
- Java資料結構與演算法教程
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 首頁
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 概述
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 環境搭建
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 演算法
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 資料結構
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 陣列
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 連結串列
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 雙向連結串列
- Java實現的資料結構與演算法 - 環形連結串列
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 棧
- 資料結構與演算法 - 表示式解析
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 佇列
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 優先佇列
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 樹
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 雜湊表
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 堆
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 圖
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 搜尋技術
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 排序技術
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 遞迴
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 有用資源
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 快速指南
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 有用資源
- Java資料結構與演算法 - 討論
Java實現的資料結構與演算法 - 環形連結串列
環形連結串列基礎
環形連結串列是連結串列的一種變體,其中第一個元素指向最後一個元素,最後一個元素指向第一個元素。單鏈表和雙向連結串列都可以轉換為環形連結串列。
單鏈表作為環形連結串列
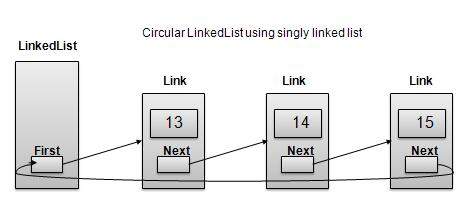
雙向連結串列作為環形連結串列
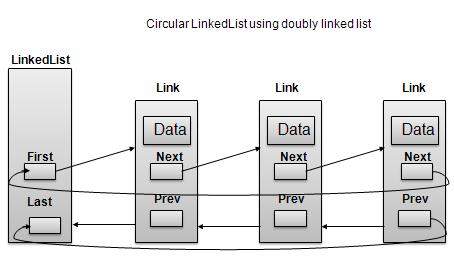
根據以上所示圖例,需要考慮以下重要事項。
在單鏈表和雙向連結串列兩種情況下,最後一個連結的“next”都指向列表的第一個連結。
在雙向連結串列中,第一個連結的“prev”指向列表的最後一個連結。
基本操作
以下是環形連結串列支援的重要操作。
插入 − 在列表開頭插入元素。
刪除 − 從列表開頭刪除元素。
顯示 − 顯示列表。
長度操作
以下程式碼演示了基於單鏈表的環形連結串列中的插入操作。
//insert link at the first location
public void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
Link link = new Link(key,data);
if (isEmpty()) {
first = link;
first.next = first;
}
else{
//point it to old first node
link.next = first;
//point first to new first node
first = link;
}
}
刪除操作
以下程式碼演示了基於單鏈表的環形連結串列中的刪除操作。
//delete link at the first location
public Link deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
Link tempLink = first;
//if only one link
if(first.next == null){
last = null;
}else {
first.next.prev = null;
}
first = first.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
顯示列表操作
以下程式碼演示了環形連結串列中的顯示列表操作。
public void display(){
//start from the beginning
Link current = first;
//navigate till the end of the list
System.out.print("[ ");
if(first != null){
while(current.next != current){
//print data
current.display();
//move to next item
current = current.next;
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
演示
Link.java
package com.tutorialspoint.list;
public class CircularLinkedList {
//this link always point to first Link
private Link first;
// create an empty linked list
public CircularLinkedList(){
first = null;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return first == null;
}
public int length(){
int length = 0;
//if list is empty
if(first == null){
return 0;
}
Link current = first.next;
while(current != first){
length++;
current = current.next;
}
return length;
}
//insert link at the first location
public void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
Link link = new Link(key,data);
if (isEmpty()) {
first = link;
first.next = first;
}
else{
//point it to old first node
link.next = first;
//point first to new first node
first = link;
}
}
//delete first item
public Link deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
Link tempLink = first;
if(first.next == first){
first = null;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
first = first.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
public void display(){
//start from the beginning
Link current = first;
//navigate till the end of the list
System.out.print("[ ");
if(first != null){
while(current.next != current){
//print data
current.display();
//move to next item
current = current.next;
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
}
DoublyLinkedListDemo.java
package com.tutorialspoint.list;
public class CircularLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
CircularLinkedList list = new CircularLinkedList();
list.insertFirst(1, 10);
list.insertFirst(2, 20);
list.insertFirst(3, 30);
list.insertFirst(4, 1);
list.insertFirst(5, 40);
list.insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("\nOriginal List: ");
list.display();
System.out.println("");
while(!list.isEmpty()){
Link temp = list.deleteFirst();
System.out.print("Deleted value:");
temp.display();
System.out.println("");
}
System.out.print("List after deleting all items: ");
list.display();
System.out.println("");
}
}
如果我們編譯並執行以上程式,則會產生以下結果:
Original List: [ {6,56} {5,40} {4,1} {3,30} {2,20} ]
Deleted value:{6,56}
Deleted value:{5,40}
Deleted value:{4,1}
Deleted value:{3,30}
Deleted value:{2,20}
Deleted value:{1,10}
List after deleting all items: [ ]
廣告