
- C語言資料結構與演算法教程
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 首頁
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 概述
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 環境配置
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 演算法
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 概念
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 陣列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 連結串列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 雙向連結串列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 迴圈連結串列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 棧
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 表示式解析
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 佇列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 優先佇列
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 樹
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 雜湊表
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 堆
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 圖
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 搜尋技術
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 排序技術
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 遞迴
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 有用資源
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 快速指南
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 有用資源
- C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 討論
C語言實現的資料結構與演算法 - 圖
概述
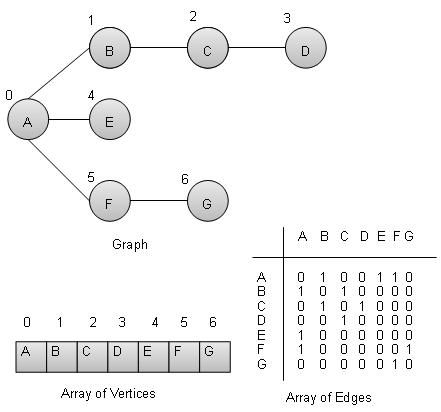
圖是一種用於模擬數學圖的資料結構。它由一組稱為頂點邊的連線對組成。我們可以使用頂點陣列和二維邊陣列來表示圖。
重要術語
頂點 − 圖的每個節點都表示為一個頂點。在下面的示例中,帶標籤的圓圈表示頂點。因此,A到G是頂點。我們可以使用如下所示的陣列來表示它們。這裡A可以用索引0表示,B可以用索引1表示,以此類推。
邊 − 邊表示兩個頂點之間的路徑或兩點之間的線。在下面的示例中,從A到B、B到C等的線表示邊。我們可以使用如下所示的二維陣列來表示陣列。這裡AB可以在第0行,第1列表示為1,BC可以在第1行,第2列表示為1,以此類推,其他組合保持為0。
鄰接 − 如果兩個節點或頂點透過一條邊連線在一起,則它們是鄰接的。在下面的示例中,B與A相鄰,C與B相鄰,以此類推。
路徑 − 路徑表示兩個頂點之間的一系列邊。在下面的示例中,ABCD表示從A到D的路徑。
基本操作
以下是圖的基本主要操作。
新增頂點 − 向圖中新增一個頂點。
新增邊 − 在圖的兩個頂點之間新增一條邊。
顯示頂點 − 顯示圖中的一個頂點。
新增頂點操作
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label){
struct vertex* vertex =
(struct vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
新增邊操作
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end){
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
顯示邊操作
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex){
printf("%c ",lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label);
}
遍歷演算法
以下是圖上重要的遍歷演算法。
深度優先搜尋 − 深度遍歷圖。
廣度優先搜尋 − 廣度遍歷圖。
深度優先搜尋演算法
深度優先搜尋演算法(DFS)以深度優先的方式遍歷圖,並使用堆疊來記住當任何迭代中出現死衚衕時要開始搜尋的下一個頂點。
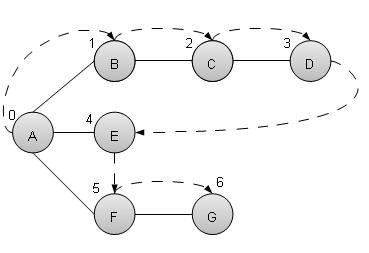
如上例所示,DFS演算法首先從A遍歷到B到C到D,然後到E,然後到F,最後到G。它採用以下規則。
規則1 − 訪問相鄰的未訪問頂點。標記為已訪問。顯示它。將其壓入堆疊。
規則2 − 如果找不到相鄰頂點,則從堆疊中彈出頂點。(它將彈出堆疊中所有沒有相鄰頂點的頂點。)
規則3 − 重複規則1和規則2,直到堆疊為空。
void depthFirstSearch(){
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//push vertex index in stack
push(0);
while(!isStackEmpty()){
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at top of the stack
int unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(peek());
//no adjacent vertex found
if(unvisitedVertex == -1){
pop();
} else {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
push(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//stack is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i=0;i < vertexCount;i++){
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
廣度優先搜尋演算法
廣度優先搜尋演算法(BFS)以廣度優先的方式遍歷圖,並使用佇列來記住當任何迭代中出現死衚衕時要開始搜尋的下一個頂點。
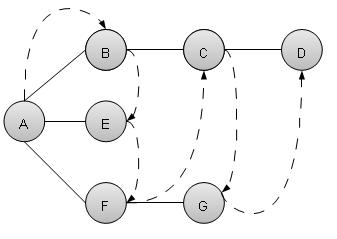
如上例所示,BFS演算法首先從A遍歷到B到E到F,然後到C和G,最後到D。它採用以下規則。
規則1 − 訪問相鄰的未訪問頂點。標記為已訪問。顯示它。將其插入佇列。
規則2 − 如果找不到相鄰頂點,則從佇列中刪除第一個頂點。
規則3 − 重複規則1和規則2,直到佇列為空。
void breadthFirstSearch(){
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//insert vertex index in queue
insert(0);
int unvisitedVertex;
while(!isQueueEmpty()){
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
int tempVertex = removeData();
//no adjacent vertex found
while((unvisitedVertex=getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1){
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
insert(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i=0;i<vertexCount;i++){
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 10
struct Vertex {
char label;
bool visited;
};
//stack variables
int stack[MAX];
int top=-1;
//queue variables
int queue[MAX];
int rear=-1;
int front=0;
int queueItemCount = 0;
//graph variables
//array of vertices
struct Vertex* lstVertices[MAX];
//adjacency matrix
int adjMatrix[MAX][MAX];
//vertex count
int vertexCount = 0;
//stack functions
void push(int item) {
stack[++top]=item;
}
int pop() {
return stack[top--];
}
int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
bool isStackEmpty(){
return top == -1;
}
//queue functions
void insert(int data){
queue[++rear] = data;
queueItemCount++;
}
int removeData(){
queueItemCount--;
return queue[front++];
}
bool isQueueEmpty(){
return queueItemCount == 0;
}
//graph functions
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label){
struct Vertex* vertex = (struct Vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct Vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end){
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex){
printf("%c ",lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label);
}
//get the adjacent unvisited vertex
int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex){
int i;
for(i=0; i<vertexCount; i++)
if(adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i]==1 && lstVertices[i]->visited==false)
return i;
return -1;
}
void depthFirstSearch(){
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//push vertex index in stack
push(0);
while(!isStackEmpty()){
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at top of the stack
int unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(peek());
//no adjacent vertex found
if(unvisitedVertex == -1){
pop();
} else {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
push(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//stack is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i=0;i < vertexCount;i++){
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
void breadthFirstSearch(){
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//insert vertex index in queue
insert(0);
int unvisitedVertex;
while(!isQueueEmpty()){
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
int tempVertex = removeData();
//no adjacent vertex found
while((unvisitedVertex=getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1){
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
insert(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i=0;i<vertexCount;i++){
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
main() {
int i, j;
for(i=0; i<MAX; i++) // set adjacency
for(j=0; j<MAX; j++) // matrix to 0
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
addVertex('A'); //0
addVertex('B'); //1
addVertex('C'); //2
addVertex('D'); //3
addVertex('E'); //4
addVertex('F'); //5
addVertex('G'); //6
/* 1 2 3
* 0 |--B--C--D
* A--|
* |
* | 4
* |-----E
* | 5 6
* | |--F--G
* |--|
*/
addEdge(0, 1); //AB
addEdge(1, 2); //BC
addEdge(2, 3); //CD
addEdge(0, 4); //AC
addEdge(0, 5); //AF
addEdge(5, 6); //FG
printf("Depth First Search: ");
//A B C D E F G
depthFirstSearch();
printf("\nBreadth First Search: ");
//A B E F C G D
breadthFirstSearch();
}
如果我們編譯並執行上述程式,則將產生以下結果:
Depth First Search: A B C D E F G Breadth First Search: A B E F C G D