
- C程式設計教程
- C語言 - 首頁
- C語言基礎
- C語言 - 概述
- C語言 - 特性
- C語言 - 歷史
- C語言 - 環境搭建
- C語言 - 程式結構
- C語言 - Hello World
- C語言 - 編譯過程
- C語言 - 註釋
- C語言 - 詞法單元
- C語言 - 關鍵字
- C語言 - 識別符號
- C語言 - 使用者輸入
- C語言 - 基本語法
- C語言 - 資料型別
- C語言 - 變數
- C語言 - 整數提升
- C語言 - 型別轉換
- C語言 - 型別強制轉換
- C語言 - 布林值
- C語言中的常量和字面量
- C語言 - 常量
- C語言 - 字面量
- C語言 - 轉義序列
- C語言 - 格式說明符
- C語言中的運算子
- C語言 - 運算子
- C語言 - 算術運算子
- C語言 - 關係運算符
- C語言 - 邏輯運算子
- C語言 - 位運算子
- C語言 - 賦值運算子
- C語言 - 一元運算子
- C語言 - 自增和自減運算子
- C語言 - 三元運算子
- C語言 - sizeof運算子
- C語言 - 運算子優先順序
- C語言 - 其他運算子
- C語言中的決策機制
- C語言 - 決策機制
- C語言 - if語句
- C語言 - if...else語句
- C語言 - 巢狀if語句
- C語言 - switch語句
- C語言 - 巢狀switch語句
- C語言中的迴圈
- C語言 - 迴圈
- C語言 - while迴圈
- C語言 - for迴圈
- C語言 - do...while迴圈
- C語言 - 巢狀迴圈
- C語言 - 無限迴圈
- C語言 - break語句
- C語言 - continue語句
- C語言 - goto語句
- C語言中的函式
- C語言 - 函式
- C語言 - 主函式
- C語言 - 按值呼叫函式
- C語言 - 按引用呼叫函式
- C語言 - 巢狀函式
- C語言 - 可變引數函式
- C語言 - 使用者自定義函式
- C語言 - 回撥函式
- C語言 - 返回語句
- C語言 - 遞迴
- C語言中的作用域規則
- C語言 - 作用域規則
- C語言 - 靜態變數
- C語言 - 全域性變數
- C語言中的陣列
- C語言 - 陣列
- C語言 - 陣列的特性
- C語言 - 多維陣列
- C語言 - 將陣列傳遞給函式
- C語言 - 從函式返回陣列
- C語言 - 變長陣列
- C語言中的指標
- C語言 - 指標
- C語言 - 指標和陣列
- C語言 - 指標的應用
- C語言 - 指標運算
- C語言 - 指標陣列
- C語言 - 指向指標的指標
- C語言 - 將指標傳遞給函式
- C語言 - 從函式返回指標
- C語言 - 函式指標
- C語言 - 指向陣列的指標
- C語言 - 指向結構體的指標
- C語言 - 指標鏈
- C語言 - 指標與陣列的區別
- C語言 - 字元指標和函式
- C語言 - 空指標
- C語言 - void指標
- C語言 - 野指標
- C語言 - 指標解引用
- C語言 - 近指標、遠指標和巨指標
- C語言 - 指標陣列的初始化
- C語言 - 指標與多維陣列的比較
- C語言中的字串
- C語言 - 字串
- C語言 - 字串陣列
- C語言 - 特殊字元
- C語言中的結構體和聯合體
- C語言 - 結構體
- C語言 - 結構體和函式
- C語言 - 結構體陣列
- C語言 - 自引用結構體
- C語言 - 查詢表
- C語言 - 點 (.) 運算子
- C語言 - 列舉 (enum)
- C語言 - 結構體填充和打包
- C語言 - 巢狀結構體
- C語言 - 匿名結構體和聯合體
- C語言 - 聯合體
- C語言 - 位域
- C語言 - typedef
- C語言中的檔案處理
- C語言 - 輸入 & 輸出
- C語言 - 檔案I/O (檔案處理)
- C語言預處理器
- C語言 - 預處理器
- C語言 - 編譯指示
- C語言 - 預處理器運算子
- C語言 - 宏
- C語言 - 標頭檔案
- C語言中的記憶體管理
- C語言 - 記憶體管理
- C語言 - 記憶體地址
- C語言 - 儲存類
- 其他主題
- C語言 - 錯誤處理
- C語言 - 可變引數
- C語言 - 命令執行
- C語言 - 數學函式
- C語言 - static關鍵字
- C語言 - 隨機數生成
- C語言 - 命令列引數
- C程式設計資源
- C語言 - 問答
- C語言 - 快速指南
- C語言 - 速查表
- C語言 - 有用資源
- C語言 - 討論
C語言中的自引用結構體
什麼是自引用結構體?
自引用結構體是C語言中的一種結構體資料型別,其中一個或多個元素是指向其自身型別變數的指標。自引用使用者定義型別在C程式設計中具有極其重要的作用。它們被廣泛用於構建複雜的動態資料結構,例如連結串列和樹。
在C程式設計中,陣列在編譯時分配所需的記憶體,並且陣列大小在執行時無法修改。自引用結構體允許您透過動態處理大小來模擬陣列。
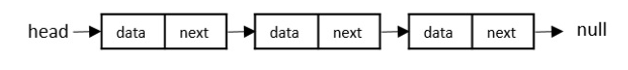
作業系統的檔案管理系統建立在動態構建的樹結構之上,這些結構由自引用結構體操作。自引用結構體也用於許多複雜的演算法中。
定義自引用結構體
定義自引用結構體的通用語法如下:
strut typename{
type var1;
type var2;
...
...
struct typename *var3;
}
讓我們透過以下示例瞭解如何使用自引用結構體。我們定義了一個名為mystruct的結構體型別。它有一個整數元素“a”,而“b”是指向mystruct型別本身的指標。
我們宣告三個mystruct型別的變數:
struct mystruct x = {10, NULL}, y = {20, NULL}, z = {30, NULL};
接下來,我們宣告三個“mystruct”指標,並將x、y和z的引用賦值給它們。
struct mystruct * p1, *p2, *p3; p1 = &x; p2 = &y; p3 = &z;
變數“x”、“y”和“z”是相互獨立的,因為它們將位於隨機位置,這與所有元素都在相鄰位置的陣列不同。
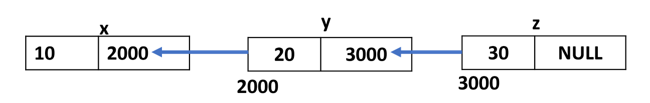
自引用結構體的示例
示例1
為了明確建立三個變數之間的連結,我們可以在“x”中儲存“y”的地址,在“y”中儲存“z”的地址。讓我們在下面的程式中實現這一點:
#include <stdio.h>
struct mystruct{
int a;
struct mystruct *b;
};
int main(){
struct mystruct x = {10, NULL}, y = {20, NULL}, z = {30, NULL};
struct mystruct * p1, *p2, *p3;
p1 = &x;
p2 = &y;
p3 = &z;
x.b = p2;
y.b = p3;
printf("Address of x: %d a: %d Address of next: %d\n", p1, x.a, x.b);
printf("Address of y: %d a: %d Address of next: %d\n", p2, y.a, y.b);
printf("Address of z: %d a: %d Address of next: %d\n", p3, z.a, z.b);
return 0;
}
輸出
執行程式碼並檢查其輸出:
Address of x: 659042000 a: 10 Address of next: 659042016 Address of y: 659042016 a: 20 Address of next: 659042032 Address of z: 659042032 a: 30 Address of next: 0
示例2
讓我們進一步改進上面的程式。我們不宣告變數然後將它們的地址儲存在指標中,而是使用malloc()函式動態分配記憶體,其地址儲存在指標變數中。然後,我們像下面這樣建立三個節點之間的連結:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct mystruct{
int a;
struct mystruct *b;
};
int main(){
struct mystruct *p1, *p2, *p3;
p1 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
p2 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
p3 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
p1 -> a = 10; p1->b=NULL;
p2 -> a = 20; p2->b=NULL;
p3 -> a =30; p3->b=NULL;
p1 -> b = p2;
p2 -> b = p3;
printf("Add of x: %d a: %d add of next: %d\n", p1, p1->a, p1->b);
printf("add of y: %d a: %d add of next: %d\n", p2, p2->a, p2->b);
printf("add of z: %d a: %d add of next: %d\n", p3, p3->a, p3->b);
return 0;
}
輸出
執行程式碼並檢查其輸出:
Add of x: 10032160 a: 10 add of next: 10032192 add of y: 10032192 a: 20 add of next: 10032224 add of z: 10032224 a: 30 add of next: 0
