如何在 Material UI 中建立增強型傳輸列表?
在這篇文章中,我們將看到一個逐步指南,用於在 React MUI 中建立增強型傳輸列表。
傳輸列表是一種列表型別,允許使用者將一個或多個列表項移動到另一個列表。在這裡,如果第一個列表中有多個專案,並且使用者希望將某些專案傳輸到第二個列表,那麼我們使用傳輸列表元件。在 React MUI 中,沒有專門用於傳輸列表的元件;而是,我們自己建立它。
Material UI 中還有一個增強列表的概念,它只是基本傳輸列表的更高階或增強版本。我們可以在增強列表中包含各種內容,例如複選框、應用自定義顏色等。
建立增強型傳輸列表的步驟
以下是建立 Material UI 中增強型傳輸列表的步驟:
步驟 1:建立 React 應用程式
在 MUI 中建立傳輸列表的第一步是建立一個 React 應用程式。要建立一個新的 React 應用程式,請在您的終端中執行以下命令:
npx create react app formcontrolproject
專案建立完成後,透過執行以下命令導航到其目錄:
cd formcontrolproject
步驟 2:將 MUI 新增到 React
建立 React 應用程式後,是時候將 Material UI 安裝到 React 應用程式中了。要安裝 MUI,請執行以下命令:
npm install @mui/material @emotion/react @emotion/styled
步驟 3:定義專案
在建立傳輸列表之前,我們必須定義列表項,並在左右兩側設定一些值。以下是定義專案項的語法:
const [lftItems, setLftItems] = useState([1, 2, 3 ]); const [rytItems, setRytItems] = useState([4, 5, 6]); const [chosenLftItems, setChosenLftItems] = useState([]); const [chosenRytItems, setChosenRytItems] = useState([]);
步驟 4:建立傳輸按鈕
要傳輸列表項,我們必須定義具有處理函式的傳輸按鈕。以下是如何在 React 中建立四個不同的按鈕:
const handlePush = () => {
…
};
const handlePull = () => {
…
};
const selectLftItem = (i) => {
…
};
const selectRightItem = (i) => {
…
};
步驟 5:在 Main 中呈現列表項
最後,一旦我們定義了所有處理列表傳輸的函式,我們現在必須使用 Stack 在 App.js 元件中呈現列表項。以下是呈現列表項的語法:
function App() {
return (
<Stack>
<Stack item sx={{ gap: 2 }}>
{lftItems.map((item, index) => (
<ListItem key={index}>
…
</ListItem>
))}
</Stack>
<Stack item>
<Stack>
<Button>
>
</Button>
<Button>
<
</Button>
</Stack>
</Stack>
<Stack sx={{ gap: 2 }}>
{rytItems.map((item, index) => (
<ListItem key={index}>
…
</ListItem>
))}
</Stack>
</Stack>
)
}
export default App;
就是這樣!現在我們已經成功地學習了在 MUI 中建立增強型傳輸列表的步驟。所以,讓我們看看一些不同方法的示例。
示例
在此示例中,我們建立了一個自定義的增強型傳輸列表,當用戶選擇任何要傳輸的專案時,複選框將被啟用。在這裡,使用者還可以一次選擇所有列表項以傳輸到其他列表。
import React from "react";
import { useState } from "react";
import { Stack } from "@mui/material";
import {List, ListItem, ListItemText, ListItemIcon} from '@mui/material';
import Checkbox from '@mui/material/Checkbox';
import Button from '@mui/material/Button';
import {Card, CardHeader} from '@mui/material/';
function not(a, b) {
return a.filter((value) => b.indexOf(value) === -1);
}
function intersection(a, b) {
return a.filter((value) => b.indexOf(value) !== -1);
}
function union(a, b) {
return [...a, ...not(b, a)];
}
const App = () => {
const [chk, setChk] = useState([]);
const [lftItems, setLftItems] = useState(["Item 11",
"Item 12",
"Item 13",
"Item 14",
"Item 15"]);
const [rightItems, setRightItems] = useState(["Item 21",
"Item 22",
"Item 23",
"Item 24",
"Item 25"]);
const chkLeftChecked = intersection(chk, lftItems);
const chkRightChecked = intersection(chk, rightItems);
const handleSingleToggle = (val) => () => {
const currentIdx = chk.indexOf(val);
const latestChecked = [...chk];
if (currentIdx === -1) {
latestChecked.push(val);
} else {
latestChecked.splice(currentIdx, 1);
}
setChk(latestChecked);
};
const chkNo = (items) => intersection(chk, items).length;
const handleMultipleToggle = (i) => () => {
if (chkNo(i) === i.length) {
setChk(not(chk, i));
} else {
setChk(union(chk, i));
}
};
const pushRight = () => {
setRightItems(rightItems.concat(chkLeftChecked));
setLftItems(not(lftItems, chkLeftChecked));
