
- Python 設計模式教程
- Python 設計模式 - 主頁
- 介紹
- Python 設計模式 - 要點
- 模型檢視控制器模式
- Python 設計模式 - 單例
- Python 設計模式 - 工廠
- Python 設計模式 - 構建器
- Python 設計模式 - 原型
- Python 設計模式 - 外觀
- Python 設計模式 - 命令
- Python 設計模式 - 介面卡
- Python 設計模式 - 裝飾器
- Python 設計模式 - 代理
- 責任鏈模式
- Python 設計模式 - 觀察者
- Python 設計模式 - 狀態
- Python 設計模式 - 策略
- Python 設計模式 - 模板
- Python 設計模式 - 輕量級
- 抽象工廠
- 面向物件
- 面向物件概念的實現
- Python 設計模式 - 迭代器
- 字典
- 列表資料結構
- Python 設計模式 - 集合
- Python 設計模式 - 佇列
- 字串和序列化
- Python 中的併發
- Python 設計模式 - 反
- 異常處理
- Python 設計模式資源
- 速查手冊
- Python 設計模式 - 資源
- 討論
面向物件概念的實現
在本章中,我們將重點關注使用面向物件概念的模式及其在 Python 中的實現。當我們圍繞操縱函數週圍資料的語句塊設計我們的程式時,這稱為面向過程的程式設計。在面向物件程式設計中,有稱為類和物件的兩個主要例項。
如何實現類和物件變數?
類和物件變數的實現如下 -
class Robot:
population = 0
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
print("(Initializing {})".format(self.name))
Robot.population += 1
def die(self):
print("{} is being destroyed!".format(self.name))
Robot.population -= 1
if Robot.population == 0:
print("{} was the last one.".format(self.name))
else:
print("There are still {:d} robots working.".format(
Robot.population))
def say_hi(self):
print("Greetings, my masters call me {}.".format(self.name))
@classmethod
def how_many(cls):
print("We have {:d} robots.".format(cls.population))
droid1 = Robot("R2-D2")
droid1.say_hi()
Robot.how_many()
droid2 = Robot("C-3PO")
droid2.say_hi()
Robot.how_many()
print("\nRobots can do some work here.\n")
print("Robots have finished their work. So let's destroy them.")
droid1.die()
droid2.die()
Robot.how_many()
輸出
上述程式生成以下輸出 -
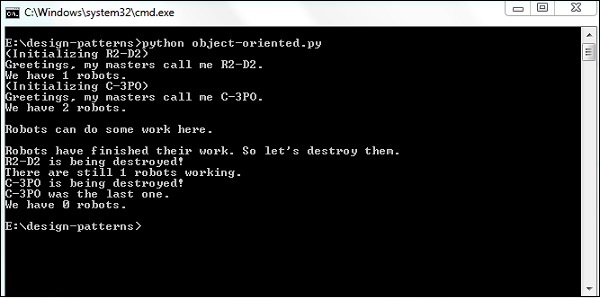
說明
此圖解有助於演示類和物件變數的本質。
“population”屬於“Robot”類。因此,它被稱為類變數或物件。
此處,我們引用人口類變數為 Robot.population 而不是 self.population。
廣告