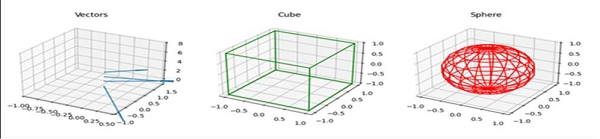
在 Matplotlib 中繪製 3D 立方體、球體和向量
從 plt.figure() 獲取 fig,並使用 add_subplot 建立三個不同的軸,其中 projection=3d。
使用 ax.set_title("圖形名稱") 設定圖形標題。使用 ax.quiver 方法繪製向量投影,使用 plot3D 繪製立方體,並在使用正弦和餘弦後使用 plot_wireframe 繪製球體。
步驟
建立一個新圖形,或啟用一個現有圖形。
要繪製向量,獲取一個二維陣列。
獲取一個壓縮物件。
將一個 ~.axes.Axes 新增到圖形中作為子圖排列的一部分,具有 3d 投影,其中 nrows = 1,ncols = 3 且索引 = 1。
繪製一個 3D 箭頭場。
設定 xlim、ylim 和 zlim。
設定軸的標題(索引為 1)。
將一個 ~.axes.Axes 新增到圖形中作為子圖排列的一部分,具有 3d 投影,其中 nrows = 1,ncols = 3 且索引 = 2。
使用 plot3D() 建立一個表面圖,其中表面和邊緣使用綠色傳遞。
設定軸的標題(索引為 2)。即“立方體”。
將一個 ~.axes.Axes 新增到圖形中作為子圖排列的一部分,具有 3d 投影,其中 nrows = 1,ncols = 3 且索引 = 3。
要製作球體,將正弦和餘弦曲線組合在同一位置。
設定軸的標題(索引為 3),即“球體”。
要顯示繪圖,請使用 plt.show() 方法。
示例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from itertools import product, combinations
fig = plt.figure()
# draw vector
soa = np.array([[0, 0, 1, 1, -2, 0], [0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 3, 2, 1, 0], [0, 0, 4, 0.5, 0.7, 0]])
X, Y, Z, U, V, W = zip(*soa)
ax = fig.add_subplot(131, projection='3d')
ax.quiver(X, Y, Z, U, V, W)
ax.set_xlim([-1, 0.5])
ax.set_ylim([-1, 1.5])
ax.set_zlim([-1, 8])
ax.set_title("Vectors")
# draw cube
ax = fig.add_subplot(132, projection='3d')
r = [-1, 1]
for s, e in combinations(np.array(list(product(r, r, r))), 2):
if np.sum(np.abs(s-e)) == r[1]-r[0]:
ax.plot3D(*zip(s, e), color="green")
ax.set_title("Cube")
# draw sphere
ax = fig.add_subplot(133, projection='3d')
u, v = np.mgrid[0:2*np.pi:20j, 0:np.pi:10j]
x = np.cos(u)*np.sin(v)
y = np.sin(u)*np.sin(v)
z = np.cos(v)
ax.plot_wireframe(x, y, z, color="red")
ax.set_title("Sphere")
plt.show()輸出

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP