
- C語言程式設計教程
- C語言 - 首頁
- C語言基礎
- C語言 - 概述
- C語言 - 特性
- C語言 - 歷史
- C語言 - 環境搭建
- C語言 - 程式結構
- C語言 - Hello World
- C語言 - 編譯過程
- C語言 - 註釋
- C語言 - 詞法單元
- C語言 - 關鍵字
- C語言 - 識別符號
- C語言 - 使用者輸入
- C語言 - 基本語法
- C語言 - 資料型別
- C語言 - 變數
- C語言 - 整型提升
- C語言 - 型別轉換
- C語言 - 型別強制轉換
- C語言 - 布林值
- C語言中的常量和字面量
- C語言 - 常量
- C語言 - 字面量
- C語言 - 轉義序列
- C語言 - 格式說明符
- C語言中的運算子
- C語言 - 運算子
- C語言 - 算術運算子
- C語言 - 關係運算符
- C語言 - 邏輯運算子
- C語言 - 位運算子
- C語言 - 賦值運算子
- C語言 - 一元運算子
- C語言 - 自增和自減運算子
- C語言 - 三元運算子
- C語言 - sizeof運算子
- C語言 - 運算子優先順序
- C語言 - 其他運算子
- C語言中的決策
- C語言 - 決策
- C語言 - if語句
- C語言 - if...else語句
- C語言 - 巢狀if語句
- C語言 - switch語句
- C語言 - 巢狀switch語句
- C語言中的迴圈
- C語言 - 迴圈
- C語言 - while迴圈
- C語言 - for迴圈
- C語言 - do...while迴圈
- C語言 - 巢狀迴圈
- C語言 - 死迴圈
- C語言 - break語句
- C語言 - continue語句
- C語言 - goto語句
- C語言中的函式
- C語言 - 函式
- C語言 - 主函式
- C語言 - 按值呼叫函式
- C語言 - 按引用呼叫函式
- C語言 - 巢狀函式
- C語言 - 可變引數函式
- C語言 - 使用者自定義函式
- C語言 - 回撥函式
- C語言 - return語句
- C語言 - 遞迴
- C語言中的作用域規則
- C語言 - 作用域規則
- C語言 - 靜態變數
- C語言 - 全域性變數
- C語言中的陣列
- C語言 - 陣列
- C語言 - 陣列的特性
- C語言 - 多維陣列
- C語言 - 將陣列傳遞給函式
- C語言 - 從函式返回陣列
- C語言 - 變長陣列
- C語言中的指標
- C語言 - 指標
- C語言 - 指標和陣列
- C語言 - 指標的應用
- C語言 - 指標運算
- C語言 - 指標陣列
- C語言 - 指向指標的指標
- C語言 - 將指標傳遞給函式
- C語言 - 從函式返回指標
- C語言 - 函式指標
- C語言 - 指向陣列的指標
- C語言 - 指向結構體的指標
- C語言 - 指標鏈
- C語言 - 指標與陣列的比較
- C語言 - 字元指標和函式
- C語言 - 空指標
- C語言 - void指標
- C語言 - 懸空指標
- C語言 - 解引用指標
- C語言 - 近指標、遠指標和巨指標
- C語言 - 指標陣列的初始化
- C語言 - 指標與多維陣列的比較
- C語言中的字串
- C語言 - 字串
- C語言 - 字串陣列
- C語言 - 特殊字元
- C語言結構體和聯合體
- C語言 - 結構體
- C語言 - 結構體和函式
- C語言 - 結構體陣列
- C語言 - 自引用結構體
- C語言 - 查詢表
- C語言 - 點(.)運算子
- C語言 - 列舉(enum)
- C語言 - 結構體填充和打包
- C語言 - 巢狀結構體
- C語言 - 匿名結構體和聯合體
- C語言 - 聯合體
- C語言 - 位域
- C語言 - typedef
- C語言中的檔案處理
- C語言 - 輸入與輸出
- C語言 - 檔案I/O(檔案處理)
- C語言預處理器
- C語言 - 預處理器
- C語言 - 預處理程式
- C語言 - 預處理器運算子
- C語言 - 宏
- C語言 - 標頭檔案
- C語言中的記憶體管理
- C語言 - 記憶體管理
- C語言 - 記憶體地址
- C語言 - 儲存類別
- 其他主題
- C語言 - 錯誤處理
- C語言 - 可變引數
- C語言 - 命令執行
- C語言 - 數學函式
- C語言 - static關鍵字
- C語言 - 隨機數生成
- C語言 - 命令列引數
- C語言程式設計資源
- C語言 - 問答
- C語言 - 快速指南
- C語言 - 速查表
- C語言 - 有用資源
- C語言 - 討論
C語言 - if語句
指令的條件執行是計算機程式的基本要求。C語言中的if語句是主要的條件語句。C語言允許使用可選的else關鍵字來指定如果if條件為假則要執行的語句。
C語言 - if語句
if語句是C語言程式設計中一種基本的決策控制語句。根據if語句中布林條件的真假,程式碼塊中的一條或多條語句將被執行。
if語句的語法
if語句的語法如下:
if(boolean_expression) {
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true */
}
if語句的工作原理?
