如何在 OpenCV Python 中匹配影像形狀?
我們使用cv2.matchShapes()函式來匹配兩個影像形狀。此函式返回一個度量值,顯示影像形狀之間的相似度。此函式使用 Hu 不變數來計算度量值。度量值越低,影像形狀之間的相似度越高。
在以下示例中,我們將匹配來自不同影像的形狀以及來自單個影像的形狀。
語法
我們使用以下語法來匹配兩個影像形狀:
ret = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt1,1,0.0)
其中,
cnt1 - 第一個影像形狀的輪廓點。
cnt2 - 第二個影像形狀的輪廓點
步驟
您可以使用以下步驟來匹配兩個影像形狀:
匯入所需的庫。在所有以下 Python 示例中,所需的 Python 庫是OpenCV。確保您已安裝它。
import cv2
使用cv2.imread()讀取輸入影像作為灰度影像。
img1 = cv2.imread('star.png',0)
img2 = cv2.imread('star1.png',0)
對灰度影像應用閾值處理以建立二值影像。
ret,thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img1,150,255,0) ret,thresh2 = cv2.threshold(img1,150,255,0)
使用cv2.findContours()函式查詢二值影像中形狀的輪廓。
contours1, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh1, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) contours2, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh2, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
從每個影像中選擇特定的輪廓,並應用形狀匹配函式cv2.matchShapes()傳遞選定的輪廓。
cnt1=contours1[0] cnt2=contours2[0] ret12 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1, cnt2, 1, 0.0)
列印結果值,即影像形狀匹配度量。值越低,匹配度越好。
print("Matching Image 1 with Image 2:", ret12)
讓我們看一些示例,以便更好地理解。
示例 1
在此程式中,我們匹配兩個影像形狀。每個影像包含一個形狀。我們還匹配每個影像中形狀本身。
# import required libraries import cv2 # Read two images as grayscale images img1 = cv2.imread('star.png',0) img2 = cv2.imread('star1.png',0) # Apply thresholding on the images to convert to binary images ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img1, 127, 255,0) ret, thresh2 = cv2.threshold(img2, 127, 255,0) # find the contours in the binary image contours1,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh1,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) print("Number of Shapes detected in Image 1:",len(contours)) cnt1 = contours1[0] contours2,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh2,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) print("Number of Shapes detected in Image 2:",len(contours)) cnt2 = contours2[0] # Compute the match scores ret11 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt1,1,0.0) ret22 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt2,cnt2,1,0.0) ret12 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt2,1,0.0) # print the matching scores print("Matching Image 1 with itself:", ret11) print("Matching Image 2 with itself:", ret22) print("Matching Image 1 with Image 2:", ret12)
將以下影像視為上述程式中提到的“star.png”和“pentagon.png”輸入影像。
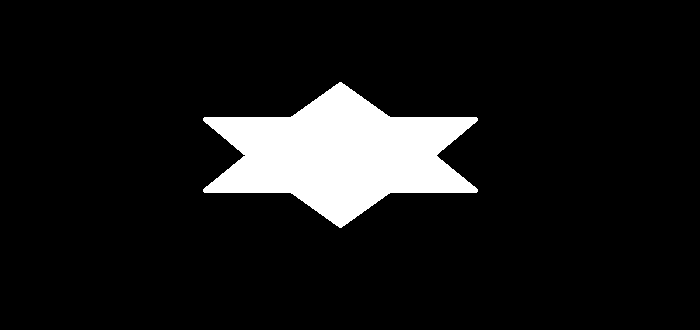
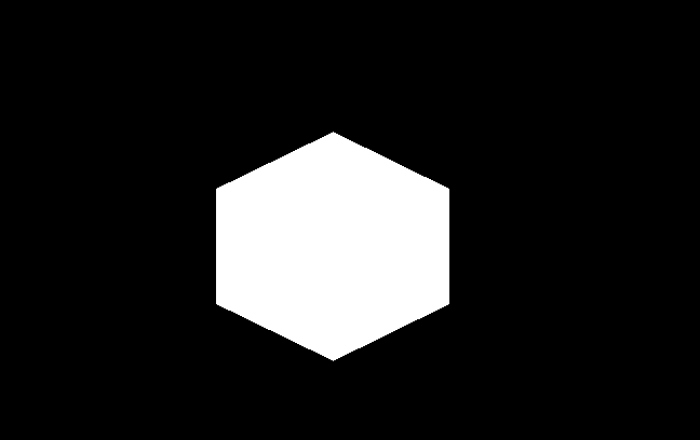
輸出
執行後,以上程式碼將產生以下輸出:
Number of Shapes detected in Image 1: 1 Number of Shapes detected in Image 2: 1 Matching Image 1 with itself: 0.0 Matching Image 2 with itself: 0.0 Matching Image 1 with Image 2: 0.6015851094057714
示例 2
在此程式中,我們匹配影像中的形狀。我們在影像中檢測到三個形狀。
import cv2 import numpy as np img = cv2.imread('convexhull.png') gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(gray,100,255,0) contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) print("Number of Shapes detected:",len(contours)) # draw contour and shape number for i, cnt in enumerate(contours): M = cv2.moments(cnt) x1, y1 = cnt[0,0] img1 = cv2.drawContours(img, [cnt], -1, (0,255,255), 3) cv2.putText(img1, f'Shape:{i+1}', (x1, y1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 255, 0), 2) cnt1 = contours[0] cnt2 = contours[1] cnt3= contours[2] ret11 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt1,1,0.0) ret12 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt2,1,0.0) ret23 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt2,cnt3,1,0.0) ret31 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt3,cnt1,1,0.0) print("Matching Shape 1 with itself:", ret11) print("Matching Shape 1 with Shape 2:", ret12) print("Matching Shape 2 with Shape 3:", ret23) print("Matching Shape 3 with Shape 1:", ret31) cv2.imshow("Shapes", img) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
我們將在本程式中使用以下影像和輸入檔案:
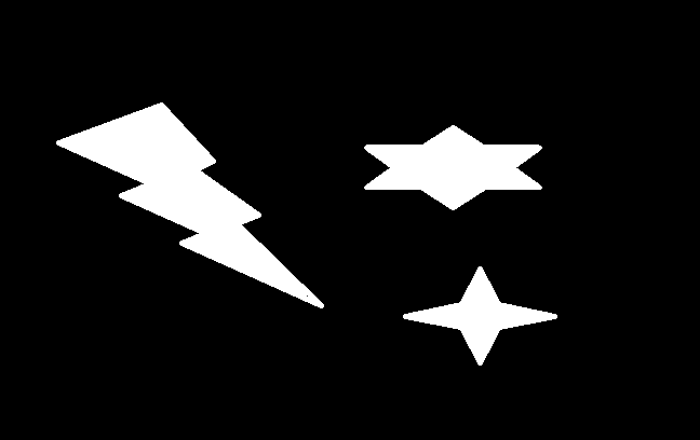
輸出
執行後,以上程式碼將產生以下輸出:
Number of Shapes detected: 3 Matching Shape 1 with itself: 0.0 Matching Shape 1 with Shape 2: 0.15261042892128207 Matching Shape 2 with Shape 3: 0.9192709496955178 Matching Shape 3 with Shape 1: 0.7521097407160106
並且我們得到以下視窗,顯示輸出:

根據以上結果,我們得出結論,形狀 1 比形狀 3 更類似於形狀 2。

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 語言程式設計
C 語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP