
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構教程
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 首頁
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 概述
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 環境
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 演算法
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 概念
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 陣列
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 連結串列
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 雙向連結串列
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 迴圈連結串列
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 棧
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 表示式解析
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 佇列
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 優先佇列
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 樹
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 雜湊表
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 堆
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 圖
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 搜尋技術
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 排序技術
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 遞迴
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 有用資源
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 快速指南
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 有用資源
- 使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 討論
使用 C 語言實現資料結構 - 堆
概述
堆表示一種特殊的基於樹的資料結構,用於表示優先佇列或用於堆排序。我們將具體討論二叉堆樹。
二叉堆樹可以歸類為具有兩個約束條件的二叉樹:
完整性 - 二叉堆樹是一個完整的二叉樹,除了最後一層可能沒有所有元素,但元素應從左到右填充。
堆特性 - 所有父節點都應大於或小於其子節點。如果父節點大於其子節點,則稱為最大堆,否則稱為最小堆。最大堆用於堆排序,最小堆用於優先佇列。我們正在考慮最小堆,並將使用陣列來實現它。
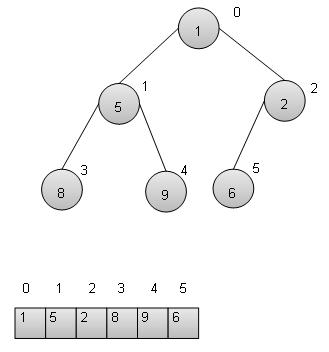
基本操作
以下是最小堆的基本主要操作:
插入 - 將元素插入堆中。
獲取最小值 - 從堆中獲取最小元素。
刪除最小值 - 從堆中刪除最小元素
插入操作
每當要插入元素時。將元素插入陣列的末尾。將堆的大小增加 1。
當堆屬性被破壞時,向上調整元素。將元素與其父節點的值進行比較,如果需要則交換它們。
void insert(int value) {
size++;
intArray[size - 1] = value;
heapUp(size - 1);
}
void heapUp(int nodeIndex){
int parentIndex, tmp;
if (nodeIndex != 0) {
parentIndex = getParentIndex(nodeIndex);
if (intArray[parentIndex] > intArray[nodeIndex]) {
tmp = intArray[parentIndex];
intArray[parentIndex] = intArray[nodeIndex];
intArray[nodeIndex] = tmp;
heapUp(parentIndex);
}
}
}
獲取最小值
獲取實現堆的陣列的第一個元素,即根節點。
int getMinimum(){
return intArray[0];
}
刪除最小值
每當要刪除元素時。獲取陣列的最後一個元素並將堆的大小減少 1。
當堆屬性被破壞時,向下調整元素。將元素與其子節點的值進行比較,如果需要則交換它們。
void removeMin() {
intArray[0] = intArray[size - 1];
size--;
if (size > 0)
heapDown(0);
}
void heapDown(int nodeIndex){
int leftChildIndex, rightChildIndex, minIndex, tmp;
leftChildIndex = getLeftChildIndex(nodeIndex);
rightChildIndex = getRightChildIndex(nodeIndex);
if (rightChildIndex >= size) {
if (leftChildIndex >= size)
return;
else
minIndex = leftChildIndex;
} else {
if (intArray[leftChildIndex] <= intArray[rightChildIndex])
minIndex = leftChildIndex;
else
minIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
if (intArray[nodeIndex] > intArray[minIndex]) {
tmp = intArray[minIndex];
intArray[minIndex] = intArray[nodeIndex];
intArray[nodeIndex] = tmp;
heapDown(minIndex);
}
}
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int intArray[10];
int size;
bool isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
int getMinimum(){
return intArray[0];
}
int getLeftChildIndex(int nodeIndex){
return 2*nodeIndex +1;
}
int getRightChildIndex(int nodeIndex){
return 2*nodeIndex +2;
}
int getParentIndex(int nodeIndex){
return (nodeIndex -1)/2;
}
bool isFull(){
return size == 10;
}
/**
* Heap up the new element,until heap property is broken.
* Steps:
* 1. Compare node's value with parent's value.
* 2. Swap them, If they are in wrong order.
* */
void heapUp(int nodeIndex){
int parentIndex, tmp;
if (nodeIndex != 0) {
parentIndex = getParentIndex(nodeIndex);
if (intArray[parentIndex] > intArray[nodeIndex]) {
tmp = intArray[parentIndex];
intArray[parentIndex] = intArray[nodeIndex];
intArray[nodeIndex] = tmp;
heapUp(parentIndex);
}
}
}
/**
* Heap down the root element being least in value,until heap property is broken.
* Steps:
* 1.If current node has no children, done.
* 2.If current node has one children and heap property is broken,
* 3.Swap the current node and child node and heap down.
* 4.If current node has one children and heap property is broken, find smaller one
* 5.Swap the current node and child node and heap down.
* */
void heapDown(int nodeIndex){
int leftChildIndex, rightChildIndex, minIndex, tmp;
leftChildIndex = getLeftChildIndex(nodeIndex);
rightChildIndex = getRightChildIndex(nodeIndex);
if (rightChildIndex >= size) {
if (leftChildIndex >= size)
return;
else
minIndex = leftChildIndex;
} else {
if (intArray[leftChildIndex] <= intArray[rightChildIndex])
minIndex = leftChildIndex;
else
minIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
if (intArray[nodeIndex] > intArray[minIndex]) {
tmp = intArray[minIndex];
intArray[minIndex] = intArray[nodeIndex];
intArray[nodeIndex] = tmp;
heapDown(minIndex);
}
}
void insert(int value) {
size++;
intArray[size - 1] = value;
heapUp(size - 1);
}
void removeMin() {
intArray[0] = intArray[size - 1];
size--;
if (size > 0)
heapDown(0);
}
main() {
/* 5 //Level 0
*
*/
insert(5);
/* 1 //Level 0
* |
* 5---| //Level 1
*/
insert(1);
/* 1 //Level 0
* |
* 5---|---3 //Level 1
*/
insert(3);
/* 1 //Level 0
* |
* 5---|---3 //Level 1
* |
* 8--| //Level 2
*/
insert(8);
/* 1 //Level 0
* |
* 5---|---3 //Level 1
* |
* 8--|--9 //Level 2
*/
insert(9);
/* 1 //Level 0
* |
* 5---|---3 //Level 1
* | |
* 8--|--9 6--| //Level 2
*/
insert(6);
/* 1 //Level 0
* |
* 5---|---2 //Level 1
* | |
* 8--|--9 6--|--3 //Level 2
*/
insert(2);
printf("%d", getMinimum());
removeMin();
/* 2 //Level 0
* |
* 5---|---3 //Level 1
* | |
* 8--|--9 6--| //Level 2
*/
printf("\n%d", getMinimum());
}
如果我們編譯並執行上述程式,它將產生以下結果:
1 2
廣告