示例3
我們可以從前面元素中儲存的地址訪問連結中的下一個元素,因為“p1 → b”指向“p2”的地址。我們可以使用while迴圈來顯示連結串列,如下例所示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct mystruct{
int a;
struct mystruct *b;
};
int main(){
struct mystruct *p1, *p2, *p3;
p1=(struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
p2=(struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
p3=(struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
p1 -> a = 10; p1 -> b = NULL;
p2 -> a = 20; p2 -> b = NULL;
p3 -> a = 30; p3 -> b = NULL;
p1 -> b = p2;
p2 -> b = p3;
while (p1 != NULL){
printf("Add of current: %d a: %d add of next: %d\n", p1, p1->a, p1->b);
p1 = p1 -> b;
}
return 0;
}
輸出
執行程式碼並檢查其輸出:
Add of current: 10032160 a: 10 add of next: 10032192 Add of current: 10032192 a: 20 add of next: 10032224 Add of current: 10032224 a: 30 add of next: 0
使用自引用結構體建立連結串列
在上面的示例中,動態構建的列表具有三個透過指標連結的離散元素。我們可以使用for迴圈透過動態分配記憶體來設定所需數量的元素,並將下一個元素的地址儲存在前面的節點中。
示例
以下示例顯示瞭如何使用自引用結構體建立連結串列:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct mystruct{
int a;
struct mystruct *b;
};
int main(){
struct mystruct *p1, *p2, *start;
int i;
p1 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
p1 -> a = 10; p1 -> b = NULL;
start = p1;
for(i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
p2 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
p2 -> a = i*2;
p2 -> b = NULL;
p1 -> b = p2;
p1 = p2;
}
p1 = start;
while(p1 != NULL){
printf("Add of current: %d a: %d add of next: %d\n", p1, p1 -> a, p1 -> b);
p1 = p1 -> b;
}
return 0;
}
輸出
執行程式碼並檢查其輸出:
Add of current: 11408416 a: 10 add of next: 11408448 Add of current: 11408448 a: 2 add of next: 11408480 Add of current: 11408480 a: 4 add of next: 11408512 Add of current: 11408512 a: 6 add of next: 11408544 Add of current: 11408544 a: 8 add of next: 11408576 Add of current: 11408576 a: 10 add of next: 0
使用自引用結構體建立雙向連結串列
連結串列從開始遍歷到到達NULL。您還可以構建一個雙向連結串列,其中結構體有兩個指標,每個指標都指向前一個和下一個元素的地址。
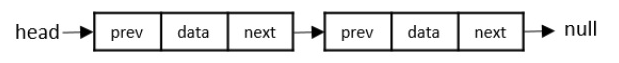
為此目的的結構體定義如下:
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
使用自引用結構體建立樹
自引用結構體也用於構建非線性資料結構,例如樹。二叉搜尋樹由下圖邏輯表示:
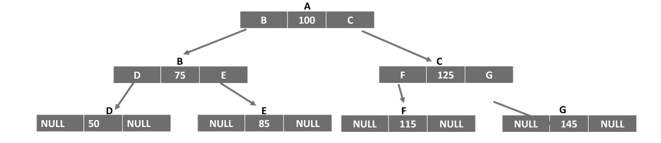
實現樹的結構體定義如下:
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
要詳細瞭解這些複雜的資料結構,您可以訪問DSA教程:資料結構演算法