
- Python 設計模式教程
- Python 設計模式 - 主頁
- 簡介
- Python 設計模式 - 要領
- 模型檢視控制器模式
- Python 設計模式 - 單例模式
- Python 設計模式 - 工廠模式
- Python 設計模式 - 構建器模式
- Python 設計模式 - 原型模式
- Python 設計模式 - 外觀模式
- Python 設計模式 - 命令模式
- Python 設計模式 - 介面卡模式
- Python 設計模式 - 裝飾器模式
- Python 設計模式 - 代理模式
- 職責鏈模式
- Python 設計模式 - 觀察者模式
- Python 設計模式 - 狀態模式
- Python 設計模式 - 策略模式
- Python 設計模式 - 模板模式
- Python 設計模式 - 享元模式
- 抽象工廠模式
- 面向物件
- 面向物件概念實現
- Python 設計模式 - 迭代器模式
- 字典
- 列表資料結構
- Python 設計模式 - 集合
- Python 設計模式 - 佇列
- 字串和序列化
- Python 中的併發
- Python 設計模式 - 反模式
- 異常處理
- Python 設計模式資源
- 快速指南
- Python 設計模式 - 資源
- 討論
Python 設計模式 - 集合
集合可以定義為無序可迭代、可變且不包含重複元素。在 Python 中,集合類是數學集合的符號。使用集合的主要優點是,它包括用於檢查特定元素的高度最佳化方法。
Python 包含一個稱為 frozenset(凍結集合)的單獨類別。這些集合是不可變物件,僅支援生成所需結果的方法和運算子。
如何實現集合?
以下程式有助於實現集合 -
# Set in Python
# Creating two sets
set1 = set()
set2 = set()
# Adding elements to set1
for i in range(1, 6):
set1.add(i)
# Adding elements to set2
for i in range(3, 8):
set2.add(i)
print("Set1 = ", set1)
print("Set2 = ", set2)
print("\n")
# Union of set1 and set2
set3 = set1 | set2# set1.union(set2)
print("Union of Set1 & Set2: Set3 = ", set3)
# Intersection of set1 and set2
set4 = set1 & set2# set1.intersection(set2)
print("Intersection of Set1 & Set2: Set4 = ", set4)
print("\n")
# Checking relation between set3 and set4
if set3 > set4: # set3.issuperset(set4)
print("Set3 is superset of Set4")
elif set3 < set4: # set3.issubset(set4)
print("Set3 is subset of Set4")
else : # set3 == set4
print("Set3 is same as Set4")
# displaying relation between set4 and set3
if set4 < set3: # set4.issubset(set3)
print("Set4 is subset of Set3")
print("\n")
# difference between set3 and set4
set5 = set3 - set4
print("Elements in Set3 and not in Set4: Set5 = ", set5)
print("\n")
# checkv if set4 and set5 are disjoint sets
if set4.isdisjoint(set5):
print("Set4 and Set5 have nothing in common\n")
# Removing all the values of set5
set5.clear()
print("After applying clear on sets Set5: ")
print("Set5 = ", set5)
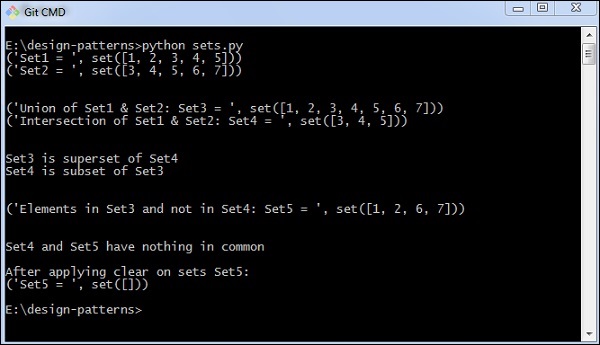
輸出
以上程式生成以下輸出 -
可以用以下程式演示 frozenset(凍結集合) -
normal_set = set(["a", "b","c"])
# Adding an element to normal set is fine
normal_set.add("d")
print("Normal Set")
print(normal_set)
# A frozen set
frozen_set = frozenset(["e", "f", "g"])
print("Frozen Set")
print(frozen_set)
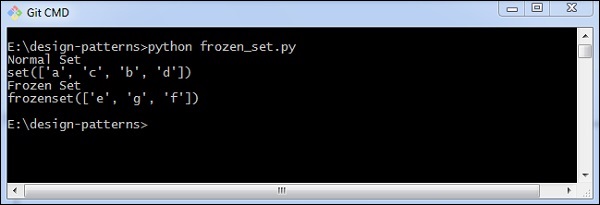
輸出
以上程式生成以下輸出 -
廣告