
- CSS 教程
- CSS - 首頁
- CSS - 路線圖
- CSS - 簡介
- CSS - 語法
- CSS - 選擇器
- CSS - 包含
- CSS - 測量單位
- CSS - 顏色
- CSS - 背景
- CSS - 字型
- CSS - 文字
- CSS - 圖片
- CSS - 連結
- CSS - 表格
- CSS - 邊框
- CSS - 塊級邊框
- CSS - 內聯邊框
- CSS - 外邊距
- CSS - 列表
- CSS - 內邊距
- CSS - 游標
- CSS - 輪廓
- CSS - 尺寸
- CSS - 捲軸
- CSS - 內聯塊
- CSS - 下拉選單
- CSS - 可見性
- CSS - 溢位
- CSS - 清除浮動
- CSS - 浮動
- CSS - 箭頭
- CSS - 調整大小
- CSS - 引號
- CSS - 順序
- CSS - 位置
- CSS - 連字元
- CSS - 懸停
- CSS - 顯示
- CSS - 聚焦
- CSS - 縮放
- CSS - 轉換
- CSS - 高度
- CSS - 連字元字元
- CSS - 寬度
- CSS - 不透明度
- CSS - Z-Index
- CSS - 底部
- CSS - 導航欄
- CSS - 覆蓋層
- CSS - 表單
- CSS - 對齊
- CSS - 圖示
- CSS - 圖片庫
- CSS - 註釋
- CSS - 載入器
- CSS - 屬性選擇器
- CSS - 組合器
- CSS - 根元素
- CSS - 盒模型
- CSS - 計數器
- CSS - 剪下
- CSS - 書寫模式
- CSS - Unicode-bidi
- CSS - min-content
- CSS - All
- CSS - Inset
- CSS - Isolation
- CSS - Overscroll
- CSS - Justify Items
- CSS - Justify Self
- CSS - Tab Size
- CSS - 指標事件
- CSS - Place Content
- CSS - Place Items
- CSS - Place Self
- CSS - Max Block Size
- CSS - Min Block Size
- CSS - Mix Blend Mode
- CSS - Max Inline Size
- CSS - Min Inline Size
- CSS - Offset
- CSS - Accent Color
- CSS - User Select
- CSS 高階
- CSS - 網格
- CSS - 網格佈局
- CSS - Flexbox
- CSS - 可見性
- CSS - 定位
- CSS - 圖層
- CSS - 偽類
- CSS - 偽元素
- CSS - @規則
- CSS - 文字效果
- CSS - 分頁媒體
- CSS - 列印
- CSS - 佈局
- CSS - 驗證
- CSS - 圖片精靈
- CSS - Important
- CSS - 資料型別
- CSS3 教程
- CSS3 - 教程
- CSS - 圓角
- CSS - 邊框圖片
- CSS - 多背景
- CSS - 顏色
- CSS - 漸變
- CSS - 盒陰影
- CSS - 盒裝飾中斷
- CSS - Caret Color
- CSS - 文字陰影
- CSS - 文字
- CSS - 2d 轉換
- CSS - 3d 轉換
- CSS - 過渡
- CSS - 動畫
- CSS - 多列
- CSS - 盒尺寸
- CSS - 工具提示
- CSS - 按鈕
- CSS - 分頁
- CSS - 變數
- CSS - 媒體查詢
- CSS - 函式
- CSS - 數學函式
- CSS - 遮罩
- CSS - 形狀
- CSS - 樣式圖片
- CSS - 特異性
- CSS - 自定義屬性
- CSS 響應式
- CSS RWD - 簡介
- CSS RWD - 視口
- CSS RWD - 網格檢視
- CSS RWD - 媒體查詢
- CSS RWD - 圖片
- CSS RWD - 影片
- CSS RWD - 框架
- CSS 工具
- CSS - PX 到 EM 轉換器
- CSS - 顏色選擇器和動畫
- CSS 資源
- CSS - 有用資源
- CSS - 討論
CSS - z-index 屬性
CSS 的z-index 屬性用於控制網頁中元素的堆疊順序,當元素在同一個堆疊上下文中重疊時。具有較高 z-index 值的元素會顯示在具有較低值的元素前面。
下圖演示了 z-index 佈局,供參考
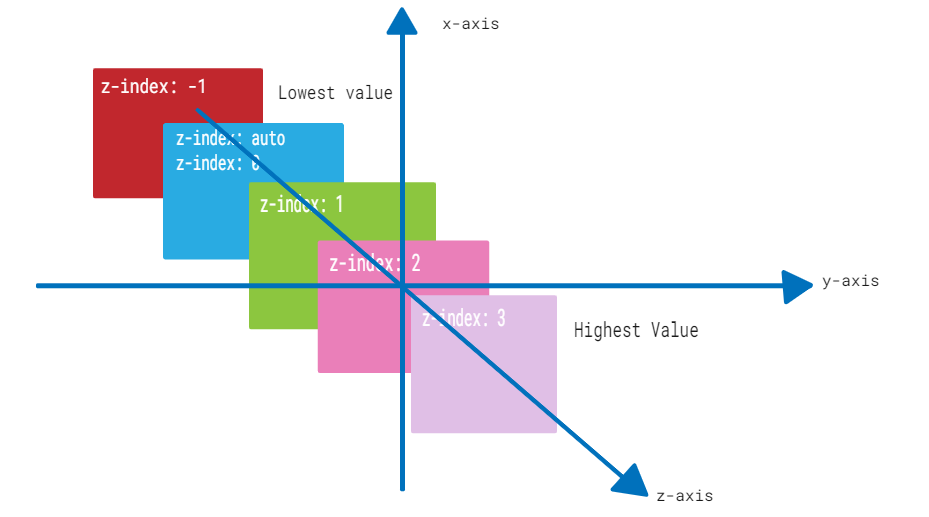
z-index 屬性可以與巢狀在其他定位元素內的定位元素一起使用。
可能的值
auto − 預設值。堆疊順序與父元素相同。
<Integer> − 正整數或負整數。它將元素的堆疊級別設定為給定的值。
應用於
所有定位元素。
DOM 語法
object.style.zIndex = "2";
CSS z-index - auto 值
CSS z-index: auto 將元素的 z-index 設定為其父元素的堆疊順序。它是 z-index 屬性的預設值。
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: absolute;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: auto;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
height: 120px;
width: 200px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 20px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
p {
margin-top: 250px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The element with z-index value of auto appears behind the element with the z-index value of 1.</p>
<div class="box1">
<span>CSS z-index: auto</span>
<div class="box2">
<span>CSS z-index: 1</span>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index - 帶正整數
CSS z-index 屬性可以具有正整數的值。在堆疊順序中,具有較高整數值的元素將顯示在具有較低值的元素上方。
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: absolute;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: absolute;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: 3;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 20px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
p {
margin-top: 250px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The element with z-index value of 1 appears behind the element with the z-index value of 2 and 3.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: 1
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: 2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: 3
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index - 帶負整數
您還可以為 z-index 屬性使用負整數。具有負 z-index 值的元素將堆疊在具有較高 z-index 值的元素下方。
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: absolute;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: -3;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: -2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: absolute;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: -1;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 20px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
p {
margin-top: 250px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The element with z-index value of -3 appears behind the element with the z-index value of -2 and -1.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: -3
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: -2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: -1
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index - 帶粘性定位
以下示例演示瞭如何使用z-index 屬性來控制具有position: sticky 屬性的元素的堆疊順序,以便它們在頁面滾動時保持固定在原位−
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: sticky;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
margin: 10px;
left: 10px;
top: 80px;
}
.box2 {
position: sticky;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 40px;
top: 200px;
}
.box3 {
position: sticky;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: 3;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 70px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Move cursor upward to see the effect.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: 1
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: 2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: 3
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index - 帶固定定位
以下示例演示瞭如何使用z-index 屬性使元素在使用者向下滾動時始終位於內容的頂部,即使它具有position: fixed 屬性−
<html>
<head>
<style>
.container {
position: relative;
height: 350px;
}
.box1 {
position: fixed;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: -3;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: fixed;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: -2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: fixed;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: -1;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 20px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
h3 {
margin-top: 320px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Scroll down the content to see the effect.</h3>
<div class="container">
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: -3
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: -2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: -1
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index - 帶靜態定位
以下示例顯示z-index 屬性不會影響具有position: static 屬性的元素的堆疊順序−
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: static;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
margin: 10px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: static;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: static;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: 3;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The z-index property has no effect on the stacking order of elements if the position property is set to static.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: 1
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: 2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: 3
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index - 帶相對定位
此示例顯示,當元素具有position: relative 屬性時,z-index 屬性會根據元素在文件流中的原始位置對其進行定位。
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: relative;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
margin: 10px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: relative;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: relative;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: 3;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The z-index property positions the element relative to its original position if position is relative.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: 1
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: 2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: 3
</div>
</body>
</html>
廣告