C語言使用一對花括號來構成程式碼塊。如果布林表示式計算結果為真,則將執行if語句內的程式碼塊。
如果布林表示式的計算結果為假,則將執行if語句結束後的第一組程式碼(右花括號之後)。
C語言將任何非零和非空值視為真。如果值為零或空,則將其視為假值。
if語句的流程圖
if語句的行為可以用以下流程圖表示:
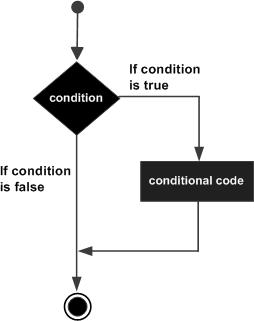
流程圖解釋
當程式控制遇到if語句時,將評估條件。
如果條件為真,則執行if塊內的語句。
如果條件為假,則程式流程將繞過條件塊。
執行if塊後的語句以繼續程式流程。
C語言中if語句的示例
此示例演示了if語句最簡單的用例。它確定並告訴使用者變數的值是否小於20。
#include <stdio.h>
int main (){
/* local variable declaration */
int a;
// run the program for different values of "a"
// Assign 12 first and 40 afterwards
a = 12; //change to 40 and run again
printf("Value of a is : %d\n", a);
// check the boolean condition using if statement
if(a < 20){
//if the condition is true, then print the following
printf("a is less than 20\n" );
}
return 0;
}
輸出
執行上述程式並檢查其輸出:
Value of a is : 12 a is less than 20
現在賦值一個大於20的數字。if條件不會被執行。
Value of a is: 40
帶有邏輯運算的if語句
您可以使用&&或||運算子在if語句的括號中放置複合布林表示式。
示例
在下面的示例中,比較了三個變數“a”、“b”和“c”。當“a”大於“b”和“c”時,將執行if塊。
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
/* local variable declaration */
int a, b, c;
/*use different values for a, b and c as
10, 5, 7
10, 20, 15
*/
// change to 10,20,15 respectively next time
a = 10; b = 5; c = 7;
if (a>=b && a>=c){
printf ("a is greater than b and c \n");
}
printf("a: %d b:%d c:%d", a, b, c);
return 0;
}
輸出
執行程式碼並檢查其輸出:
//when values for a, b and c are 10 5 7 a is greater than b and c a: 10 b:5 c:7 //when values for a, b and c are 10 20 15 a: 10 b:20 c:15
請注意,條件塊後面的語句在塊執行後執行。如果條件為假,程式將直接跳轉到塊後面的語句。
多個if語句
如果您有多個條件要檢查,則可以多次使用if語句。
示例
在此示例中,透過對賬單金額應用折扣來計算應付淨額。
如果金額在1000到5000之間,則適用的折扣為5%;如果金額超過5000,則適用的折扣為10%。對於低於1000的購買,不適用任何折扣。
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
// local variable declaration
int amount;
float discount, net;
/*Run the program for different values
of amount – 500, 2250 and 5200. Blocks in
respective conditions will be executed*/
// change to 2250 and 5200 and run again
amount = 500;
if (amount < 1000){
discount=0;
}
if (amount >= 1000 && amount<5000){
discount=5;
}
if (amount >= 5000){
discount=10;
}
net = amount - amount*discount/100;
printf("Amount: %d Discount: %f Net payable: %f", amount, discount, net);
return 0;
}
輸出
//when the bill amount is 500 Amount: 500 Discount: 0.000000 Net payable: 500.000000 //when the bill amount is 2250 Amount: 2250 Discount: 5.000000 Net payable: 2137.500000 //when the bill amount is 5200 Amount: 5200 Discount: 10.000000 Net payable: 4680.000000
使用if語句檢查多個條件
您也可以在單個if語句中使用邏輯運算子來檢查多個條件。
示例
在此程式中,只有當“phy”和“maths”分數的平均值大於等於50時,學生才被判定為及格。此外,學生兩門科目的分數都必須超過35分。否則,學生將被判定為不及格。
#include <stdio.h>
int main (){
/* local variable declaration */
int phy, maths;
float avg;
/*use different values of phy and maths
to check conditional execution*/
//change to 40, 40 and 80, 40
phy = 50; maths = 50;
avg = (float)(phy + maths)/2;
printf("Phy: %d Maths: %d Avg: %f\n", phy, maths, avg);
if (avg >= 50 && (maths >= 35 && phy >= 35)){
printf("Result: Pass");
}
if (avg<50) {
printf("Result: Fail\n");
}
return 0;
}
輸出
執行程式碼並檢查其輸出:
//when marks in Phy and Maths - 50 50 Phy: 50 Maths: 50 Avg: 50.000000 Result: Pass //when marks in Phy and Maths - 40 40 Phy: 40 Maths: 40 Avg: 40.000000 Result: Fail //when marks in Phy and Maths - 80 40 Phy: 80 Maths: 40 Avg: 60.000000 Result: Pass