
- Java 資料結構與演算法 教程
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 首頁
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 概述
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 環境搭建
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 演算法
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 資料結構
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 陣列
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 連結串列
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 雙向連結串列
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 迴圈連結串列
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 棧
- 資料結構與演算法 - 表示式解析
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 佇列
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 優先佇列
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 樹
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 雜湊表
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 堆
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 圖
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 搜尋技術
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 排序技術
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 遞迴
- Java 資料結構與演算法 有用資源
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 快速指南
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 有用資源
- Java 資料結構與演算法 - 討論
Java 資料結構與演算法 - 棧
概述
棧是一種資料結構,它只允許在一端進行資料操作。它只允許訪問最後插入的資料。棧也被稱為後進先出 (LIFO) 資料結構,並且 Push 和 Pop 操作以這樣一種方式相關聯:只有最後一個被 Push(新增到棧中)的專案才能被 Pop(從棧中移除)。
棧的表示
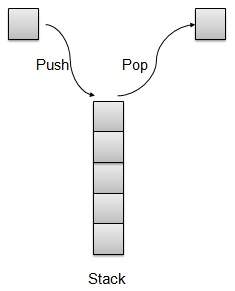
我們將在本文中使用陣列來實現棧。
基本操作
以下是棧的兩個主要操作。
Push − 將元素推入棧頂。
Pop − 從棧頂彈出元素。
棧還支援其他一些操作。
Peek − 獲取棧頂元素。
isFull − 檢查棧是否已滿。
isEmpty − 檢查棧是否為空。
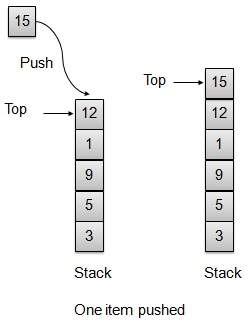
Push 操作
每當一個元素被推入棧時,棧會將該元素儲存在儲存區的頂部,並遞增頂部索引以備後用。如果儲存區已滿,則通常會顯示錯誤訊息。
// push item on the top of the stack
public void push(int data) {
if(!isFull()){
// increment top by 1 and insert data
intArray[++top] = data;
}else{
System.out.println("Cannot add data. Stack is full.");
}
}
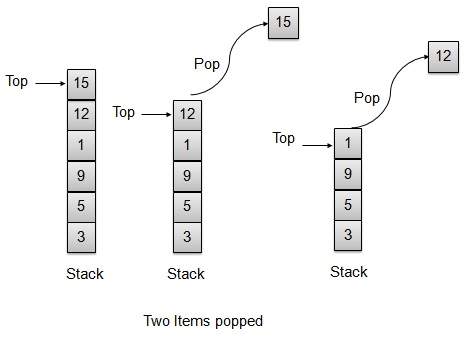
Pop 操作
每當需要從棧中彈出元素時,棧會從儲存區的頂部檢索該元素,並遞減頂部索引以備後用。
// pop item from the top of the stack
public int pop() {
// retrieve data and decrement the top by 1
return intArray[top--];
}
棧的實現
Stack.java
package com.tutorialspoint.datastructure;
public class Stack {
private int size; // size of the stack
private int[] intArray; // stack storage
private int top; // top of the stack
// Constructor
public Stack(int size){
this.size = size;
intArray = new int[size]; //initialize array
top = -1; //stack is initially empty
}
// Operation : Push
// push item on the top of the stack
public void push(int data) {
if(!isFull()){
// increment top by 1 and insert data
intArray[++top] = data;
}else{
System.out.println("Cannot add data. Stack is full.");
}
}
// Operation : Pop
// pop item from the top of the stack
public int pop() {
//retrieve data and decrement the top by 1
return intArray[top--];
}
// Operation : Peek
// view the data at top of the stack
public int peek() {
//retrieve data from the top
return intArray[top];
}
// Operation : isFull
// return true if stack is full
public boolean isFull(){
return (top == size-1);
}
// Operation : isEmpty
// return true if stack is empty
public boolean isEmpty(){
return (top == -1);
}
}
演示程式
StackDemo.java
package com.tutorialspoint.datastructure;
public class StackDemo {
public static void main (String[] args){
// make a new stack
Stack stack = new Stack(10);
// push items on to the stack
stack.push(3);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(9);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(12);
stack.push(15);
System.out.println("Element at top of the stack: " + stack.peek());
System.out.println("Elements: ");
// print stack data
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
int data = stack.pop();
System.out.println(data);
}
System.out.println("Stack full: " + stack.isFull());
System.out.println("Stack empty: " + stack.isEmpty());
}
}
如果我們編譯並執行上述程式,則會產生以下結果:
Element at top of the stack: 15 Elements: 15 12 1 9 5 3 Stack full: false Stack empty: true
廣告