
- C語言資料結構教程
- C語言資料結構 - 首頁
- C語言資料結構 - 概述
- C語言資料結構 - 環境搭建
- C語言資料結構 - 演算法
- C語言資料結構 - 概念
- C語言資料結構 - 陣列
- C語言資料結構 - 連結串列
- C語言資料結構 - 雙向連結串列
- C語言資料結構 - 迴圈連結串列
- C語言資料結構 - 棧
- C語言資料結構 - 表示式解析
- C語言資料結構 - 佇列
- C語言資料結構 - 優先佇列
- C語言資料結構 - 樹
- C語言資料結構 - 雜湊表
- C語言資料結構 - 堆
- C語言資料結構 - 圖
- C語言資料結構 - 搜尋技術
- C語言資料結構 - 排序技術
- C語言資料結構 - 遞迴
- C語言資料結構 - 有用資源
- C語言資料結構 - 快速指南
- C語言資料結構 - 有用資源
- C語言資料結構 - 討論
C語言資料結構 - 樹
概述
樹由節點和邊連線而成。我們將專門討論二叉樹或二叉搜尋樹。
二叉樹是一種特殊的資料結構,用於資料儲存目的。二叉樹有一個特殊的條件,即每個節點最多可以有兩個子節點。二叉樹結合了有序陣列和連結串列的優點,搜尋速度像有序陣列一樣快,插入或刪除操作像連結串列一樣快。
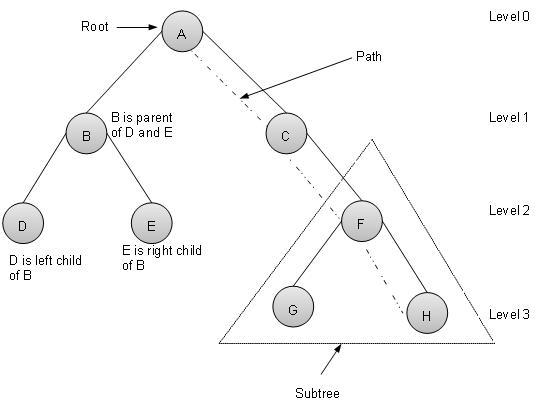
術語
以下是關於樹的一些重要術語。
路徑 - 路徑指的是沿著樹的邊的一系列節點。
根節點 - 樹頂部的節點稱為根節點。每棵樹只有一個根節點,並且從根節點到任何節點都只有一條路徑。
父節點 - 除根節點之外的任何節點都有一條向上連線到稱為父節點的節點的邊。
子節點 - 下方透過邊向下連線到給定節點的節點稱為其子節點。
葉子節點 - 沒有子節點的節點稱為葉子節點。
子樹 - 子樹表示節點的後代。
訪問 - 訪問指的是當控制權在節點上時檢查節點的值。
遍歷 - 遍歷意味著以特定順序依次經過節點。
層級 - 節點的層級表示節點的代數。如果根節點在第 0 層,則其子節點在第 1 層,其孫子節點在第 2 層,依此類推。
鍵 - 鍵表示節點的值,根據該值執行節點的搜尋操作。
二叉搜尋樹表現出特殊的行為。節點的左子節點的值必須小於其父節點的值,節點的右子節點的值必須大於其父節點的值。
二叉搜尋樹表示
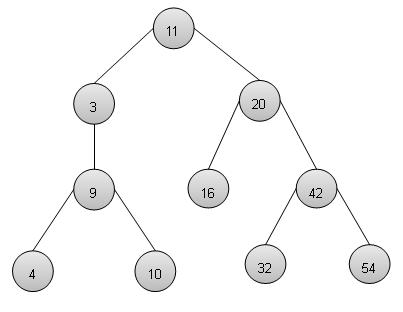
我們將使用節點物件來實現樹,並透過引用將它們連線起來。
基本操作
以下是樹的基本主要操作。
搜尋 - 在樹中搜索一個元素。
插入 - 在樹中插入一個元素。
先序遍歷 - 以先序方式遍歷樹。
中序遍歷 - 以中序方式遍歷樹。
後序遍歷 - 以後序方式遍歷樹。
節點
定義一個節點,它包含一些資料,以及指向其左右子節點的引用。
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
搜尋操作
當要搜尋一個元素時。從根節點開始搜尋,如果資料小於鍵值,則在左子樹中搜索元素,否則在右子樹中搜索元素。對每個節點遵循相同的演算法。
struct node* search(int data){
struct node *current = root;
printf("Visiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data){
if(current != NULL)
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data){
current = current->leftChild;
}//else go to right tree
else{
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL){
return NULL;
}
}
return current;
}
插入操作
當要插入一個元素時。首先找到其合適的位置。從根節點開始搜尋,如果資料小於鍵值,則在左子樹中搜索空位置並插入資料。否則,在右子樹中搜索空位置並插入資料。
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL){
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1){
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data){
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL){
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else{
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL){
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
先序遍歷
這是一個簡單的三步過程。
訪問根節點
遍歷左子樹
遍歷右子樹
void preOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
printf("%d ",root->data);
preOrder(root->leftChild);
preOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
中序遍歷
這是一個簡單的三步過程。
遍歷左子樹
訪問根節點
遍歷右子樹
void inOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
inOrder(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
後序遍歷
這是一個簡單的三步過程。
遍歷左子樹
遍歷右子樹
訪問根節點
void postOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
postOrder(root->leftChild);
postOrder(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
}
}
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL){
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1){
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data){
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL){
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else{
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL){
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
struct node* search(int data){
struct node *current = root;
printf("Visiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data){
if(current != NULL)
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data){
current = current->leftChild;
}//else go to right tree
else{
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL){
return NULL;
}
}
return current;
}
void preOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
printf("%d ",root->data);
preOrder(root->leftChild);
preOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
void inOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
inOrder(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
void postOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
postOrder(root->leftChild);
postOrder(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
}
}
void traverse(int traversalType){
switch(traversalType){
case 1:
printf("\nPreorder traversal: ");
preOrder(root);
break;
case 2:
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inOrder(root);
break;
case 3:
printf("\nPostorder traversal: ");
postOrder(root);
break;
}
}
int main()
{
/* 11 //Level 0
*/
insert(11);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* |---20 //Level 1
*/
insert(20);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
*/
insert(3);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* |
* |--42 //Level 2
*/
insert(42);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* |
* |--42 //Level 2
* |
* |--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(54);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* |
* 16--|--42 //Level 2
* |
* |--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(16);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* |
* 16--|--42 //Level 2
* |
* 32--|--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(32);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* | |
* |--9 16--|--42 //Level 2
* |
* 32--|--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(9);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* | |
* |--9 16--|--42 //Level 2
* | |
* 4--| 32--|--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(4);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* | |
* |--9 16--|--42 //Level 2
* | |
* 4--|--10 32--|--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(10);
struct node * temp = search(32);
if(temp!=NULL){
printf("Element found.\n");
printf("( %d )",temp->data);
printf("\n");
} else {
printf("Element not found.\n");
}
struct node *node1 = search(2);
if(node1!=NULL){
printf("Element found.\n");
printf("( %d )",node1->data);
printf("\n");
} else {
printf("Element not found.\n");
}
//pre-order traversal
//root, left ,right
traverse(1);
//in-order traversal
//left, root ,right
traverse(2);
//post order traversal
//left, right, root
traverse(3);
}
輸出
如果我們編譯並執行以上程式,它將產生以下輸出:
Visiting elements: 11 20 42 Element found.(32) Visiting elements: 11 3 Element not found. Preorder traversal: 11 3 9 4 10 20 16 42 32 54 Inorder traversal: 3 4 9 10 11 16 20 32 42 54 Postorder traversal: 4 10 9 3 16 32 54 42 20 11