
- Three.js 教程
- Three.js - 首頁
- Three.js - 簡介
- Three.js - 安裝
- Three.js - Hello Cube 應用
- Three.js - 渲染器和響應性
- Three.js - 響應式設計
- Three.js - 除錯和統計
- Three.js - 相機
- Three.js - 控制器
- Three.js - 燈光與陰影
- Three.js - 幾何體
- Three.js - 材質
- Three.js - 紋理
- Three.js - 繪製線條
- Three.js - 動畫
- Three.js - 建立文字
- Three.js - 載入3D模型
- Three.js - 庫和外掛
- Three.js 有用資源
- Three.js - 快速指南
- Three.js - 有用資源
- Three.js - 討論
Three.js - 渲染器與響應性
場景的基本功能
您知道場景是用於容納相機、燈光和我們想要在螢幕上渲染的物件的容器。讓我們來看一下場景物件的一些基本功能:
新增物件
`add(object)` 函式用於將物件新增到場景中。
const scene = THREE.Scene() scene.add(cube) // adds the cube scene.add(sphere) // adds a sphere
移除物件
`remove(object)` 函式用於從場景中移除物件。
scene.remove(cube) // removes the last added cube scene.remove(sphere) // removes a sphere
子物件
`scene.children` 返回場景中所有物件的陣列,包括相機和燈光。
console.log(scene.children) // outputs all the objects in the scene console.log(scene.children.length) // outputs number of elements on the scene
注意 - 我們可以使用物件的 `name` 屬性為任何物件命名。名稱對於除錯非常方便,也可以直接從場景中訪問物件。
檢視以下示例。
scene.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Three.js – The scene
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-family: -applesystem, BlinkMacSystemFont, 'Segoe UI', Roboto, Oxygen, Ubuntu,
Cantarell, 'Open Sans', 'Helvetica Neue', sans-serif;
}
html,
body {
height: 100vh;
width: 100vw;
background-color: #262626;
overflow: hidden;
}
#btn-conatiner {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
height: 10vh;
width: 100%;
}
@media screen and (max-width:600px){
#btn-container{
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
}
.btn {
padding: 5px 15px;
margin: 5px 15px;
font-weight: bold;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.add {
color: green;
}
.rem {
color: red;
}
#threejs-container {
position: block;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/three.js/r128/three.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dat-gui/0.7.7/dat.gui.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="btn-conatiner">
<button class="btn add">Add Cube</button>
<button class="btn rem">Remove Cube</button>
</div>
<div id="threejs-container"></div>
<script type="module">
// Experimenting with different methods of scene
// add, remove, children, getElementById
// sizes
let width = window.innerWidth
let height = window.innerHeight
const gui = new dat.GUI()
// scene
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
scene.background = new THREE.Color(0x262626)
// lights
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.5)
scene.add(ambientLight)
const light = new THREE.PointLight(0xffffff, 0.5)
light.position.set(-10, 10, -10)
// for shadow
light.castShadow = true
light.shadow.mapSize.width = 1024
light.shadow.mapSize.height = 1024
light.shadow.camera.near = 0.1
light.shadow.camera.far = 1000
scene.add(light)
// camera
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, width / height, 0.1, 1000)
camera.position.set(0, 10, 40)
camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0)
gui.add(camera.position, 'z', 10, 200, 1).name('camera-z')
// plane
const planeGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(100, 100)
const plane = new THREE.Mesh(
planeGeometry,
new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({ color: 0xffffff, side: THREE.DoubleSide })
)
plane.rotateX(Math.PI / 2)
plane.position.y = -1.75
plane.receiveShadow = true
scene.add(plane)
// scene.add
function addCube() {
const cubeSize = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 3)
const cubeGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(cubeSize, cubeSize, cubeSize)const cubeMaterial = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: Math.random() * 0xffffff
})
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(cubeGeometry, cubeMaterial)
cube.castShadow = true
cube.name = 'cube-' + scene.children.length
cube.position.x = -30 + Math.round(Math.random() * 50)
cube.position.y = Math.round(Math.random() * 5)
cube.position.z = -20 + Math.round(Math.random() * 50)
scene.add(cube)
}
const add = document.querySelector('.add')
add.addEventListener('click', () => {
addCube()
console.log('cube added')
})
// scene.remove
function removeCube() {
const allChildren = scene.children
const lastObject = allChildren[allChildren.length - 1]
if (lastObject.name) {
scene.remove(lastObject)
}
}
const remove = document.querySelector('.rem')
remove.addEventListener('click', () => {
removeCube()
console.log('cube removed')
})
// scene.children
console.log(scene.children)
// responsivenesswindow.addEventListener('resize', () => {
width = window.innerWidth
height = window.innerHeight
camera.aspect = width / height
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
renderer.render(scene, camera)
})
// renderer
const renderer = new THREE.WebGL1Renderer()
renderer.setSize(width, height)
renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(window.devicePixelRatio, 2))
// animation
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
renderer.render(scene, camera)
}
// rendering the scene
const container = document.querySelector('#threejs-container')
container.append(renderer.domElement)
renderer.render(scene, camera)
animate()
</script>
</body>
</html>
開啟您的控制檯以檢視場景中的元素。
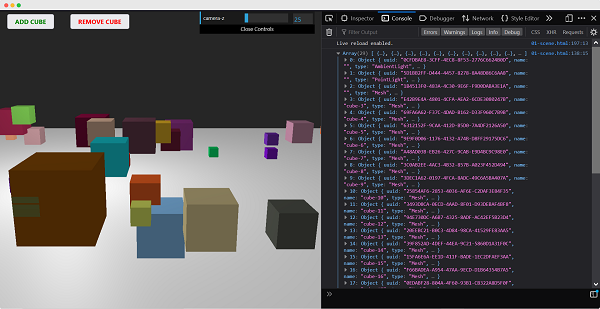
使用 name 屬性
`scene.getObjectByName(name)` 函式直接根據名稱從場景中返回物件。
您還可以新增另一個引數 - `recursive`。
scene.getObjectByName(name, recursive)
如果將 `recursive` 引數設定為 `true`,Three.js 將搜尋物件的完整樹以查詢具有指定名稱的物件。
向場景新增霧
此屬性允許您設定場景的霧。霧會渲染一種薄霧,隱藏遠處的物體。
scene.fog = new THREE.Fog(0xffffff, 0.015, 100)
這行程式碼定義了白色霧 (0xffffff)。您可以使用前面兩個屬性來調整霧的顯示方式。0.015 值設定 near 屬性,100 值設定 far 屬性。使用這些屬性,您可以確定霧的起始位置以及霧變濃的速度。
使用 `THREE.Fog` 物件,霧會線性增加。還有一種不同的方法可以設定場景的霧;為此,請使用以下定義:
scene.fog = new THREE.FogExp2(0xffffff, 0.01)
這次,我們沒有指定 near 和 far,只指定顏色 (0xffffff) 和霧的密度 (0.01)。最好對這些屬性進行一些實驗,以獲得您想要的效果。
使用 overrideMaterial 屬性
`overrideMaterial` 屬性強制場景中的所有物件使用相同的材質。
scene.overrideMaterial = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({ color: 0xffffff })
在這裡,場景上的所有物件都使用相同的材質,即 `MeshLambertMaterial`。
注意 - `THREE.Scene` 是一種有時也稱為場景圖的結構。場景圖是一種可以儲存圖形場景所有必要資訊的結構。在 Three.js 中,這意味著 `THREE.Scene` 包含渲染所需的所有物件、燈光和其他物件。

渲染器
渲染器使用相機和場景中的資訊在螢幕上(即 `
在 Hello Cube 應用中,我們使用了 `WebGLRenderer`。還有一些其他渲染器可用,但 `WebGLRenderer` 迄今為止是最強大的渲染器,通常也是您唯一需要的渲染器。
注意 - 存在基於 canvas 的渲染器、基於 CSS 的渲染器和基於 SVG 的渲染器。雖然它們可以工作並可以渲染簡單的場景,但我不會推薦使用它們。它們沒有積極開發,非常佔用 CPU,並且缺少諸如良好的材質支援和陰影之類的功能。