
- Biopython 教程
- Biopython - 首頁
- Biopython - 簡介
- Biopython - 安裝
- 建立簡單的應用程式
- Biopython - 序列
- 高階序列操作
- 序列 I/O 操作
- Biopython - 序列比對
- Biopython - BLAST 概述
- Biopython - Entrez 資料庫
- Biopython - PDB 模組
- Biopython - 基序物件
- Biopython - BioSQL 模組
- Biopython - 群體遺傳學
- Biopython - 基因組分析
- Biopython - 表型微陣列
- Biopython - 繪圖
- Biopython - 聚類分析
- Biopython - 機器學習
- Biopython - 測試技術
- Biopython 資源
- Biopython - 快速指南
- Biopython - 有用資源
- Biopython - 討論
Biopython - BioSQL 模組
BioSQL 是一種通用資料庫模式,主要設計用於儲存序列及其所有關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 引擎的相關資料。它的設計方式使其能夠儲存來自所有流行的生物資訊學資料庫(如 GenBank、Swissport 等)的資料。它也可以用於儲存內部資料。
BioSQL 目前為以下資料庫提供特定的模式:
- MySQL (biosqldb-mysql.sql)
- PostgreSQL (biosqldb-pg.sql)
- Oracle (biosqldb-ora/*.sql)
- SQLite (biosqldb-sqlite.sql)
它還為基於 Java 的 HSQLDB 和 Derby 資料庫提供最小的支援。
BioPython 提供非常簡單、易用和高階的 ORM 功能來處理基於 BioSQL 的資料庫。BioPython 提供了一個名為 BioSQL 的模組,用於執行以下功能:
- 建立/刪除 BioSQL 資料庫
- 連線到 BioSQL 資料庫
- 解析序列資料庫(如 GenBank、Swisport、BLAST 結果、Entrez 結果等),並將其直接載入到 BioSQL 資料庫中
- 從 BioSQL 資料庫中獲取序列資料
- 從 NCBI BLAST 獲取分類資料並將其儲存在 BioSQL 資料庫中
- 對 BioSQL 資料庫執行任何 SQL 查詢
BioSQL 資料庫模式概述
在深入瞭解 BioSQL 之前,讓我們先了解 BioSQL 模式的一些基礎知識。BioSQL 模式提供了 25 多個表來儲存序列資料、序列特徵、序列類別/本體和分類資訊。一些重要的表如下:
- biodatabase
- bioentry
- biosequence
- seqfeature
- taxon
- taxon_name
- antology
- term
- dxref
建立 BioSQL 資料庫
在本節中,讓我們使用 BioSQL 團隊提供的模式建立一個示例 BioSQL 資料庫 biosql。我們將使用 SQLite 資料庫,因為它非常易於入門且設定簡單。
在這裡,我們將使用以下步驟建立一個基於 SQLite 的 BioSQL 資料庫:
步驟 1 - 下載 SQLite 資料庫引擎並安裝它。
步驟 2 - 從 GitHub URL 下載 BioSQL 專案。 https://github.com/biosql/biosql
步驟 3 - 開啟控制檯,使用 mkdir 建立一個目錄並進入該目錄。
cd /path/to/your/biopython/sample mkdir sqlite-biosql cd sqlite-biosql
步驟 4 - 執行以下命令以建立一個新的 SQLite 資料庫。
> sqlite3.exe mybiosql.db SQLite version 3.25.2 2018-09-25 19:08:10 Enter ".help" for usage hints. sqlite>
步驟 5 - 從 BioSQL 專案複製 biosqldb-sqlite.sql 檔案(`/sql/biosqldb-sqlite.sql`)並將其儲存在當前目錄中。
步驟 6 - 執行以下命令以建立所有表。
sqlite> .read biosqldb-sqlite.sql
現在,所有表都已建立到我們的新資料庫中。
步驟 7 - 執行以下命令以檢視資料庫中的所有新表。
sqlite> .headers on sqlite> .mode column sqlite> .separator ROW "\n" sqlite> SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type = 'table'; biodatabase taxon taxon_name ontology term term_synonym term_dbxref term_relationship term_relationship_term term_path bioentry bioentry_relationship bioentry_path biosequence dbxref dbxref_qualifier_value bioentry_dbxref reference bioentry_reference comment bioentry_qualifier_value seqfeature seqfeature_relationship seqfeature_path seqfeature_qualifier_value seqfeature_dbxref location location_qualifier_value sqlite>
前三個命令是配置命令,用於配置 SQLite 以格式化的方式顯示結果。
步驟 8 - 將 BioPython 團隊提供的示例 GenBank 檔案 ls_orchid.gbk 複製到當前目錄 https://raw.githubusercontent.com/biopython/biopython/master/Doc/examples/ls_orchid.gbk 並將其儲存為 orchid.gbk。
步驟 9 - 使用以下程式碼建立一個 python 指令碼 load_orchid.py 並執行它。
from Bio import SeqIO
from BioSQL import BioSeqDatabase
import os
server = BioSeqDatabase.open_database(driver = 'sqlite3', db = "orchid.db")
db = server.new_database("orchid")
count = db.load(SeqIO.parse("orchid.gbk", "gb"), True) server.commit()
server.close()
以上程式碼解析檔案中的記錄,將其轉換為 python 物件並將其插入 BioSQL 資料庫。我們將在後面的章節中分析程式碼。
最後,我們建立了一個新的 BioSQL 資料庫並將一些示例資料載入到其中。我們將在下一章討論重要的表。
簡單的 ER 圖
biodatabase 表位於層次結構的頂部,其主要目的是將一組序列資料組織到一個組/虛擬資料庫中。biodatabase 中的每個條目都引用一個單獨的資料庫,並且不會與其他資料庫混合。BioSQL 資料庫中的所有相關表都引用 biodatabase 條目。
bioentry 表儲存序列的所有詳細資訊,除了序列資料本身。特定bioentry 的序列資料將儲存在biosequence 表中。
taxon 和 taxon_name 是分類詳細資訊,每個條目都引用此表以指定其分類資訊。
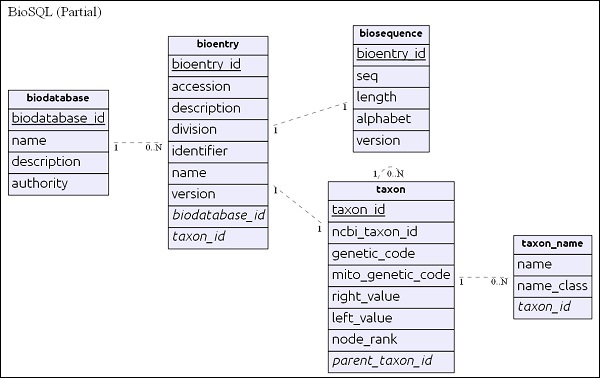
在瞭解模式後,讓我們在下一節中檢視一些查詢。
BioSQL 查詢
讓我們深入研究一些 SQL 查詢,以更好地瞭解資料是如何組織的以及表是如何相互關聯的。在繼續之前,讓我們使用以下命令開啟資料庫並設定一些格式化命令:
> sqlite3 orchid.db SQLite version 3.25.2 2018-09-25 19:08:10 Enter ".help" for usage hints. sqlite> .header on sqlite> .mode columns
.header 和 .mode 是格式化選項,可以更好地視覺化資料。您也可以使用任何 SQLite 編輯器來執行查詢。
列出系統中可用的虛擬序列資料庫,如下所示:
select * from biodatabase; *** Result *** sqlite> .width 15 15 15 15 sqlite> select * from biodatabase; biodatabase_id name authority description --------------- --------------- --------------- --------------- 1 orchid sqlite>
這裡,我們只有一個數據庫,orchid。
列出資料庫orchid 中可用的條目(前 3 個),使用以下程式碼
select
be.*,
bd.name
from
bioentry be
inner join
biodatabase bd
on bd.biodatabase_id = be.biodatabase_id
where
bd.name = 'orchid' Limit 1,
3;
*** Result ***
sqlite> .width 15 15 10 10 10 10 10 50 10 10
sqlite> select be.*, bd.name from bioentry be inner join biodatabase bd on
bd.biodatabase_id = be.biodatabase_id where bd.name = 'orchid' Limit 1,3;
bioentry_id biodatabase_id taxon_id name accession identifier division description version name
--------------- --------------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
---------- ---------- ----------- ---------- --------- ---------- ----------
2 1 19 Z78532 Z78532 2765657 PLN
C.californicum 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS1 and ITS2 DN 1
orchid
3 1 20 Z78531 Z78531 2765656 PLN
C.fasciculatum 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS1 and ITS2 DN 1
orchid
4 1 21 Z78530 Z78530 2765655 PLN
C.margaritaceum 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS1 and ITS2 D 1
orchid
sqlite>
列出與條目(登入號 - Z78530,名稱 - C. fasciculatum 5.8S rRNA 基因和 ITS1 和 ITS2 DNA)關聯的序列詳細資訊,使用以下程式碼:
select
substr(cast(bs.seq as varchar), 0, 10) || '...' as seq,
bs.length,
be.accession,
be.description,
bd.name
from
biosequence bs
inner join
bioentry be
on be.bioentry_id = bs.bioentry_id
inner join
biodatabase bd
on bd.biodatabase_id = be.biodatabase_id
where
bd.name = 'orchid'
and be.accession = 'Z78532';
*** Result ***
sqlite> .width 15 5 10 50 10
sqlite> select substr(cast(bs.seq as varchar), 0, 10) || '...' as seq,
bs.length, be.accession, be.description, bd.name from biosequence bs inner
join bioentry be on be.bioentry_id = bs.bioentry_id inner join biodatabase bd
on bd.biodatabase_id = be.biodatabase_id where bd.name = 'orchid' and
be.accession = 'Z78532';
seq length accession description name
------------ ---------- ---------- ------------ ------------ ---------- ---------- -----------------
CGTAACAAG... 753 Z78532 C.californicum 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS1 and ITS2 DNA orchid
sqlite>
使用以下程式碼獲取與條目(登入號 - Z78530,名稱 - C. fasciculatum 5.8S rRNA 基因和 ITS1 和 ITS2 DNA)關聯的完整序列:
select
bs.seq
from
biosequence bs
inner join
bioentry be
on be.bioentry_id = bs.bioentry_id
inner join
biodatabase bd
on bd.biodatabase_id = be.biodatabase_id
where
bd.name = 'orchid'
and be.accession = 'Z78532';
*** Result ***
sqlite> .width 1000
sqlite> select bs.seq from biosequence bs inner join bioentry be on
be.bioentry_id = bs.bioentry_id inner join biodatabase bd on bd.biodatabase_id =
be.biodatabase_id where bd.name = 'orchid' and be.accession = 'Z78532';
seq
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------
CGTAACAAGGTTTCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGGAAGGATCATTGTTGAGACAACAGAATATATGATCGAGTGAATCT
GGAGGACCTGTGGTAACTCAGCTCGTCGTGGCACTGCTTTTGTCGTGACCCTGCTTTGTTGTTGGGCCTCC
TCAAGAGCTTTCATGGCAGGTTTGAACTTTAGTACGGTGCAGTTTGCGCCAAGTCATATAAAGCATCACTGATGAATGACATTATTGT
CAGAAAAAATCAGAGGGGCAGTATGCTACTGAGCATGCCAGTGAATTTTTATGACTCTCGCAACGGATATCTTGGCTC
TAACATCGATGAAGAACGCAG
sqlite>
列出與生物資料庫 orchid 關聯的分類單元
select distinct
tn.name
from
biodatabase d
inner join
bioentry e
on e.biodatabase_id = d.biodatabase_id
inner join
taxon t
on t.taxon_id = e.taxon_id
inner join
taxon_name tn
on tn.taxon_id = t.taxon_id
where
d.name = 'orchid' limit 10;
*** Result ***
sqlite> select distinct tn.name from biodatabase d inner join bioentry e on
e.biodatabase_id = d.biodatabase_id inner join taxon t on t.taxon_id =
e.taxon_id inner join taxon_name tn on tn.taxon_id = t.taxon_id where d.name =
'orchid' limit 10;
name
------------------------------
Cypripedium irapeanum
Cypripedium californicum
Cypripedium fasciculatum
Cypripedium margaritaceum
Cypripedium lichiangense
Cypripedium yatabeanum
Cypripedium guttatum
Cypripedium acaule
pink lady's slipper
Cypripedium formosanum
sqlite>
將資料載入到 BioSQL 資料庫
讓我們在本節中學習如何將序列資料載入到 BioSQL 資料庫中。我們在上一節中已經有了將資料載入到資料庫的程式碼,程式碼如下:
from Bio import SeqIO
from BioSQL import BioSeqDatabase
import os
server = BioSeqDatabase.open_database(driver = 'sqlite3', db = "orchid.db")
DBSCHEMA = "biosqldb-sqlite.sql"
SQL_FILE = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), DBSCHEMA)
server.load_database_sql(SQL_FILE)
server.commit()
db = server.new_database("orchid")
count = db.load(SeqIO.parse("orchid.gbk", "gb"), True) server.commit()
server.close()
我們將深入瞭解程式碼的每一行及其作用:
第 1 行 - 載入 SeqIO 模組。
第 2 行 - 載入 BioSeqDatabase 模組。此模組提供與 BioSQL 資料庫互動的所有功能。
第 3 行 - 載入 os 模組。
第 5 行 - open_database 開啟指定的資料庫 (db),並使用配置的驅動程式 (driver),並返回到 BioSQL 資料庫 (server) 的控制代碼。Biopython 支援 sqlite、mysql、postgresql 和 oracle 資料庫。
第 6-10 行 - load_database_sql 方法載入來自外部檔案的 sql 並執行它。commit 方法提交事務。我們可以跳過此步驟,因為我們已經使用模式建立了資料庫。
第 12 行 - new_database 方法建立新的虛擬資料庫 orchid 並返回一個控制代碼 db 以對 orchid 資料庫執行命令。
第 13 行 - load 方法將序列條目(可迭代的 SeqRecord)載入到 orchid 資料庫中。SqlIO.parse 解析 GenBank 資料庫,並將其中的所有序列作為可迭代的 SeqRecord 返回。load 方法的第二個引數 (True) 指示它從 NCBI blast 網站獲取序列資料的分類詳細資訊,如果系統中尚不存在。
第 14 行 - commit 提交事務。
第 15 行 - close 關閉資料庫連線並銷燬伺服器控制代碼。
獲取序列資料
讓我們從 orchid 資料庫中獲取識別符號為 2765658 的序列,如下所示:
from BioSQL import BioSeqDatabase
server = BioSeqDatabase.open_database(driver = 'sqlite3', db = "orchid.db")
db = server["orchid"]
seq_record = db.lookup(gi = 2765658)
print(seq_record.id, seq_record.description[:50] + "...")
print("Sequence length %i," % len(seq_record.seq))
這裡,server["orchid"] 返回一個控制代碼,用於從虛擬資料庫 orchid 中獲取資料。lookup 方法提供了一個根據條件選擇序列的選項,我們選擇了識別符號為 2765658 的序列。lookup 將序列資訊作為 SeqRecord 物件返回。由於我們已經知道如何使用 SeqRecord,因此很容易從中獲取資料。
刪除資料庫
刪除資料庫就像使用正確的資料庫名稱呼叫 remove_database 方法然後提交它一樣簡單,如下所示:
from BioSQL import BioSeqDatabase
server = BioSeqDatabase.open_database(driver = 'sqlite3', db = "orchid.db")
server.remove_database("orchids")
server.commit()