C++二叉樹的簡潔編碼
假設我們有一個二叉樹。眾所周知,二叉樹的簡潔編碼接近最低可能的儲存空間。第n個卡塔蘭數由具有n個不同節點的結構不同的二叉樹的數量決定。如果n很大,則約為4n;因此,我們需要至少約log2(4)n = 2n位來對其進行編碼。因此,簡潔的二叉樹將消耗2n + O(n)位。
所以,如果輸入是這樣的:
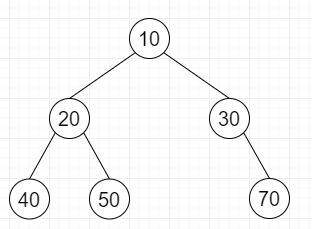
那麼輸出將是:
編碼:
結構列表:1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
資料列表:10 20 40 50 30 70
解碼:如上所示的樹。
為了解決這個問題,我們將遵循以下步驟:
- 定義一個函式Encode(),它將接收根節點、名為struc的列表和名為data的列表作為引數。
- 如果根節點等於NULL,則:
- 在struc的末尾插入0
- 返回
- 在struc的末尾插入1
- 在data的末尾插入根節點的值
- Encode(根節點的左子節點, struc, data)
- Encode(根節點的右子節點, struc, data)
- 定義一個函式Decode(),它將接收名為struc的列表和名為data的列表作為引數。
- 如果struc的大小小於等於0,則:
- 返回NULL
- vb := struc的第一個元素
- 從struc中刪除第一個元素
- 如果b等於1,則:
- key := data的第一個元素
- 從data中刪除第一個元素
- root = 建立一個具有key值的新節點
- root的左子節點 := Decode(struc, data)
- root的右子節點 := Decode(struc, data)
- 返回root
- 返回NULL
示例 (C++)
讓我們看看下面的實現來更好地理解:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode {
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data) {
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void Encode(TreeNode *root, list<bool>&struc, list<int>&data){
if(root == NULL){
struc.push_back(0);
return;
}
struc.push_back(1);
data.push_back(root->val);
Encode(root->left, struc, data);
Encode(root->right, struc, data);
}
TreeNode *Decode(list<bool>&struc, list<int>&data){
if(struc.size() <= 0)
return NULL;
bool b = struc.front();
struc.pop_front();
if(b == 1){
int key = data.front();
data.pop_front();
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(key);
root->left = Decode(struc, data);
root->right = Decode(struc, data);
return root;
}
return NULL;
}
void preorder_trav(TreeNode* root){
if(root){
cout << "key: "<< root->val;
if(root->left)
cout << " | left child: "<< root->left->val;
if(root->right)
cout << " | right child: "<< root->right->val;
cout << endl;
preorder_trav(root->left);
preorder_trav(root->right);
}
}
main() {
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(10);
root->left = new TreeNode(20);
root->right = new TreeNode(30);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(40);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(50);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(70);
cout << "The Tree\n";
preorder_trav(root);
list<bool> struc;
list<int> data;
Encode(root, struc, data);
cout << "\nEncoded Tree\n";
cout << "Structure List\n";
list<bool>::iterator si; // Structure iterator
for(si = struc.begin(); si != struc.end(); ++si)
cout << *si << " ";
cout << "\nData List\n";
list<int>::iterator di; // Data iIterator
for(di = data.begin(); di != data.end(); ++di)
cout << *di << " ";
TreeNode *newroot = Decode(struc, data);
cout << "\n\nPreorder traversal of decoded tree\n";
preorder_trav(newroot);
}輸入
root->left = new TreeNode(20); root->right = new TreeNode(30); root->left->left = new TreeNode(40); root->left->right = new TreeNode(50); root->right->right = new TreeNode(70);
輸出
The Tree key: 10 | left child: 20 | right child: 30 key: 20 | left child: 40 | right child: 50 key: 40 key: 50 key: 30 | right child: 70 key: 70 Encoded Tree Structure List 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 Data List 10 20 40 50 30 70 Preorder traversal of decoded tree key: 10 | left child: 20 | right child: 30 key: 20 | left child: 40 | right child: 50 key: 40 key: 50 key: 30 | right child: 70 key: 70

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP