
- C語言資料結構與演算法教程
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 首頁
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 概述
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 環境配置
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 演算法
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 概念
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 陣列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 連結串列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 雙向連結串列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 迴圈連結串列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 棧
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 表示式解析
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 佇列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 優先佇列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 樹
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 雜湊表
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 堆
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 圖
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 搜尋技術
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 排序技術
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 遞迴
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 有用資源
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 快速指南
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 有用資源
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 討論
C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 連結串列
概述
連結串列是由一系列連結組成的序列,每個連結都包含一個指向另一個連結的指標。連結串列是僅次於陣列的第二常用資料結構。以下是一些理解連結串列概念的重要術語。
連結 (Link) − 連結串列的每個連結都可以儲存稱為元素的資料。
下一個 (Next) − 連結串列的每個連結都包含一個指向下一個連結的指標,稱為 Next。
連結串列 (LinkedList) − 連結串列包含一個指向第一個連結的指標,稱為 First。
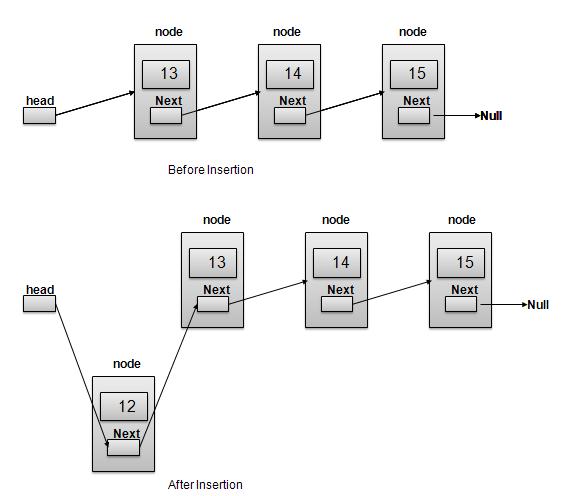
連結串列表示

根據上圖所示,以下是要考慮的重要事項。
連結串列包含一個稱為 first 的連結元素。
每個連結都包含一個或多個數據欄位和一個稱為 next 的連結欄位。
每個連結都使用其 next 連結與其下一個連結連結。
最後一個連結的連結為 null,用於標記列表的結尾。
連結串列的型別
以下是連結串列的各種型別。
單向連結串列 (Simple Linked List) − 只能向前導航專案。
雙向連結串列 (Doubly Linked List) − 可以向前和向後導航專案。
迴圈連結串列 (Circular Linked List) − 最後一個專案包含指向第一個元素的 next 指標,而第一個元素包含指向最後一個元素的 prev 指標。
基本操作
以下是連結串列支援的基本操作。
插入 (Insertion) − 在列表開頭新增一個元素。
刪除 (Deletion) − 刪除列表開頭的元素。
顯示 (Display) − 顯示整個列表。
搜尋 (Search) − 使用給定的鍵搜尋元素。
刪除 (Delete) − 使用給定的鍵刪除元素。
插入操作
插入是一個三步過程:
建立一個包含提供的資料的新連結。
將新連結指向舊的第一個連結。
將第一個連結指向這個新連結。
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
刪除操作
刪除是一個兩步過程:
獲取第一個連結指向的連結作為臨時連結。
將第一個連結指向臨時連結的下一個連結。

//delete first item
struct node* deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
導航操作
導航是一個遞迴步驟過程,是許多操作(如搜尋、刪除等)的基礎:
獲取第一個連結指向的連結作為當前連結。
檢查當前連結是否不為空,並顯示它。
將當前連結指向當前連結的下一個連結,並轉到上述步驟。

注意:
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
while(ptr != NULL){
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf(" ]");
}
高階操作
以下是為列表指定的高階操作。
排序 (Sort) − 基於特定順序對列表進行排序。
反轉 (Reverse) − 反轉連結串列。
排序操作
我們使用氣泡排序來排序列表。
void sort(){
int i, j, k, tempKey, tempData ;
struct node *current;
struct node *next;
int size = length();
k = size ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < size - 1 ; i++, k-- ) {
current = head ;
next = head->next ;
for ( j = 1 ; j < k ; j++ ) {
if ( current->data > next->data ) {
tempData = current->data ;
current->data = next->data;
next->data = tempData ;
tempKey = current->key;
current->key = next->key;
next->key = tempKey;
}
current = current->next;
next = next->next;
}
}
}
反轉操作
以下程式碼演示瞭如何反轉單鏈表。
void reverse(struct node** head_ref) {
struct node* prev = NULL;
struct node* current = *head_ref;
struct node* next;
while (current != NULL) {
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
*head_ref = prev;
}
示例
LinkedListDemo.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
while(ptr != NULL){
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf(" ]");
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
//delete first item
struct node* deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
int length(){
int length = 0;
struct node *current;
for(current = head; current!=NULL;
current = current->next){
length++;
}
return length;
}
//find a link with given key
struct node* find(int key){
//start from the first link
struct node* current = head;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL){
return NULL;
}
//navigate through list
while(current->key != key){
//if it is last node
if(current->next == NULL){
return NULL;
} else {
//go to next link
current = current->next;
}
}
//if data found, return the current Link
return current;
}
//delete a link with given key
struct node* delete(int key){
//start from the first link
struct node* current = head;
struct node* previous = NULL;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL){
return NULL;
}
//navigate through list
while(current->key != key){
//if it is last node
if(current->next == NULL){
return NULL;
} else {
//store reference to current link
previous = current;
//move to next link
current = current->next;
}
}
//found a match, update the link
if(current == head) {
//change first to point to next link
head = head->next;
} else {
//bypass the current link
previous->next = current->next;
}
return current;
}
void sort(){
int i, j, k, tempKey, tempData ;
struct node *current;
struct node *next;
int size = length();
k = size ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < size - 1 ; i++, k-- ) {
current = head ;
next = head->next ;
for ( j = 1 ; j < k ; j++ ) {
if ( current->data > next->data ) {
tempData = current->data ;
current->data = next->data;
next->data = tempData ;
tempKey = current->key;
current->key = next->key;
next->key = tempKey;
}
current = current->next;
next = next->next;
}
}
}
void reverse(struct node** head_ref) {
struct node* prev = NULL;
struct node* current = *head_ref;
struct node* next;
while (current != NULL) {
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
*head_ref = prev;
}
main() {
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Original List: ");
//print list
printList();
while(!isEmpty()){
struct node *temp = deleteFirst();
printf("\nDeleted value:");
printf("(%d,%d) ",temp->key,temp->data);
}
printf("\nList after deleting all items: ");
printList();
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("\nRestored List: ");
printList();
printf("\n");
struct node *foundLink = find(4);
if(foundLink != NULL){
printf("Element found: ");
printf("(%d,%d) ",foundLink->key,foundLink->data);
printf("\n");
} else {
printf("Element not found.");
}
delete(4);
printf("List after deleting an item: ");
printList();
printf("\n");
foundLink = find(4);
if(foundLink != NULL){
printf("Element found: ");
printf("(%d,%d) ",foundLink->key,foundLink->data);
printf("\n");
} else {
printf("Element not found.");
}
printf("\n");
sort();
printf("List after sorting the data: ");
printList();
reverse(&head);
printf("\nList after reversing the data: ");
printList();
}
輸出
如果我們編譯並執行上述程式,它將產生以下輸出:
Original List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) ] Deleted value:(6,56) Deleted value:(5,40) Deleted value:(4,1) Deleted value:(3,30) Deleted value:(2,20) Deleted value:(1,10) List after deleting all items: [ ] Restored List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) ] Element found: (4,1) List after deleting an item: [ (6,56) (5,40) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) ] Element not found. List after sorting the data: [ (1,10) (2,20) (3,30) (5,40) (6,56) ] List after reversing the data: [ (6,56) (5,40) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) ]