setChk(not(chk, chkLeftChecked));
};
const pushLeft = () => {
setLftItems(lftItems.concat(chkRightChecked));
setRightItems(not(rightItems, chkRightChecked));
setChk(not(chk, chkRightChecked));
};
const ListComponent = (listItemName, ListItems) => (
<Card sx={{ p: 3 }}>
<CardHeader
sx={{ p: 2 }}
avatar={
<Checkbox
onClick={handleMultipleToggle(ListItems)}
checked={chkNo(ListItems) === ListItems.length && ListItems.length !== 0}
indeterminate={
chkNo(ListItems) !== ListItems.length && chkNo(ListItems) !== 0
}
disabled={ListItems.length === 0}
/>
}
title={listItemName}
subheader={`${chkNo(ListItems)}/${ListItems.length} selected`}
/>
<hr />
<List sx={{overflow: 'auto',}}>
{ListItems.map((value) => {
const labelId = `transfer-list-all-item-${value}-label`;
return (
<ListItem
key={value}
onClick={handleSingleToggle(value)}
>
<ListItemIcon>
<Checkbox
checked={chk.indexOf(value) !== -1}
tabIndex={-1}
disableRipple
/>
</ListItemIcon>
<ListItemText id={labelId} primary={value} />
</ListItem>
);
})}
</List>
</Card>
);
return (
<div style={{
padding: 40,
display: 'flex',
flexDirection: 'column',
gap: 20,
backgroundColor: 'lightcyan'
}}>
<Stack direction="row" container spacing={5}>
<Stack item>{ListComponent('Select from below', lftItems)}</Stack>
<Stack item>
<Stack container direction="column" sx={{ gap: 5 }} alignItems="center">
<Button
variant="contained"
color="info"
onClick={pushRight}
disabled={chkLeftChecked.length === 0}
>
>
</Button>
<Button
variant="contained"
color="info"
onClick={pushLeft}
disabled={chkRightChecked.length === 0}
>
<
</Button>
</Stack>
</Stack>
<Stack item>{ListComponent('Selected', rightItems)}</Stack>
</Stack>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
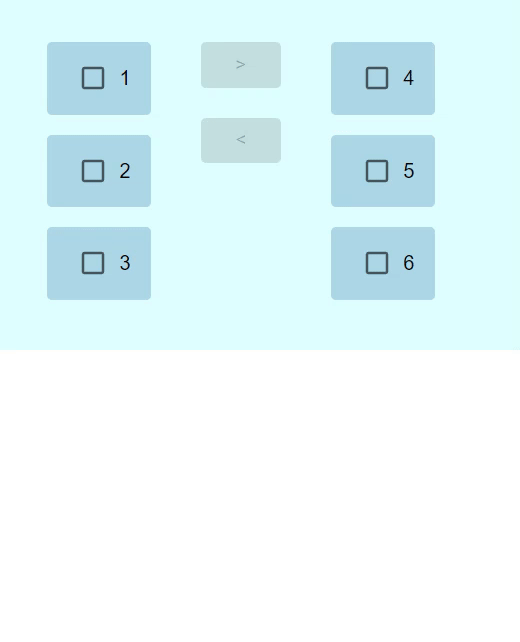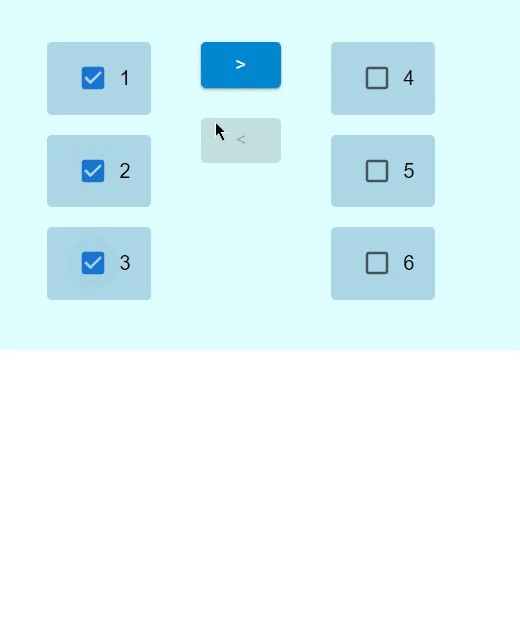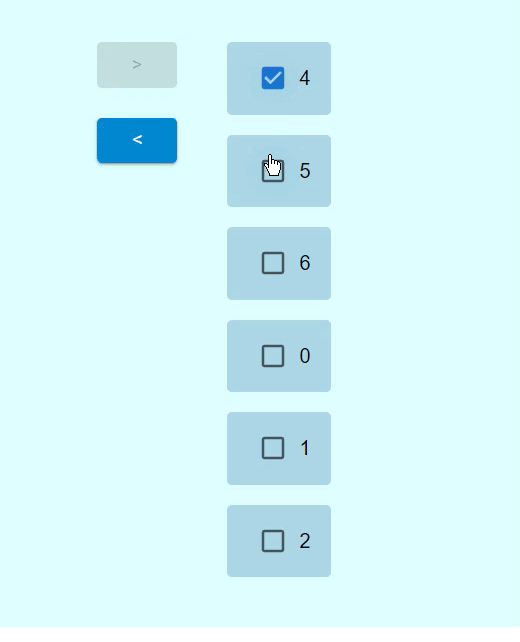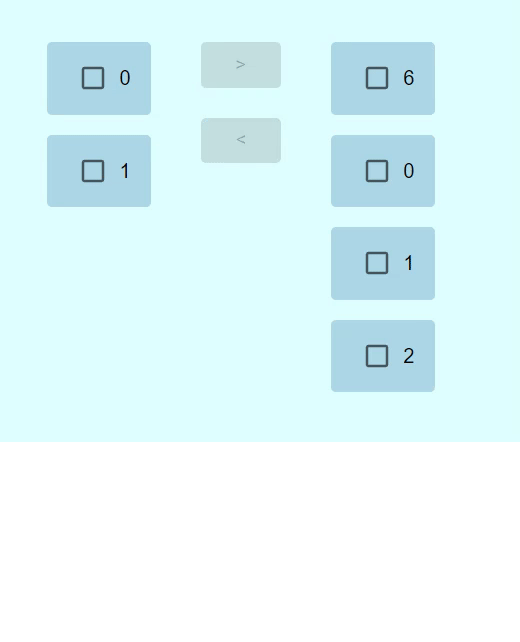
輸出
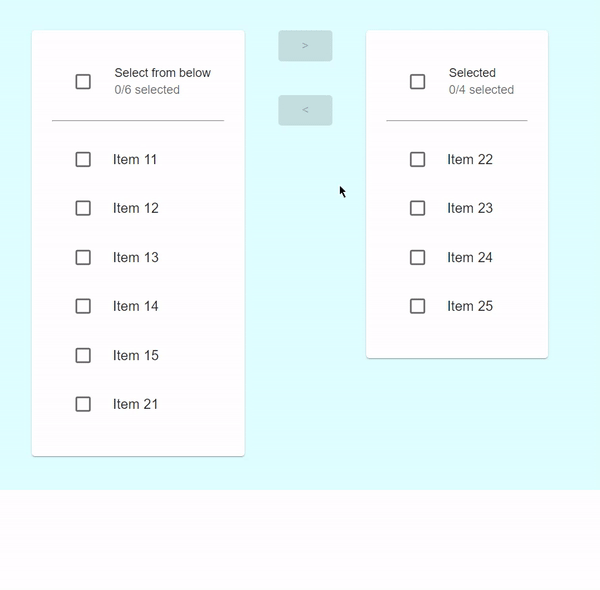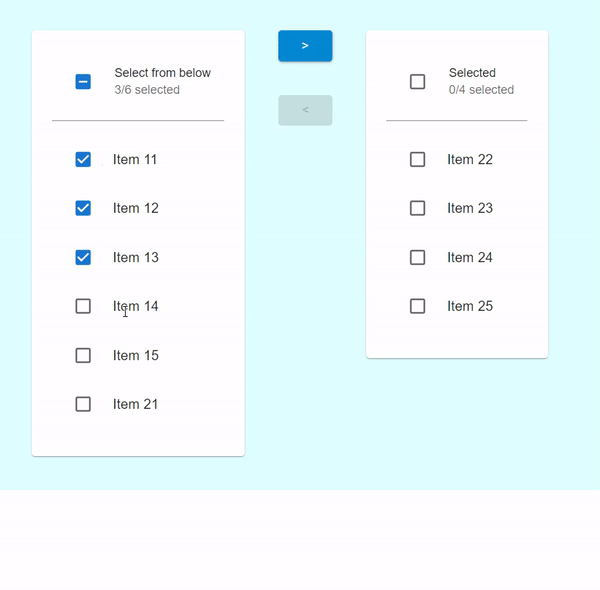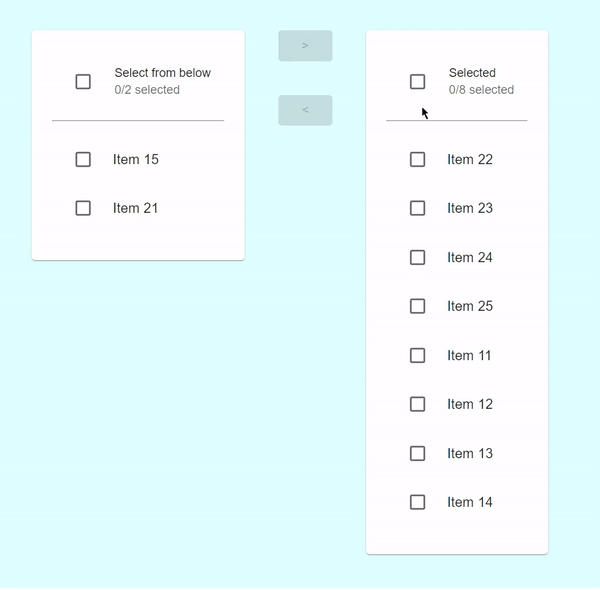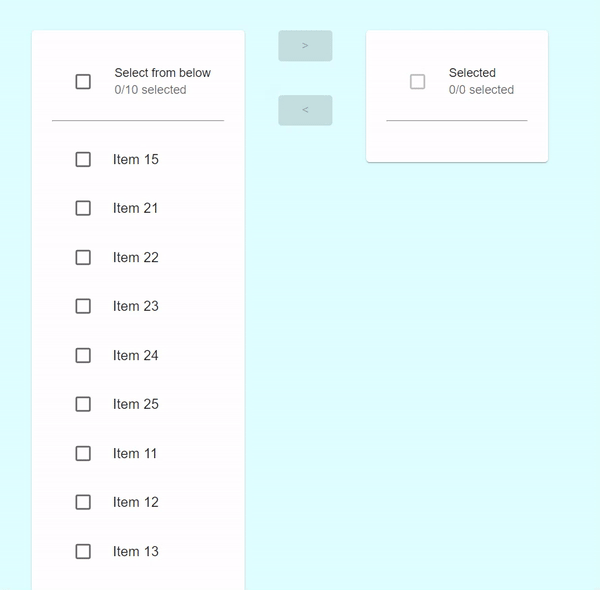
示例
在此示例中,我們建立了一個自定義的增強型傳輸列表,當用戶選擇任何要傳輸的專案時,複選框將被啟用。在這裡,列表項使用不同的顏色進行自定義。
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { Stack, Checkbox, ListItem, ListItemText, Button } from "@mui/material";
const App = () => {
const [lftItems, setLftItems] = useState([1, 2, 3]);
const [rytItems, setRytItems] = useState([4, 5, 6]);
const [chosenLftItems, setChosenLftItems] = useState([]);
const [chosenRytItems, setChosenRytItems] = useState([]);
const handlePush = () => {
setRytItems((before) => [...before, ...chosenLftItems]);
setLftItems((prevItems) =>
prevItems.filter((_, index) => !chosenLftItems.includes(index))
);
setChosenLftItems([]);
};
const handlePull = () => {
setLftItems((before) => [...before, ...chosenRytItems]);
setRytItems((prevItems) =>
prevItems.filter((_, index) => !chosenRytItems.includes(index))
);
setChosenRytItems([]);
};
const selectLftItem = (i) => {
if (chosenLftItems.includes(i)) {
setChosenLftItems((beforeSelected) =>
beforeSelected.filter((item) => item !== i)
);
} else {
setChosenLftItems((beforeSelected) => [...beforeSelected, i]);
}
};
const selectRightItem = (i) => {
