
Python深度學習 - 實現
在這個深度學習實現中,我們的目標是預測某家銀行的客戶流失或流轉資料——哪些客戶可能離開這家銀行的服務。所使用的資料集相對較小,包含10000行和14列。我們使用Anaconda發行版以及Theano、TensorFlow和Keras等框架。Keras構建在Tensorflow和Theano之上,它們充當Keras的後端。
# Artificial Neural Network # Installing Theano pip install --upgrade theano # Installing Tensorflow pip install –upgrade tensorflow # Installing Keras pip install --upgrade keras
步驟1:資料預處理
In[]:
# Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Importing the database
dataset = pd.read_csv('Churn_Modelling.csv')
步驟2
我們建立資料集特徵矩陣和目標變數矩陣,目標變數是第14列,標記為“Exited”。
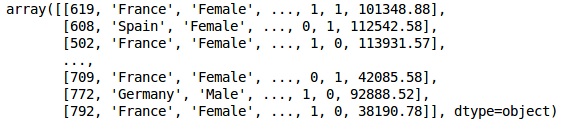
資料的初始外觀如下所示:
In[]: X = dataset.iloc[:, 3:13].values Y = dataset.iloc[:, 13].values X
輸出
步驟3
Y
輸出
array([1, 0, 1, ..., 1, 1, 0], dtype = int64)
步驟4
我們透過編碼字串變數來簡化分析。我們使用ScikitLearn函式“LabelEncoder”自動將各列中的不同標籤編碼為0到n_classes-1之間的值。
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, OneHotEncoder labelencoder_X_1 = LabelEncoder() X[:,1] = labelencoder_X_1.fit_transform(X[:,1]) labelencoder_X_2 = LabelEncoder() X[:, 2] = labelencoder_X_2.fit_transform(X[:, 2]) X
輸出
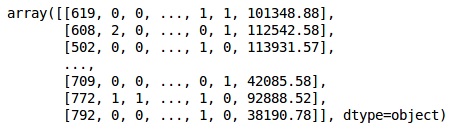
在上面的輸出中,國家名稱被替換為0、1和2;而男性和女性分別被替換為0和1。
步驟5
標籤編碼資料
我們使用相同的ScikitLearn庫和另一個名為OneHotEncoder的函式來傳遞列號,從而建立一個虛擬變數。
onehotencoder = OneHotEncoder(categorical features = [1]) X = onehotencoder.fit_transform(X).toarray() X = X[:, 1:] X
現在,前兩列表示國家,第四列表示性別。
輸出

我們總是將資料分成訓練集和測試集;我們在訓練資料上訓練模型,然後在測試資料上檢查模型的準確性,這有助於評估模型的效率。
步驟6
我們使用ScikitLearn的train_test_split函式將我們的資料分成訓練集和測試集。我們將訓練集與測試集的比例保持為80:20。
#Splitting the dataset into the Training set and the Test Set from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2)
有些變數的值以千計,而有些變數的值只有幾十或幾。我們對資料進行縮放,使其更具代表性。
步驟7
在這段程式碼中,我們使用StandardScaler函式擬合併轉換訓練資料。我們標準化縮放,以便使用相同的擬合方法來轉換/縮放測試資料。
# Feature Scaling
fromsklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler sc = StandardScaler() X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train) X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
輸出
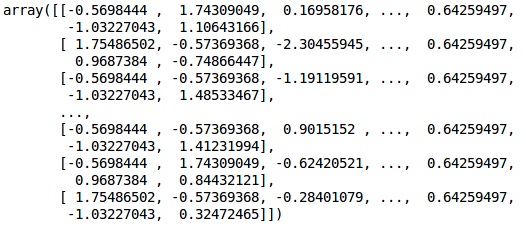
資料現在已正確縮放。最後,我們完成了資料預處理。現在,我們將開始構建我們的模型。
步驟8
我們在這裡匯入所需的模組。我們需要Sequential模組來初始化神經網路,以及dense模組來新增隱藏層。
# Importing the Keras libraries and packages import keras from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense
步驟9
我們將模型命名為Classifier,因為我們的目標是分類客戶流失。然後我們使用Sequential模組進行初始化。
#Initializing Neural Network classifier = Sequential()
步驟10
我們使用dense函式逐一新增隱藏層。在下面的程式碼中,我們將看到許多引數。
我們的第一個引數是output_dim。這是我們新增到此層中的節點數。init是隨機梯度下降的初始化。在神經網路中,我們為每個節點分配權重。在初始化時,權重應該接近於零,我們使用uniform函式隨機初始化權重。input_dim引數僅在第一層需要,因為模型不知道我們的輸入變數的數量。這裡輸入變數的總數是11。在第二層中,模型會自動從第一隱藏層知道輸入變數的數量。
執行以下程式碼行以新增輸入層和第一隱藏層:
classifier.add(Dense(units = 6, kernel_initializer = 'uniform', activation = 'relu', input_dim = 11))
執行以下程式碼行以新增第二隱藏層:
classifier.add(Dense(units = 6, kernel_initializer = 'uniform', activation = 'relu'))
執行以下程式碼行以新增輸出層:
classifier.add(Dense(units = 1, kernel_initializer = 'uniform', activation = 'sigmoid'))
步驟11
編譯ANN
到目前為止,我們已經向分類器添加了多層。我們現在將使用compile方法編譯它們。在最終編譯中新增的引數控制著整個神經網路,因此我們必須小心這一步。
以下是引數的簡要說明。
第一個引數是Optimizer。這是一種用於尋找最優權重集的演算法。這種演算法稱為隨機梯度下降 (SGD)。在這裡,我們使用幾種型別中的一種,稱為“Adam最佳化器”。SGD取決於損失,因此我們的第二個引數是損失。如果我們的因變數是二元的,我們使用稱為‘binary_crossentropy’的對數損失函式;如果我們的因變數在輸出中有多於兩個類別,則我們使用‘categorical_crossentropy’。我們希望根據accuracy來提高神經網路的效能,因此我們新增metrics作為準確性。
# Compiling Neural Network classifier.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'binary_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy'])
步驟12
此步驟需要執行多行程式碼。
將ANN擬合到訓練集
我們現在在訓練資料上訓練我們的模型。我們使用fit方法來擬合我們的模型。我們還最佳化權重以提高模型效率。為此,我們必須更新權重。Batch size是在更新權重之後觀測值的數量。Epoch是迭代的總數。批次大小和時期值是透過反覆試驗的方法選擇的。
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train, batch_size = 10, epochs = 50)
進行預測和評估模型
# Predicting the Test set results y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test) y_pred = (y_pred > 0.5)
預測單個新的觀測值
# Predicting a single new observation """Our goal is to predict if the customer with the following data will leave the bank: Geography: Spain Credit Score: 500 Gender: Female Age: 40 Tenure: 3 Balance: 50000 Number of Products: 2 Has Credit Card: Yes Is Active Member: Yes
步驟13
預測測試集結果
預測結果將給出客戶離開公司的機率。我們將把該機率轉換為二進位制0和1。
# Predicting the Test set results y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test) y_pred = (y_pred > 0.5)
new_prediction = classifier.predict(sc.transform (np.array([[0.0, 0, 500, 1, 40, 3, 50000, 2, 1, 1, 40000]]))) new_prediction = (new_prediction > 0.5)
步驟14
這是我們評估模型效能的最後一步。我們已經有了原始結果,因此我們可以構建混淆矩陣來檢查模型的準確性。
製作混淆矩陣
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred) print (cm)
輸出
loss: 0.3384 acc: 0.8605 [ [1541 54] [230 175] ]
根據混淆矩陣,我們可以計算模型的準確率為:
Accuracy = 1541+175/2000=0.858
我們達到了85.8%的準確率,這很好。
前向傳播演算法
在本節中,我們將學習如何編寫程式碼來對簡單的神經網路進行前向傳播(預測):
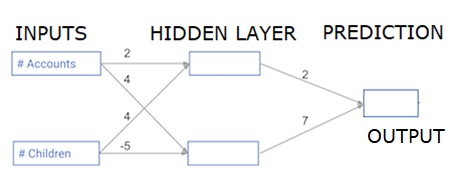
每個資料點都是一個客戶。第一個輸入是他們有多少個賬戶,第二個輸入是他們有多少個孩子。該模型將預測使用者明年將進行多少筆交易。
輸入資料預載入為input_data,權重在一個名為weights的字典中。隱藏層中第一個節點的權重陣列位於weights['node_0']中,隱藏層中第二個節點的權重陣列位於weights['node_1']中。
饋送到輸出節點的權重在weights中可用。
修正線性啟用函式
“啟用函式”是在每個節點工作的函式。它將節點的輸入轉換為某種輸出。
修正線性啟用函式(稱為ReLU)廣泛用於非常高效能的網路。此函式以單個數字作為輸入,如果輸入為負,則返回0;如果輸入為正,則返回輸入作為輸出。
以下是一些示例:
- relu(4) = 4
- relu(-2) = 0
我們填寫relu()函式的定義:
- 我們使用max()函式來計算relu()的輸出值。
- 我們應用relu()函式到node_0_input來計算node_0_output。
- 我們應用relu()函式到node_1_input來計算node_1_output。
import numpy as np
input_data = np.array([-1, 2])
weights = {
'node_0': np.array([3, 3]),
'node_1': np.array([1, 5]),
'output': np.array([2, -1])
}
node_0_input = (input_data * weights['node_0']).sum()
node_0_output = np.tanh(node_0_input)
node_1_input = (input_data * weights['node_1']).sum()
node_1_output = np.tanh(node_1_input)
hidden_layer_output = np.array(node_0_output, node_1_output)
output =(hidden_layer_output * weights['output']).sum()
print(output)
def relu(input):
'''Define your relu activation function here'''
# Calculate the value for the output of the relu function: output
output = max(input,0)
# Return the value just calculated
return(output)
# Calculate node 0 value: node_0_output
node_0_input = (input_data * weights['node_0']).sum()
node_0_output = relu(node_0_input)
# Calculate node 1 value: node_1_output
node_1_input = (input_data * weights['node_1']).sum()
node_1_output = relu(node_1_input)
# Put node values into array: hidden_layer_outputs
hidden_layer_outputs = np.array([node_0_output, node_1_output])
# Calculate model output (do not apply relu)
odel_output = (hidden_layer_outputs * weights['output']).sum()
print(model_output)# Print model output
輸出
0.9950547536867305 -3
將網路應用於許多觀測值/資料行
在本節中,我們將學習如何定義一個名為predict_with_network()的函式。此函式將為從上面網路中獲取的多個數據觀測值(作為input_data)生成預測。使用上面網路中給出的權重。relu()函式定義也正在使用。
讓我們定義一個名為predict_with_network()的函式,它接受兩個引數 - input_data_row和weights - 並返回網路的預測作為輸出。
我們計算每個節點的輸入值和輸出值,並將它們儲存為:node_0_input、node_0_output、node_1_input和node_1_output。
為了計算節點的輸入值,我們將相關的陣列相乘並計算它們的總和。
為了計算節點的輸出值,我們將relu()函式應用於節點的輸入值。我們使用“for迴圈”來迭代input_data:
我們還使用我們的predict_with_network()為input_data的每一行 - input_data_row生成預測。我們還將每個預測新增到results中。
# Define predict_with_network() def predict_with_network(input_data_row, weights): # Calculate node 0 value node_0_input = (input_data_row * weights['node_0']).sum() node_0_output = relu(node_0_input) # Calculate node 1 value node_1_input = (input_data_row * weights['node_1']).sum() node_1_output = relu(node_1_input) # Put node values into array: hidden_layer_outputs hidden_layer_outputs = np.array([node_0_output, node_1_output]) # Calculate model output input_to_final_layer = (hidden_layer_outputs*weights['output']).sum() model_output = relu(input_to_final_layer) # Return model output return(model_output) # Create empty list to store prediction results results = [] for input_data_row in input_data: # Append prediction to results results.append(predict_with_network(input_data_row, weights)) print(results)# Print results
輸出
[0, 12]
在這裡,我們使用了relu函式,其中relu(26) = 26,relu(-13)=0,依此類推。
深度多層神經網路
在這裡,我們編寫程式碼來對具有兩個隱藏層的神經網路進行前向傳播。每個隱藏層都有兩個節點。輸入資料已預載入為input_data。第一個隱藏層中的節點稱為node_0_0和node_0_1。
它們的權重分別預載入為weights['node_0_0']和weights['node_0_1']。
第二個隱藏層中的節點稱為node_1_0和node_1_1。它們的權重分別預載入為weights['node_1_0']和weights['node_1_1']。
然後,我們使用預載入為weights['output']的權重建立來自隱藏節點的模型輸出。
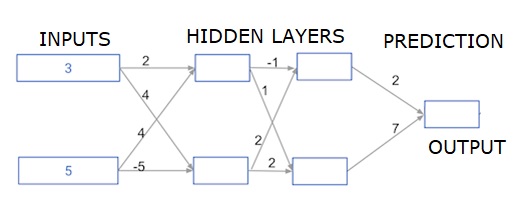
我們使用其權重weights['node_0_0']和給定的input_data計算node_0_0_input。然後應用relu()函式以獲得node_0_0_output。
我們對node_0_1_input執行與上述相同的操作以獲得node_0_1_output。
我們使用其權重weights['node_1_0']和第一隱藏層的輸出 - hidden_0_outputs計算node_1_0_input。然後應用relu()函式以獲得node_1_0_output。
我們對node_1_1_input執行與上述相同的操作以獲得node_1_1_output。
我們使用weights['output']和第二隱藏層的輸出hidden_1_outputs陣列計算model_output。我們不將relu()函式應用於此輸出。
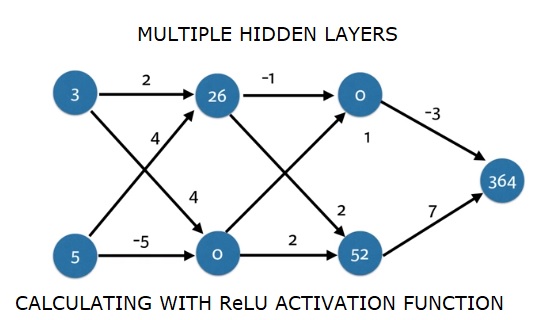
import numpy as np
input_data = np.array([3, 5])
weights = {
'node_0_0': np.array([2, 4]),
'node_0_1': np.array([4, -5]),
'node_1_0': np.array([-1, 1]),
'node_1_1': np.array([2, 2]),
'output': np.array([2, 7])
}
def predict_with_network(input_data):
# Calculate node 0 in the first hidden layer
node_0_0_input = (input_data * weights['node_0_0']).sum()
node_0_0_output = relu(node_0_0_input)
# Calculate node 1 in the first hidden layer
node_0_1_input = (input_data*weights['node_0_1']).sum()
node_0_1_output = relu(node_0_1_input)
# Put node values into array: hidden_0_outputs
hidden_0_outputs = np.array([node_0_0_output, node_0_1_output])
# Calculate node 0 in the second hidden layer
node_1_0_input = (hidden_0_outputs*weights['node_1_0']).sum()
node_1_0_output = relu(node_1_0_input)
# Calculate node 1 in the second hidden layer
node_1_1_input = (hidden_0_outputs*weights['node_1_1']).sum()
node_1_1_output = relu(node_1_1_input)
# Put node values into array: hidden_1_outputs
hidden_1_outputs = np.array([node_1_0_output, node_1_1_output])
# Calculate model output: model_output
model_output = (hidden_1_outputs*weights['output']).sum()
# Return model_output
return(model_output)
output = predict_with_network(input_data)
print(output)
輸出
364