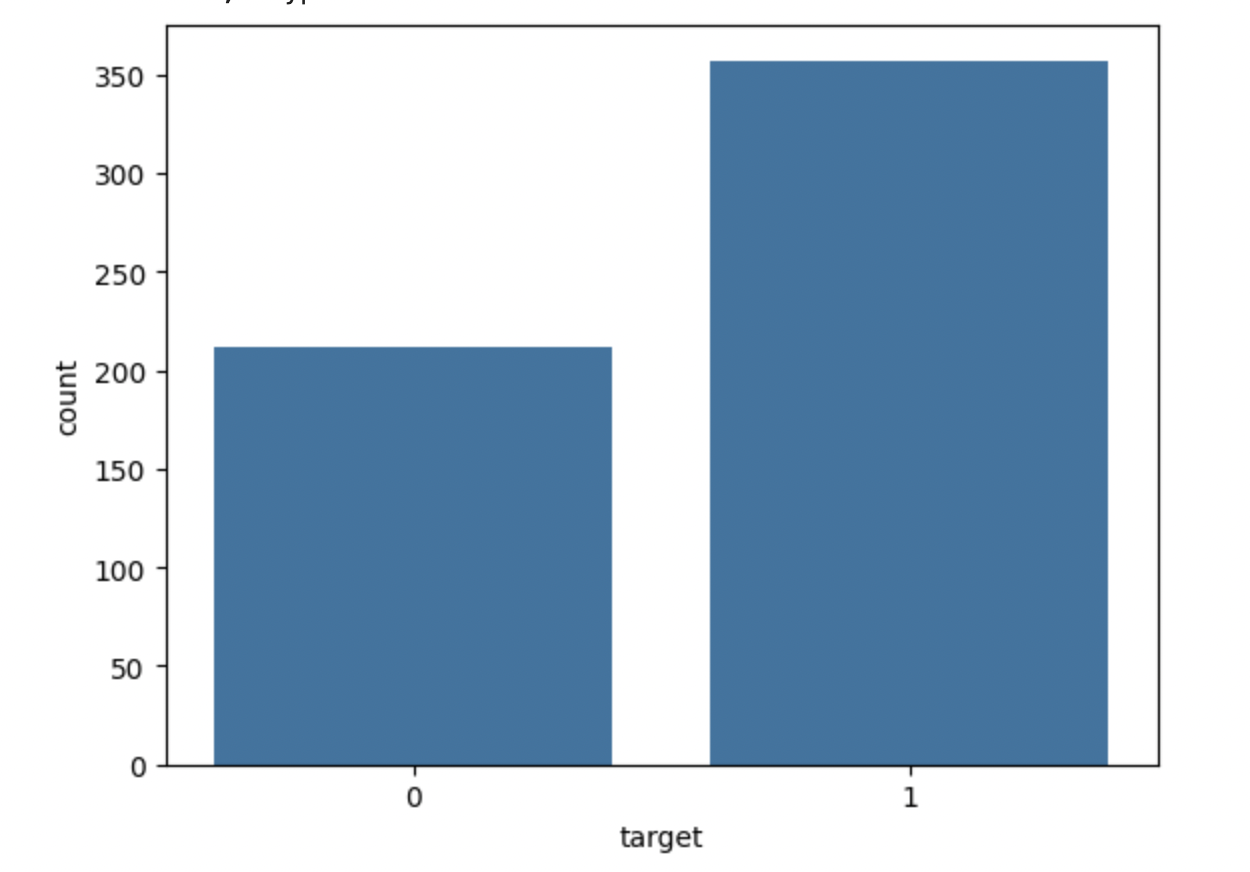
檢查目標變數的分佈以查詢類別平衡。這將使您能夠識別資料集是否不平衡。
# Class distribution print(df['target'].value_counts()) sns.countplot(x='target', data=df) plt.show()
輸出
這將顯示以下輸出:
target 1 357 0 212 Name: count, dtype: int64
總結
按照這些步驟,您可以建立和測試用於Python中分類問題的LightGBM模型。可以透過根據需要調整引數和準備步驟,將此技術修改為適用於不同的資料集和問題。