
- CSS 教程
- CSS - 首頁
- CSS - 路線圖
- CSS - 簡介
- CSS - 語法
- CSS - 選擇器
- CSS - 包含
- CSS - 測量單位
- CSS - 顏色
- CSS - 背景
- CSS - 字型
- CSS - 文字
- CSS - 圖片
- CSS - 連結
- CSS - 表格
- CSS - 邊框
- CSS - 塊級邊框
- CSS - 內聯邊框
- CSS - 外邊距
- CSS - 列表
- CSS - 內邊距
- CSS - 游標
- CSS - 輪廓
- CSS - 尺寸
- CSS - 捲軸
- CSS - 塊內元素
- CSS - 下拉選單
- CSS - 可見性
- CSS - 溢位
- CSS - 清除浮動
- CSS - 浮動
- CSS - 箭頭
- CSS - 可調整大小
- CSS - 引號
- CSS - 順序
- CSS - 定位
- CSS - 連字元
- CSS - 懸停
- CSS - 顯示
- CSS - 聚焦
- CSS - 縮放
- CSS - 位移
- CSS - 高度
- CSS - 連字元字元
- CSS - 寬度
- CSS - 不透明度
- CSS - z-index
- CSS - 底部
- CSS - 導航欄
- CSS - 覆蓋層
- CSS - 表單
- CSS - 對齊
- CSS - 圖示
- CSS - 圖片庫
- CSS - 註釋
- CSS - 載入器
- CSS - 屬性選擇器
- CSS - 組合器
- CSS - 根元素
- CSS - 盒模型
- CSS - 計數器
- CSS - 剪裁
- CSS - 書寫模式
- CSS - Unicode-bidi
- CSS - min-content
- CSS - all
- CSS - inset
- CSS - isolation
- CSS - overscroll
- CSS - justify-items
- CSS - justify-self
- CSS - tab-size
- CSS - pointer-events
- CSS - place-content
- CSS - place-items
- CSS - place-self
- CSS - max-block-size
- CSS - min-block-size
- CSS - mix-blend-mode
- CSS - max-inline-size
- CSS - min-inline-size
- CSS - offset
- CSS - accent-color
- CSS - user-select
- CSS 高階
- CSS - 網格
- CSS - 網格佈局
- CSS - Flexbox
- CSS - 可見性
- CSS - 定位
- CSS - 層
- CSS - 偽類
- CSS - 偽元素
- CSS - @規則
- CSS - 文字效果
- CSS - 分頁媒體
- CSS - 列印
- CSS - 佈局
- CSS - 驗證
- CSS - 圖片精靈
- CSS - !important
- CSS - 資料型別
- CSS3 教程
- CSS3 - 教程
- CSS - 圓角
- CSS - 邊框圖片
- CSS - 多重背景
- CSS - 顏色
- CSS - 漸變
- CSS - 盒陰影
- CSS - box-decoration-break
- CSS - caret-color
- CSS - 文字陰影
- CSS - 文字
- CSS - 2D 變換
- CSS - 3D 變換
- CSS - 過渡
- CSS - 動畫
- CSS - 多列
- CSS - box-sizing
- CSS - 提示框
- CSS - 按鈕
- CSS - 分頁
- CSS - 變數
- CSS - 媒體查詢
- CSS - 函式
- CSS - 數學函式
- CSS - 遮罩
- CSS - 形狀
- CSS - 樣式圖片
- CSS - 特效性
- CSS - 自定義屬性
- CSS 響應式
- CSS RWD - 簡介
- CSS RWD - 視口
- CSS RWD - 網格檢視
- CSS RWD - 媒體查詢
- CSS RWD - 圖片
- CSS RWD - 影片
- CSS RWD - 框架
- CSS 工具
- CSS - PX 到 EM 轉換器
- CSS - 顏色選擇器和動畫
- CSS 資源
- CSS - 有用資源
- CSS - 討論
CSS - 特效性
想象一下,如果我們使用不同的選擇器在 CSS 中多次宣告一個屬性會發生什麼。CSS 使用**特效性**順序來確定哪個選擇器具有最高的優先順序。
例如,如果使用類選擇器和 ID 選擇器在 HTML 元素上指定了兩個或多個 CSS 規則,則在具有最高特效性值的選擇器(在本例中為 ID 選擇器)中宣告的屬性將應用於該元素。
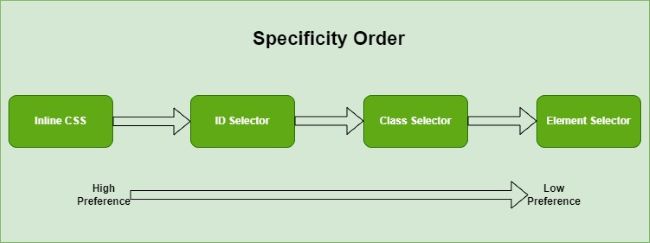
特效性層次結構
CSS 中的每個**選擇器**都具有一個特效性級別。以下是 CSS 選擇器的特效性順序。
- **內聯樣式:** 使用 style 屬性為元素定義的樣式具有最高優先順序。
<h1 style="color: blue;"> Example </h1>
<style>
#mainDiv {
color: blue;
}
</style>
<style>
.subDivs {
color: blue;
}
</style>
<style>
div {
color: blue;
}
</style>
如何計算特效性?
要計算特效性值,您需要記住這些值。內聯樣式的特效性值為 1000。ID 選擇器的值為 100。對於類選擇器、屬性選擇器和偽類,特效性值為 10。最後,對於元素選擇器和偽元素,特效性值為 1。萬用字元選擇器沒有特效性值,為了比較的目的,我們可以認為其值為 0。
| 選擇器 | 特效性 | 計算 |
|---|---|---|
| <div style="color: green"></div> | 1000 | 1000 |
| #uniqueId | 100 | 100 |
| .mainClass | 10 | 10 |
| div | 1 | 1 |
| div #uniqueId | 101 | 100+1 |
| div .mainClass | 11 | 10+1 |
| div .mainClass .navbar | 21 | 10+10+1 |
| div #uniqueId .navbar | 111 | 100+10+1 |
特效性規則示例
下面的示例程式碼將說明 CSS 特效性。
具有最高特效性值的選擇器將生效
以下示例使用多個選擇器將 color 屬性應用於段落,在第一種情況下,ID 選擇器生效,在第二種情況下,內聯 CSS 生效。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/*Multiple selectors for paragraph */
p {
color: black;
font-weight: bold;
}
.special {
color: blue;
}
#unique {
color: darkgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="unique" class="special">
This paragraph will be darkgreen. Id selector wins!!!!
</p>
<p class="special">
This paragraph will be blue. Class selector wins!!!!
</p>
<p class="special" style="color: darkblue;">
This paragraph will be darkblue. Inline style wins!!!!
</p>
</body>
</html>
特效性值相等,最新的規則獲勝
以下示例顯示,當兩個類選擇器目標相同的段落並嘗試對其應用相同的樣式時,最後定義的類將生效。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p {
color: black;
font-weight: bold;
}
.special {
color: blue;
}
.superSpecial{
color: gold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="special superSpecial">
This paragraph is gold color. Class superSpecial wins!!!
</p>
</body>
</html>
內部 CSS 樣式優先於外部樣式表
在 HTML 文件內使用 style 標籤定義的選擇器比外部匯入的樣式表具有更高的優先順序。
/*From imported external CSS file:*/
#uniqueID {
color: red;
}
/*In HTML file:*/
<style>
#uniqueID {
color: yellow;
}
</style>
元素將設定為黃色。
覆蓋特效性規則
以下示例演示,如果屬性標記為!important,則特效性順序將變得無關緊要。
示例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p {
color: black;
font-weight: bold;
}
.special {
color: blue;
}
#unique {
color: darkgreen;
}
p {
color: darkred !important;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="unique" class="special">
This paragraph is darkred. The !important keyword wins
over every other selector!!!
</p>
<p class="special" style="color: green">
This paragraph is darkred. The !important keyword wins
even over inline style!!!
</p>
</body>
</html>
廣告