if (chosenRytItems.includes(i)) {
setChosenRytItems((beforeSelected) =>
beforeSelected.filter((item) => item !== i)
);
} else {
setChosenRytItems((beforeSelected) => [...beforeSelected, i]);
}
};
return (
<div
style={{
padding: 40,
display: "flex",
flexDirection: "column",
gap: 20,
backgroundColor: "lightcyan"
}}>
<Stack direction="row" container spacing={5}>
<Stack sx={{ gap: 2 }}>
{lftItems.map((item, index) => (
<ListItem
key={index}
onClick={() => selectLftItem(index)}
sx={{
backgroundColor: "lightblue",
borderRadius: 1,
cursor: "pointer"
}}>
<Checkbox
checked={chosenLftItems.includes(index)}
color="primary"
/>
<ListItemText primary={item} />
</ListItem>
))}
</Stack>
<Stack item>
<Stack
container
justifyContent="center"
direction="column"
sx={{ gap: 3 }}
alignItems="center"
>
<Button
variant="contained"
color="info"
onClick={handlePush}
disabled={chosenLftItems.length === 0}
>
>
</Button>
<Button
variant="contained"
color="info"
onClick={handlePull}
disabled={chosenRytItems.length === 0}
>
<
</Button>
</Stack>
</Stack>
<Stack sx={{ gap: 2 }}>
{rytItems.map((item, index) => (
<ListItem
key={index}
onClick={() => selectRightItem(index)}
sx={{
backgroundColor: "lightblue",
borderRadius: 1,
cursor: "pointer"
}}
>
<Checkbox
checked={chosenRytItems.includes(index)}
color="primary"
/>
<ListItemText primary={item} />
</ListItem>
))}
</Stack>
</Stack>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
輸出
結論
本文討論了在 React MUI 中建立增強型傳輸列表的完整細節。在本文中,我們學習了建立增強型傳輸列表的完整步驟,以及使用不同方法的不同示例。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP