
- XML DOM 基礎
- XML DOM - 首頁
- XML DOM - 概述
- XML DOM - 模型
- XML DOM - 節點
- XML DOM - 節點樹
- XML DOM - 方法
- XML DOM - 載入
- XML DOM - 遍歷
- XML DOM - 導航
- XML DOM - 訪問
- XML DOM 操作
- XML DOM - 獲取節點
- XML DOM - 設定節點
- XML DOM - 建立節點
- XML DOM - 新增節點
- XML DOM - 替換節點
- XML DOM - 刪除節點
- XML DOM - 克隆節點
- XML DOM 物件
- DOM - 節點物件
- DOM - 節點列表物件
- DOM - 命名節點對映物件
- DOM - DOMImplementation
- DOM - DocumentType 物件
- DOM - 處理指令
- DOM - 實體物件
- DOM - 實體引用物件
- DOM - 符號物件
- DOM - 元素物件
- DOM - 屬性物件
- DOM - CDATASection 物件
- DOM - 註釋物件
- DOM - XMLHttpRequest 物件
- DOM - DOMException 物件
- XML DOM 有用資源
- XML DOM 快速指南
- XML DOM - 有用資源
- XML DOM - 討論
XML DOM 快速指南
XML DOM - 概述
Document Object Model (DOM) 是 W3C 標準。它定義了訪問 HTML 和 XML 等文件的標準。
W3C 給出的 DOM 定義如下:W3C
文件物件模型 (DOM) 是 HTML 和 XML 文件的應用程式程式設計介面 (API)。它定義了文件的邏輯結構以及訪問和操作文件的方式。
DOM 定義了訪問所有 XML 元素的物件、屬性和方法(介面)。它分為三個不同的部分/級別:
核心 DOM - 任何結構化文件的標準模型
XML DOM - XML 文件的標準模型
HTML DOM - HTML 文件的標準模型
XML DOM 是 XML 的標準物件模型。XML 文件具有稱為節點的資訊單元層次結構;DOM 是描述這些節點及其之間關係的標準程式設計介面。
XML DOM 還提供了一個 API,允許開發人員在樹的任何位置新增、編輯、移動或刪除節點,以建立應用程式。
以下是 DOM 結構圖。該圖顯示瞭解析器透過遍歷每個節點來將 XML 文件評估為 DOM 結構。
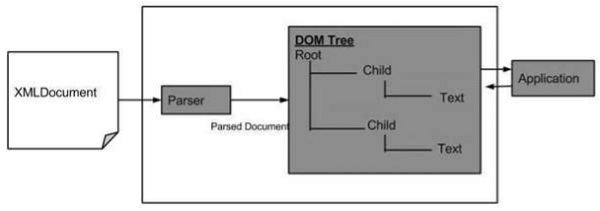
XML DOM 的優點
以下是 XML DOM 的優點。
XML DOM 與語言和平臺無關。
XML DOM 是可遍歷的 - XML DOM 中的資訊以層次結構組織,允許開發人員在層次結構中導航以查詢特定資訊。
XML DOM 是可修改的 - 它具有動態特性,為開發人員提供在樹的任何位置新增、編輯、移動或刪除節點的範圍。
XML DOM 的缺點
如果 XML 結構很大,它會消耗更多記憶體,因為編寫的程式會一直駐留在記憶體中,除非顯式刪除。
由於大量使用記憶體,與 SAX 相比,其執行速度較慢。
XML DOM - 模型
現在我們知道了 DOM 的含義,讓我們看看 DOM 結構是什麼。DOM 文件是節點或資訊的集合,以層次結構組織。某些型別的節點可能具有各種型別的子節點,而其他節點是葉節點,在文件結構中其下不能有任何內容。以下是節點型別的列表,以及它們可能作為子節點具有的節點型別列表:
文件 - 元素(最多一個)、處理指令、註釋、文件型別(最多一個)
文件片段 - 元素、處理指令、註釋、文字、CDATASection、實體引用
實體引用 - 元素、處理指令、註釋、文字、CDATASection、實體引用
元素 - 元素、文字、註釋、處理指令、CDATASection、實體引用
屬性 - 文字、實體引用
處理指令 - 沒有子節點
註釋 - 沒有子節點
文字 - 沒有子節點
CDATASection - 沒有子節點
實體 - 元素、處理指令、註釋、文字、CDATASection、實體引用
符號 - 沒有子節點
示例
考慮以下 XML 文件node.xml的 DOM 表示。
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<Company>
<Employee category = "technical">
<FirstName>Tanmay</FirstName>
<LastName>Patil</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "non-technical">
<FirstName>Taniya</FirstName>
<LastName>Mishra</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234667898</ContactNo>
</Employee>
</Company>
上述 XML 文件的文件物件模型如下:
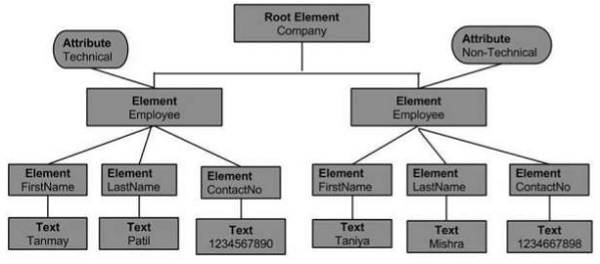
從上面的流程圖中,我們可以推斷:
節點物件只能有一個父節點物件。它位於所有節點之上。這裡它是Company。
父節點可以有多個節點,稱為子節點。這些子節點可以有附加的節點,稱為屬性節點。在上面的示例中,我們有兩個屬性節點Technical和Non-technical。屬性節點實際上並不是元素節點的子節點,但仍然與之關聯。
這些子節點又可以有多個子節點。節點內的文字稱為文字節點。
同一級別的節點物件稱為兄弟節點。
DOM 識別:
表示介面並操作文件的物件。
物件和介面之間的關係。
XML DOM - 節點
在本節中,我們將學習 XML DOM 節點。每個 XML DOM 都以稱為節點的層次單元維護資訊,而 DOM 描述這些節點及其之間的關係。
節點型別
下圖顯示了所有節點型別:
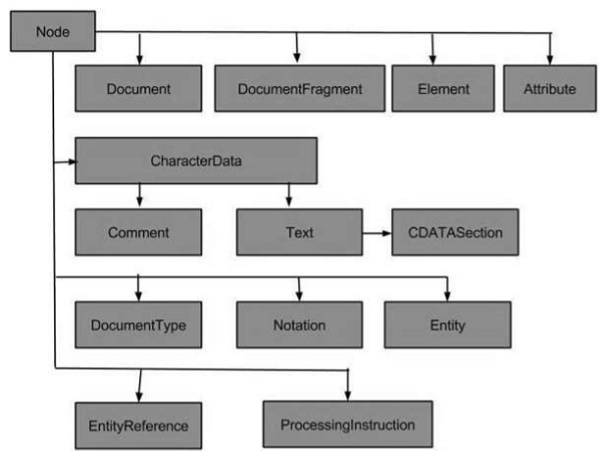
XML 中最常見的節點型別是:
文件節點 - 完整的 XML 文件結構是一個文件節點。
元素節點 - 每個 XML 元素都是一個元素節點。這也是唯一可以具有屬性的節點型別。
屬性節點 - 每個屬性都被認為是一個屬性節點。它包含有關元素節點的資訊,但實際上並不被認為是元素的子節點。
文字節點 - 文件文字被認為是文字節點。它可以包含更多資訊或只是空格。
一些不太常見的節點型別是:
CDATA 節點 - 此節點包含解析器不應分析的資訊。相反,它應該只作為純文字傳遞。
註釋節點 - 此節點包含有關資料的資訊,通常會被應用程式忽略。
處理指令節點 - 此節點包含專門針對應用程式的資訊。
文件片段節點
實體節點
實體引用節點
符號節點
XML DOM - 節點樹
在本節中,我們將學習 XML DOM 節點樹。在 XML 文件中,資訊以層次結構維護;此層次結構稱為節點樹。此層次結構允許開發人員在樹中導航以查詢特定資訊,因此允許訪問節點。然後可以更新這些節點的內容。
節點樹的結構從根元素開始,一直擴充套件到子元素,直到最低級別。
示例
以下示例演示了一個簡單的 XML 文件,其節點樹結構如下所示:
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<Company>
<Employee category = "Technical">
<FirstName>Tanmay</FirstName>
<LastName>Patil</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Non-Technical">
<FirstName>Taniya</FirstName>
<LastName>Mishra</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234667898</ContactNo>
</Employee>
</Company>
如上例所示,其圖示表示(其 DOM)如下:

樹的最頂層節點稱為根。根節點是 <Company>,它又包含 <Employee> 的兩個節點。這些節點稱為子節點。
根節點 <Company> 的子節點 <Employee> 又包含它自己的子節點(<FirstName>、<LastName>、<ContactNo>)。
根節點 <Company> 的兩個子節點 <Employee> 具有屬性值 Technical 和 Non-Technical,稱為屬性節點。
每個節點內的文字稱為文字節點。
XML DOM - 方法
DOM 作為 API 包含表示 XML 文件中可以找到的不同型別資訊(例如元素和文字)的介面。這些介面包括使用這些物件所需的方法和屬性。屬性定義節點的特性,而方法提供操作節點的方式。
下表列出了 DOM 類和介面:
| 序號 | 介面和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | DOMImplementation 它提供許多方法來執行獨立於文件物件模型任何特定例項的操作。 |
| 2 | DocumentFragment 它是“輕量級”或“最小”文件物件,它(作為 Document 的超類)在成熟的文件中錨定 XML/HTML 樹。 |
| 3 | Document 它表示 XML 文件的頂級節點,它提供對文件中所有節點(包括根元素)的訪問。 |
| 4 | Node 它表示 XML 節點。 |
| 5 | NodeList 它表示Node物件的只讀列表。 |
| 6 | NamedNodeMap 它表示可以按名稱訪問的節點集合。 |
| 7 | Data 它透過一組屬性和方法擴充套件Node,用於訪問 DOM 中的字元資料。 |
| 8 | Attribute 它表示 Element 物件中的屬性。 |
| 9 | Element 它表示元素節點。派生自 Node。 |
| 10 | Text 它表示文字節點。派生自 CharacterData。 |
| 11 | Comment 它表示註釋節點。派生自 CharacterData。 |
| 12 | ProcessingInstruction 它表示“處理指令”。它在 XML 中用作在文件文字中保留處理器特定資訊的一種方式。 |
| 13 | CDATA Section 它表示 CDATA 部分。派生自 Text。 |
| 14 | Entity 它表示實體。派生自 Node。 |
| 15 | EntityReference 這表示樹中的實體引用。派生自 Node。 |
我們將在各自的章節中討論上述每個介面的方法和屬性。
XML DOM - 載入
在本節中,我們將學習 XML 的載入和解析。
為了描述 API 提供的介面,W3C 使用了一種稱為介面定義語言 (IDL) 的抽象語言。使用 IDL 的優點是開發人員可以學習如何使用自己喜歡的語言使用 DOM,並且可以輕鬆切換到不同的語言。
缺點是,由於它是抽象的,因此 Web 開發人員無法直接使用 IDL。由於程式語言之間的差異,它們需要在抽象介面及其具體語言之間進行對映——或繫結——。DOM 已對映到 JavaScript、JScript、Java、C、C++、PLSQL、Python 和 Perl 等程式語言。
在接下來的章節中,我們將使用 Javascript 作為程式語言來載入 XML 檔案。
解析器
解析器是一個軟體應用程式,它被設計用來分析文件(在本例中為 XML 文件)並對資訊執行特定操作。一些基於 DOM 的解析器列在下面的表格中:
| 序號 | 解析器及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
JAXP Sun Microsystem 的 Java API for XML Parsing (JAXP) |
| 2 | XML4J IBM 的 Java XML 解析器 (XML4J) |
| 3 | msxml Microsoft 的 XML 解析器 (msxml) 2.0 版本內置於 Internet Explorer 5.5 中 |
| 4 | 4DOM 4DOM 是 Python 程式語言的解析器 |
| 5 | XML::DOM XML::DOM 是一個 Perl 模組,用於使用 Perl 操作 XML 文件 |
| 6 | Xerces Apache 的 Xerces Java 解析器 |
在像 DOM 這樣的基於樹的 API 中,解析器遍歷 XML 檔案並建立相應的 DOM 物件。然後您可以來回遍歷 DOM 結構。
載入和解析 XML
載入 XML 文件時,XML 內容可以有兩種形式:
- 直接作為 XML 檔案
- 作為 XML 字串
內容作為 XML 檔案
下面的例子演示瞭如何使用 Ajax 和 Javascript 載入 XML (node.xml) 資料,當 XML 內容作為 XML 檔案接收時。在這裡,Ajax 函式獲取 xml 檔案的內容並將其儲存在 XML DOM 中。一旦建立了 DOM 物件,它就會被解析。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div>
<b>FirstName:</b> <span id = "FirstName"></span><br>
<b>LastName:</b> <span id = "LastName"></span><br>
<b>ContactNo:</b> <span id = "ContactNo"></span><br>
<b>Email:</b> <span id = "Email"></span>
</div>
<script>
//if browser supports XMLHttpRequest
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) { // Create an instance of XMLHttpRequest object.
code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else { // code for IE6, IE5
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
// sets and sends the request for calling "node.xml"
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
// sets and returns the content as XML DOM
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
//parsing the DOM object
document.getElementById("FirstName").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("LastName").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("LastName")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("ContactNo").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ContactNo")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("Email").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Email")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
</body>
</html>
node.xml
<Company>
<Employee category = "Technical" id = "firstelement">
<FirstName>Tanmay</FirstName>
<LastName>Patil</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>
<Email>tanmaypatil@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Non-Technical">
<FirstName>Taniya</FirstName>
<LastName>Mishra</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234667898</ContactNo>
<Email>taniyamishra@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Management">
<FirstName>Tanisha</FirstName>
<LastName>Sharma</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234562350</ContactNo>
<Email>tanishasharma@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
</Company>
大部分程式碼細節都在指令碼程式碼中。
Internet Explorer 使用 ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP") 建立 XMLHttpRequest 物件的例項,其他瀏覽器使用 XMLHttpRequest() 方法。
responseXML 將 XML 內容直接轉換為 XML DOM。
一旦 XML 內容轉換為 JavaScript XML DOM,就可以使用 JS DOM 方法和屬性訪問任何 XML 元素。我們使用了 DOM 屬性,例如 childNodes、nodeValue 和 DOM 方法,例如 getElementsById(ID)、getElementsByTagName(tags_name)。
執行
將此檔案儲存為 loadingexample.html 並將其在瀏覽器中開啟。您將收到以下輸出:

內容作為 XML 字串
下面的例子演示瞭如何使用 Ajax 和 Javascript 載入 XML 資料,當 XML 內容作為 XML 檔案接收時。在這裡,Ajax 函式獲取 xml 檔案的內容並將其儲存在 XML DOM 中。一旦建立了 DOM 物件,它就會被解析。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
// loads the xml string in a dom object
function loadXMLString(t) { // for non IE browsers
if (window.DOMParser) {
// create an instance for xml dom object parser = new DOMParser();
xmlDoc = parser.parseFromString(t,"text/xml");
}
// code for IE
else { // create an instance for xml dom object
xmlDoc = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLDOM");
xmlDoc.async = false;
xmlDoc.loadXML(t);
}
return xmlDoc;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// a variable with the string
var text = "<Employee>";
text = text+"<FirstName>Tanmay</FirstName>";
text = text+"<LastName>Patil</LastName>";
text = text+"<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>";
text = text+"<Email>tanmaypatil@xyz.com</Email>";
text = text+"</Employee>";
// calls the loadXMLString() with "text" function and store the xml dom in a variable
var xmlDoc = loadXMLString(text);
//parsing the DOM object
y = xmlDoc.documentElement.childNodes;
for (i = 0;i<y.length;i++) {
document.write(y[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue);
document.write("<br>");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
大部分程式碼細節都在指令碼程式碼中。
Internet Explorer 使用 ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLDOM") 將 XML 資料載入到 DOM 物件中,其他瀏覽器使用 DOMParser() 函式和 parseFromString(text, 'text/xml') 方法。
變數 text 應該包含一個包含 XML 內容的字串。
一旦 XML 內容轉換為 JavaScript XML DOM,就可以使用 JS DOM 方法和屬性訪問任何 XML 元素。我們使用了 DOM 屬性,例如 childNodes、nodeValue。
執行
將此檔案儲存為 loadingexample.html 並將其在瀏覽器中開啟。您將看到以下輸出:

現在我們已經瞭解了 XML 內容如何轉換為 JavaScript XML DOM,您現在可以使用 XML DOM 方法訪問任何 XML 元素。
XML DOM - 遍歷
在本章中,我們將討論 XML DOM 遍歷。我們在上一章學習瞭如何載入 XML 文件並解析由此獲得的 DOM 物件。這個已解析的 DOM 物件可以被遍歷。遍歷是一個系統地迴圈遍歷節點樹中每個元素的過程。
示例
下面的例子 (traverse_example.htm) 演示了 DOM 遍歷。在這裡,我們遍歷 <Employee> 元素的每個子節點。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
table,th,td {
border:1px solid black;
border-collapse:collapse
}
</style>
<body>
<div id = "ajax_xml"></div>
<script>
//if browser supports XMLHttpRequest
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// Create an instance of XMLHttpRequest object.
code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {// code for IE6, IE5
var xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
// sets and sends the request for calling "node.xml"
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
// sets and returns the content as XML DOM
var xml_dom = xmlhttp.responseXML;
// this variable stores the code of the html table
var html_tab = '<table id = "id_tabel" align = "center">
<tr>
<th>Employee Category</th>
<th>FirstName</th>
<th>LastName</th>
<th>ContactNo</th>
<th>Email</th>
</tr>';
var arr_employees = xml_dom.getElementsByTagName("Employee");
// traverses the "arr_employees" array
for(var i = 0; i<arr_employees.length; i++) {
var employee_cat = arr_employees[i].getAttribute('category');
// gets the value of 'category' element of current "Element" tag
// gets the value of first child-node of 'FirstName'
// element of current "Employee" tag
var employee_firstName =
arr_employees[i].getElementsByTagName('FirstName')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
// gets the value of first child-node of 'LastName'
// element of current "Employee" tag
var employee_lastName =
arr_employees[i].getElementsByTagName('LastName')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
// gets the value of first child-node of 'ContactNo'
// element of current "Employee" tag
var employee_contactno =
arr_employees[i].getElementsByTagName('ContactNo')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
// gets the value of first child-node of 'Email'
// element of current "Employee" tag
var employee_email =
arr_employees[i].getElementsByTagName('Email')[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
// adds the values in the html table
html_tab += '<tr>
<td>'+ employee_cat+ '</td>
<td>'+ employee_firstName+ '</td>
<td>'+ employee_lastName+ '</td>
<td>'+ employee_contactno+ '</td>
<td>'+ employee_email+ '</td>
</tr>';
}
html_tab += '</table>';
// adds the html table in a html tag, with id = "ajax_xml"
document.getElementById('ajax_xml').innerHTML = html_tab;
</script>
</body>
</html>
這段程式碼載入了 node.xml。
XML 內容被轉換為 JavaScript XML DOM 物件。
使用 getElementsByTagName() 方法獲得元素陣列(帶有標籤 Element)。
接下來,我們遍歷這個陣列並在表格中顯示子節點值。
執行
將此檔案儲存為 traverse_example.html 到伺服器路徑(此檔案和 node.xml 應該在伺服器的同一路徑下)。您將收到以下輸出:
XML DOM - 導航
到目前為止,我們學習了 DOM 結構、如何載入和解析 XML DOM 物件以及如何遍歷 DOM 物件。在這裡,我們將瞭解如何在一個 DOM 物件中導航節點之間。XML DOM 包含節點的各種屬性,這些屬性幫助我們遍歷節點,例如:
- parentNode
- childNodes
- firstChild
- lastChild
- nextSibling
- previousSibling
以下是節點樹的圖表,顯示了它與其他節點的關係。
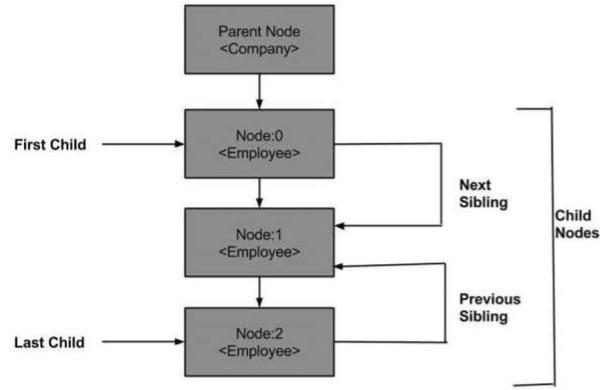
DOM - 父節點
此屬性將父節點指定為節點物件。
示例
下面的例子 (navigate_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析成 XML DOM 物件。然後透過子節點導航到父節點:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
var y = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0];
document.write(y.parentNode.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>
正如您在上面的例子中看到的,子節點 Employee 導航到它的父節點。
執行
將此檔案儲存為 navigate_example.html 到伺服器路徑(此檔案和 node.xml 應該在伺服器的同一路徑下)。在輸出中,我們得到 Employee 的父節點,即 Company。
第一個子節點
此屬性的型別為 Node,表示 NodeList 中存在的第一個子節點名稱。
示例
下面的例子 (first_node_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析成 XML DOM 物件,然後導航到 DOM 物件中存在的第一個子節點。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
function get_firstChild(p) {
a = p.firstChild;
while (a.nodeType != 1) {
a = a.nextSibling;
}
return a;
}
var firstchild = get_firstChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0]);
document.write(firstchild.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>
函式 get_firstChild(p) 用於避免空節點。它有助於從節點列表中獲取 firstChild 元素。
x = get_firstChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0]) 獲取標籤名稱為 Employee 的第一個子節點。
執行
將此檔案儲存為 first_node_example.htm 到伺服器路徑(此檔案和 node.xml 應該在伺服器的同一路徑下)。在輸出中,我們得到 Employee 的第一個子節點,即 FirstName。
最後一個子節點
此屬性的型別為 Node,表示 NodeList 中存在的最後一個子節點名稱。
示例
下面的例子 (last_node_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析成 XML DOM 物件,然後導航到 xml DOM 物件中存在的最後一個子節點。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
function get_lastChild(p) {
a = p.lastChild;
while (a.nodeType != 1){
a = a.previousSibling;
}
return a;
}
var lastchild = get_lastChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0]);
document.write(lastchild.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案儲存為 last_node_example.htm 到伺服器路徑(此檔案和 node.xml 應該在伺服器的同一路徑下)。在輸出中,我們得到 Employee 的最後一個子節點,即 Email。
下一個兄弟節點
此屬性的型別為 Node,表示下一個子節點,即 NodeList 中存在的指定子元素的下一個兄弟節點。
示例
下面的例子 (nextSibling_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析成 XML DOM 物件,然後立即導航到 xml 文件中存在的下一個節點。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
function get_nextSibling(p) {
a = p.nextSibling;
while (a.nodeType != 1) {
a = a.nextSibling;
}
return a;
}
var nextsibling = get_nextSibling(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0]);
document.write(nextsibling.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案儲存為 nextSibling_example.htm 到伺服器路徑(此檔案和 node.xml 應該在伺服器的同一路徑下)。在輸出中,我們得到 FirstName 的下一個兄弟節點,即 LastName。
上一個兄弟節點
此屬性的型別為 Node,表示上一個子節點,即 NodeList 中存在的指定子元素的上一個兄弟節點。
示例
下面的例子 (previoussibling_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析成 XML DOM 物件,然後導航到 xml 文件中最後一個子節點之前的節點。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest)
{
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
function get_previousSibling(p) {
a = p.previousSibling;
while (a.nodeType != 1) {
a = a.previousSibling;
}
return a;
}
prevsibling = get_previousSibling(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Email")[0]);
document.write(prevsibling.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案儲存為 previoussibling_example.htm 到伺服器路徑(此檔案和 node.xml 應該在伺服器的同一路徑下)。在輸出中,我們得到 Email 的上一個兄弟節點,即 ContactNo。
XML DOM - 訪問
在本章中,我們將學習如何訪問 XML DOM 節點,這些節點被認為是 XML 文件的資訊單元。XML DOM 的節點結構允許開發人員在樹中查詢特定資訊,同時訪問資訊。
訪問節點
您可以透過以下三種方式訪問節點:
使用 getElementsByTagName () 方法
透過迴圈或遍歷節點樹
透過使用節點關係導航節點樹
getElementsByTagName ()
此方法允許透過指定節點名稱來訪問節點的資訊。它還允許訪問節點列表和節點列表長度的資訊。
語法
getElementByTagName() 方法具有以下語法:
node.getElementByTagName("tagname");
其中,
node - 是文件節點。
tagname - 包含要獲取其值的節點的名稱。
示例
以下是一個簡單的程式,它說明了 getElementByTagName 方法的用法。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div>
<b>FirstName:</b> <span id = "FirstName"></span><br>
<b>LastName:</b> <span id = "LastName"></span><br>
<b>Category:</b> <span id = "Employee"></span><br>
</div>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {// code for IE6, IE5
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
document.getElementById("FirstName").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("LastName").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("LastName")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("Employee").innerHTML =
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0].attributes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的例子中,我們正在訪問 FirstName、LastName 和 Employee 節點的資訊。
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue; 此行使用 getElementByTagName() 方法訪問子節點 FirstName 的值。
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0].attributes[0].nodeValue; 此行使用 getElementByTagName() 方法訪問節點 Employee 的屬性值。
遍歷節點
這在章節DOM 遍歷中用例子進行了講解。
導航節點
這在章節DOM 導航中用例子進行了講解。
XML DOM - 獲取節點
在本章中,我們將學習如何獲取 XML DOM 物件的節點值。XML 文件具有稱為節點的資訊單元的層次結構。節點物件有一個屬性 nodeValue,它返回元素的值。
在接下來的章節中,我們將討論:
獲取元素的節點值
獲取節點的屬性值
以下所有示例中使用的 node.xml 如下:
<Company>
<Employee category = "Technical">
<FirstName>Tanmay</FirstName>
<LastName>Patil</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>
<Email>tanmaypatil@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Non-Technical">
<FirstName>Taniya</FirstName>
<LastName>Mishra</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234667898</ContactNo>
<Email>taniyamishra@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Management">
<FirstName>Tanisha</FirstName>
<LastName>Sharma</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234562350</ContactNo>
<Email>tanishasharma@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
</Company>
獲取節點值
getElementsByTagName() 方法返回文件中所有具有給定標籤名稱的 Elements 的 NodeList,按文件順序排列。
示例
下面的例子 (getnode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析成 XML DOM 物件,並提取子節點 Firstname(索引為 0)的節點值:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else{
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('FirstName')[0]
y = x.childNodes[0];
document.write(y.nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案儲存為 getnode_example.htm 到伺服器路徑(此檔案和 node.xml 應該在伺服器的同一路徑下)。在輸出中,我們得到節點值 Tanmay。
獲取屬性值
屬性是 XML 節點元素的一部分。一個節點元素可以有多個唯一的屬性。屬性提供了關於 XML 節點元素的更多資訊。更準確地說,它們定義了節點元素的屬性。XML 屬性始終是名稱-值對。屬性的值稱為屬性節點。
getAttribute() 方法透過元素名稱檢索屬性值。
示例
下面的示例 (get_attribute_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並提取類別Employee(索引為 2)的屬性值:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/dom/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('Employee')[2];
document.write(x.getAttribute('category'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的get_attribute_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。在輸出中,我們得到屬性值為Management。
XML DOM - 設定節點
在本章中,我們將學習如何在 XML DOM 物件中更改節點的值。節點值可以按如下方式更改:
var value = node.nodeValue;
如果node是Attribute,則value變數將是屬性的值;如果node是Text節點,它將是文字內容;如果node是Element,它將為null。
以下部分將演示每種節點型別(屬性、文字節點和元素)的節點值設定。
以下所有示例中使用的 node.xml 如下:
<Company>
<Employee category = "Technical">
<FirstName>Tanmay</FirstName>
<LastName>Patil</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>
<Email>tanmaypatil@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Non-Technical">
<FirstName>Taniya</FirstName>
<LastName>Mishra</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234667898</ContactNo>
<Email>taniyamishra@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Management">
<FirstName>Tanisha</FirstName>
<LastName>Sharma</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234562350</ContactNo>
<Email>tanishasharma@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
</Company>
更改文字節點的值
當我們說更改節點元素的值時,我們的意思是編輯元素的文字內容(也稱為文字節點)。下面的示例演示如何更改元素的文字節點。
示例
下面的示例 (set_text_node_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並更改元素文字節點的值。在本例中,將每個Employee的Email更改為support@xyz.com並列印值。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Email");
for(i = 0;i<x.length;i++) {
x[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue = "support@xyz.com";
document.write(i+');
document.write(x[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue);
document.write('<br>');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的set_text_node_example.htm(此檔案和node.xml應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。您將收到以下輸出:
0) support@xyz.com 1) support@xyz.com 2) support@xyz.com
更改屬性節點的值
下面的示例演示如何更改元素的屬性節點。
示例
下面的示例 (set_attribute_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並更改元素屬性節點的值。在本例中,將每個Employee的Category分別更改為admin-0, admin-1, admin-2並列印值。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee");
for(i = 0 ;i<x.length;i++){
newcategory = x[i].getAttributeNode('category');
newcategory.nodeValue = "admin-"+i;
document.write(i+');
document.write(x[i].getAttributeNode('category').nodeValue);
document.write('<br>');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的set_node_attribute_example.htm(此檔案和node.xml應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。結果如下:
0) admin-0 1) admin-1 2) admin-2
XML DOM - 建立節點
在本章中,我們將討論如何使用文件物件的幾種方法建立新節點。這些方法提供了一個範圍來建立新的元素節點、文字節點、註釋節點、CDATA 節點和屬性節點。如果新建立的節點已存在於元素物件中,則它將被新的節點替換。以下部分將透過示例演示這一點。
建立新的Element節點
createElement()方法建立一個新的元素節點。如果新建立的元素節點已存在於元素物件中,則它將被新的節點替換。
語法
使用createElement()方法的語法如下:
var_name = xmldoc.createElement("tagname");
其中,
var_name - 是儲存新元素名稱的使用者定義變數名。
("tagname") - 是要建立的新元素節點的名稱。
示例
下面的示例 (createnewelement_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並在 XML 文件中建立一個新的元素節點PhoneNo。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
new_element = xmlDoc.createElement("PhoneNo");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0];
x.appendChild(new_element);
document.write(x.getElementsByTagName("PhoneNo")[0].nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>
new_element = xmlDoc.createElement("PhoneNo"); 建立新的元素節點<PhoneNo>
x.appendChild(new_element); x儲存指定子節點<FirstName>的名稱,新元素節點將附加到該子節點。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的createnewelement_example.htm(此檔案和node.xml應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。在輸出中,我們得到屬性值為PhoneNo。
建立新的Text節點
createTextNode()方法建立一個新的文字節點。
語法
使用createTextNode()的語法如下:
var_name = xmldoc.createTextNode("tagname");
其中,
var_name - 是儲存新文字節點名稱的使用者定義變數名。
("tagname") - 括號內是要建立的新文字節點的名稱。
示例
下面的示例 (createtextnode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並在 XML 文件中建立一個新的文字節點Im new text node。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
create_e = xmlDoc.createElement("PhoneNo");
create_t = xmlDoc.createTextNode("Im new text node");
create_e.appendChild(create_t);
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0];
x.appendChild(create_e);
document.write(" PhoneNO: ");
document.write(x.getElementsByTagName("PhoneNo")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>
上面程式碼的詳細資訊如下:
create_e = xmlDoc.createElement("PhoneNo"); 建立一個新的元素<PhoneNo>。
create_t = xmlDoc.createTextNode("Im new text node"); 建立一個新的文字節點"Im new text node"。
x.appendChild(create_e); 文字節點"Im new text node"附加到元素<PhoneNo>。
document.write(x.getElementsByTagName("PhoneNo")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue); 將新文字節點的值寫入元素<PhoneNo>。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的createtextnode_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。在輸出中,我們得到屬性值,即PhoneNO: Im new text node。
建立新的Comment節點
createComment()方法建立一個新的註釋節點。註釋節點包含在程式中是為了方便理解程式碼功能。
語法
使用createComment()的語法如下:
var_name = xmldoc.createComment("tagname");
其中,
var_name - 是儲存新註釋節點名稱的使用者定義變數名。
("tagname") - 是要建立的新註釋節點的名稱。
示例
下面的示例 (createcommentnode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並在 XML 文件中建立一個新的註釋節點"Company is the parent node"。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
create_comment = xmlDoc.createComment("Company is the parent node");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Company")[0];
x.appendChild(create_comment);
document.write(x.lastChild.nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
create_comment = xmlDoc.createComment("Company is the parent node") **建立指定的註釋行**。
x.appendChild(create_comment) 在這一行中,'x'儲存元素<Company>的名稱,註釋行將附加到該元素。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的createcommentnode_example.htm(此檔案和node.xml應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。在輸出中,我們得到屬性值為Company is the parent node。
建立新的CDATA Section節點
createCDATASection()方法建立一個新的 CDATA 節點。如果新建立的 CDATA 節點已存在於元素物件中,則它將被新的節點替換。
語法
使用createCDATASection()的語法如下:
var_name = xmldoc.createCDATASection("tagname");
其中,
var_name - 是儲存新 CDATA 節點名稱的使用者定義變數名。
("tagname") - 是要建立的新 CDATA 節點的名稱。
示例
下面的示例 (createcdatanode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並在 XML 文件中建立一個新的 CDATA 節點"Create CDATA Example"。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
create_CDATA = xmlDoc.createCDATASection("Create CDATA Example");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0];
x.appendChild(create_CDATA);
document.write(x.lastChild.nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
create_CDATA = xmlDoc.createCDATASection("Create CDATA Example") 建立一個新的 CDATA 節點"Create CDATA Example"
x.appendChild(create_CDATA) 在這裡,x儲存索引為 0 的指定元素<Employee>,CDATA 節點值將附加到該元素。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的createcdatanode_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。在輸出中,我們得到屬性值為Create CDATA Example。
建立新的Attribute節點
要建立新的屬性節點,可以使用setAttributeNode()方法。如果新建立的屬性節點已存在於元素物件中,則它將被新的節點替換。
語法
使用createElement()方法的語法如下:
var_name = xmldoc.createAttribute("tagname");
其中,
var_name - 是儲存新屬性節點名稱的使用者定義變數名。
("tagname") - 是要建立的新屬性節點的名稱。
示例
下面的示例 (createattributenode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並在 XML 文件中建立一個新的屬性節點section。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
create_a = xmlDoc.createAttribute("section");
create_a.nodeValue = "A";
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee");
x[0].setAttributeNode(create_a);
document.write("New Attribute: ");
document.write(x[0].getAttribute("section"));
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
create_a=xmlDoc.createAttribute("Category") 建立一個名為<section>的屬性。
create_a.nodeValue="Management" 為屬性<section>建立值"A"。
x[0].setAttributeNode(create_a) 此屬性值被設定為索引為 0 的節點元素<Employee>。
XML DOM - 新增節點
在本章中,我們將討論將節點新增到現有元素。它提供了一種方法來:
在現有子節點之前或之後附加新的子節點
在文字節點內插入資料
新增屬性節點
可以使用以下方法將節點新增到/附加到 DOM 中的元素:
- appendChild()
- insertBefore()
- insertData()
appendChild()
appendChild()方法在現有子節點之後新增新的子節點。
語法
appendChild()方法的語法如下:
Node appendChild(Node newChild) throws DOMException
其中,
newChild - 要新增的節點
此方法返回新增的Node。
示例
下面的示例 (appendchildnode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並將新的子節點PhoneNo附加到元素<FirstName>。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
create_e = xmlDoc.createElement("PhoneNo");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0];
x.appendChild(create_e);
document.write(x.getElementsByTagName("PhoneNo")[0].nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
使用 createElement() 方法建立一個新的元素PhoneNo。
使用 appendChild() 方法將新的元素PhoneNo新增到元素FirstName。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的appendchildnode_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。在輸出中,我們得到屬性值為PhoneNo。
insertBefore()
insertBefore()方法在指定的子節點之前插入新的子節點。
語法
insertBefore()方法的語法如下:
Node insertBefore(Node newChild, Node refChild) throws DOMException
其中,
newChild - 要插入的節點
refChild - 參考節點,即必須在該節點之前插入新節點的節點。
此方法返回正在插入的Node。
示例
下面的示例 (insertnodebefore_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並在指定的元素<Email>之前插入新的子節點Email。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
create_e = xmlDoc.createElement("Email");
x = xmlDoc.documentElement;
y = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Email");
document.write("No of Email elements before inserting was: " + y.length);
document.write("<br>");
x.insertBefore(create_e,y[3]);
y=xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Email");
document.write("No of Email elements after inserting is: " + y.length);
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
使用 createElement() 方法建立一個新的元素Email。
使用 insertBefore() 方法在元素Email之前新增新的元素Email。
y.length給出在新的元素之前和之後新增的元素的總數。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的insertnodebefore_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。我們將收到以下輸出:
No of Email elements before inserting was: 3 No of Email elements after inserting is: 4
insertData()
insertData() 方法在指定的 16 位單元偏移量處插入字串。
語法
insertData() 方法具有以下語法:
void insertData(int offset, java.lang.String arg) throws DOMException
其中,
offset − 要插入字元的偏移量。
arg − 要插入資料的關鍵字。它用括號括起 offset 和 string 兩個引數,並用逗號分隔。
示例
下面的示例 (addtext_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 ("node.xml") 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並在指定位置將新資料 MiddleName 插入到 <FirstName> 元素中。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0].childNodes[0];
document.write(x.nodeValue);
x.insertData(6,"MiddleName");
document.write("<br>");
document.write(x.nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>
x.insertData(6,"MiddleName"); − 這裡,x 儲存指定子節點名稱,即 <FirstName>。然後,我們從位置 6 開始,將資料 "MiddleName" 插入到此文字節點中。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的 addtext_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。輸出結果如下:
Tanmay TanmayMiddleName
XML DOM - 替換節點
本章將學習 XML DOM 物件中的替換節點操作。眾所周知,DOM 中的所有內容都維護在一個稱為節點的分層資訊單元中,替換節點提供了另一種更新這些指定節點或文字節點的方法。
以下是替換節點的兩種方法:
- replaceChild()
- replaceData()
replaceChild()
replaceChild() 方法用新節點替換指定的節點。
語法
insertData() 方法具有以下語法:
Node replaceChild(Node newChild, Node oldChild) throws DOMException
其中,
newChild − 要新增到子列表中的新節點。
oldChild − 要替換的節點。
此方法返回被替換的節點。
示例
下面的示例 (replacenode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並將指定的節點 <FirstName> 替換為新節點 <Name>。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
x = xmlDoc.documentElement;
z = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName");
document.write("<b>Content of FirstName element before replace operation</b><br>");
for (i=0;i<z.length;i++) {
document.write(z[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue);
document.write("<br>");
}
//create a Employee element, FirstName element and a text node
newNode = xmlDoc.createElement("Employee");
newTitle = xmlDoc.createElement("Name");
newText = xmlDoc.createTextNode("MS Dhoni");
//add the text node to the title node,
newTitle.appendChild(newText);
//add the title node to the book node
newNode.appendChild(newTitle);
y = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0]
//replace the first book node with the new node
x.replaceChild(newNode,y);
z = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName");
document.write("<b>Content of FirstName element after replace operation</b><br>");
for (i = 0;i<z.length;i++) {
document.write(z[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue);
document.write("<br>");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的 replacenode_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。輸出結果如下:
Content of FirstName element before replace operation Tanmay Taniya Tanisha Content of FirstName element after replace operation Taniya Tanisha
replaceData()
replaceData() 方法用指定的字串替換從指定的 16 位單元偏移量開始的字元。
語法
replaceData() 方法具有以下語法:
void replaceData(int offset, int count, java.lang.String arg) throws DOMException
其中
offset − 開始替換的偏移量。
count − 要替換的 16 位單元數。如果 offset 和 count 的總和超過長度,則替換資料末尾的所有 16 位單元。
arg − 必須替換範圍的 DOMString。
示例
下面的示例 (replacedata_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件並進行替換。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ContactNo")[0].childNodes[0];
document.write("<b>ContactNo before replace operation:</b> "+x.nodeValue);
x.replaceData(1,5,"9999999");
document.write("<br>");
document.write("<b>ContactNo after replace operation:</b> "+x.nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
x.replaceData(2,3,"999"); − 這裡 x 儲存指定元素 <ContactNo> 的文字,其文字將被新文字 "9999999" 替換,從位置 1 開始到長度為 5 的位置。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的 replacedata_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。輸出結果如下:
ContactNo before replace operation: 1234567890 ContactNo after replace operation: 199999997890
XML DOM - 刪除節點
本章將學習 XML DOM 的 刪除節點 操作。刪除節點操作將從文件中刪除指定的節點。此操作可用於刪除文字節點、元素節點或屬性節點。
以下是用於刪除節點操作的方法:
removeChild()
removeAttribute()
removeChild()
removeChild() 方法從子節點列表中刪除由 oldChild 指定的子節點,並將其返回。刪除子節點等同於刪除與其關聯的文字節點。因此,刪除子節點會刪除與其關聯的文字節點。
語法
使用 removeChild() 的語法如下:
Node removeChild(Node oldChild) throws DOMException
其中,
oldChild − 要刪除的節點。
此方法返回被刪除的節點。
示例 - 刪除當前節點
下面的示例 (removecurrentnode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並從父節點中刪除指定的節點 <ContactNo>。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
document.write("<b>Before remove operation, total ContactNo elements: </b>");
document.write(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ContactNo").length);
document.write("<br>");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ContactNo")[0];
x.parentNode.removeChild(x);
document.write("<b>After remove operation, total ContactNo elements: </b>");
document.write(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ContactNo").length);
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ContactNo")[0] 獲取索引為 0 的 <ContactNo> 元素。
x.parentNode.removeChild(x); 從父節點中刪除索引為 0 的 <ContactNo> 元素。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的 removecurrentnode_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。結果如下:
Before remove operation, total ContactNo elements: 3 After remove operation, total ContactNo elements: 2
示例 - 刪除文字節點
下面的示例 (removetextNode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並刪除指定的子節點 <FirstName>。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0];
document.write("<b>Text node of child node before removal is:</b> ");
document.write(x.childNodes.length);
document.write("<br>");
y = x.childNodes[0];
x.removeChild(y);
document.write("<b>Text node of child node after removal is:</b> ");
document.write(x.childNodes.length);
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0]; − 將索引為 0 的第一個 <FirstName> 元素獲取到 x 中。
y = x.childNodes[0]; − 在此行中,y 儲存要刪除的子節點。
x.removeChild(y); − 刪除指定的子節點。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的 removetextNode_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。結果如下:
Text node of child node before removal is: 1 Text node of child node after removal is: 0
removeAttribute()
removeAttribute() 方法按名稱刪除元素的屬性。
語法
使用 removeAttribute() 的語法如下:
void removeAttribute(java.lang.String name) throws DOMException
其中,
name − 要刪除的屬性的名稱。
示例
下面的示例 (removeelementattribute_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並刪除指定的屬性節點。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('Employee');
document.write(x[1].getAttribute('category'));
document.write("<br>");
x[1].removeAttribute('category');
document.write(x[1].getAttribute('category'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
在上面的示例中:
document.write(x[1].getAttribute('category')); − 呼叫索引為 1 的屬性 category 的值。
x[1].removeAttribute('category'); − 刪除屬性值。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的 removeelementattribute_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。結果如下:
Non-Technical null
XML DOM - 克隆節點
本章將討論 XML DOM 物件上的 克隆節點 操作。克隆節點操作用於建立指定節點的副本。cloneNode() 用於此操作。
cloneNode()
此方法返回此節點的副本,即充當節點的通用複製建構函式。副本節點沒有父節點 (parentNode 為 null) 也沒有使用者資料。
語法
cloneNode() 方法具有以下語法:
Node cloneNode(boolean deep)
deep − 如果為 true,則遞迴克隆指定節點下的子樹;如果為 false,則僅克隆節點本身(及其屬性,如果它是元素)。
此方法返回副本節點。
示例
下面的示例 (clonenode_example.htm) 將 XML 文件 (node.xml) 解析為 XML DOM 物件,並建立第一個 Employee 元素的深層副本。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/node.xml");
x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName('Employee')[0];
clone_node = x.cloneNode(true);
xmlDoc.documentElement.appendChild(clone_node);
firstname = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName");
lastname = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("LastName");
contact = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ContactNo");
email = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Email");
for (i = 0;i < firstname.length;i++) {
document.write(firstname[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue+'
'+lastname[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue+',
'+contact[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue+', '+email[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue);
document.write("<br>");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
正如你在上面的示例中看到的,我們已將 cloneNode() 引數設定為 true。因此,Employee 元素下的每個子元素都被複制或克隆。
執行
將此檔案儲存為伺服器路徑上的 clonenode_example.htm(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。輸出結果如下:
Tanmay Patil, 1234567890, tanmaypatil@xyz.com Taniya Mishra, 1234667898, taniyamishra@xyz.com Tanisha Sharma, 1234562350, tanishasharma@xyz.com Tanmay Patil, 1234567890, tanmaypatil@xyz.com
你會注意到,第一個 Employee 元素被完整克隆。
DOM - 節點物件
Node 介面是整個文件物件模型的主要資料型別。節點用於表示整個文件樹中的單個 XML 元素。
節點可以是任何型別的節點,例如屬性節點、文字節點或任何其他節點。屬性 nodeName、nodeValue 和 attributes 作為一種機制包含在內,用於在不向下轉換為特定派生介面的情況下獲取節點資訊。
屬性
下表列出了 Node 物件的屬性:
| Attribute | 型別 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| attributes | NamedNodeMap | 這是 NamedNodeMap 型別,包含此節點的屬性(如果它是元素),否則為 null。此屬性已被移除。請參考 規範 |
| baseURI | DOMString | 用於指定節點的絕對基本 URI。 |
| childNodes | NodeList | 這是一個 NodeList,包含此節點的所有子節點。如果沒有子節點,則這是一個不包含任何節點的 NodeList。 |
| firstChild | Node | 指定節點的第一個子節點。 |
| lastChild | Node | 指定節點的最後一個子節點。 |
| localName | DOMString | 用於指定節點區域性名稱。此屬性已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| namespaceURI | DOMString | 指定節點的名稱空間 URI。此屬性已被移除。請參考 規範 |
| nextSibling | Node | 返回緊跟在此節點後的節點。如果沒有這樣的節點,則返回 null。 |
| nodeName | DOMString | 此節點的名稱,取決於其型別。 |
| nodeType | 無符號短整型 | 表示底層物件型別的程式碼。 |
| nodeValue | DOMString | 用於指定節點的值,取決於其型別。 |
| ownerDocument | Document | 指定與節點關聯的 Document 物件。 |
| parentNode | Node | 此屬性指定節點的父節點。 |
| prefix | DOMString | 此屬性返回節點的名稱空間字首。此屬性已被移除。請參考 規範 |
| previousSibling | Node | 指定緊在此節點之前的節點。 |
| textContent | DOMString | 指定節點的文字內容。 |
節點型別
我們已列出節點型別如下:
- ELEMENT_NODE
- ATTRIBUTE_NODE
- ENTITY_NODE
- ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE
- DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE
- TEXT_NODE
- CDATA_SECTION_NODE
- COMMENT_NODE
- PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE
- DOCUMENT_NODE
- DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE
- NOTATION_NODE
方法
下表列出了不同的 Node 物件方法:
| 序號 | 方法和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | appendChild(Node newChild) 此方法在指定元素節點的最後一個子節點之後新增一個節點。它返回新增的節點。 |
| 2 | cloneNode(boolean deep) 此方法用於在派生類中被重寫時建立重複節點。它返回重複的節點。 |
| 3 | compareDocumentPosition(Node other) 此方法用於根據文件順序比較當前節點相對於指定節點的位置。返回 無符號短整型,說明節點相對於參考節點的位置。 |
| 4 | getFeature(DOMString feature, DOMString version) 返回實現指定功能和版本的專用 API 的 DOM 物件(如果有),如果沒有物件則返回 null。此屬性已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| 5 | getUserData(DOMString key) 檢索此節點上與某個鍵關聯的物件。必須首先透過呼叫 setUserData 和相同的鍵將物件設定為此節點。返回與此節點上給定鍵關聯的 DOMUserData,如果不存在則返回 null。此方法已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| 6 | hasAttributes() 返回此節點(如果它是元素)是否具有任何屬性。如果指定節點中存在任何屬性,則返回 true;否則返回 false。此方法已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| 7 | hasChildNodes() 返回此節點是否具有任何子節點。如果當前節點具有子節點,則此方法返回 true,否則返回 false。 |
| 8 | insertBefore(Node newChild, Node refChild) 此方法用於將新節點作為此節點的子節點插入,直接位於此節點的現有子節點之前。它返回正在插入的節點。 |
| 9 | isDefaultNamespace(DOMString namespaceURI) 此方法接受名稱空間 URI 作為引數,如果名稱空間是給定節點上的預設名稱空間,則返回值為 true 的 布林值;否則返回 false。 |
| 10 | isEqualNode(Node arg) 此方法測試兩個節點是否相等。如果節點相等,則返回 true;否則返回 false。 |
| 11 | isSameNode(Node other) 此方法返回當前節點是否與給定節點相同。如果節點相同,則返回 true;否則返回 false。此方法已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| 12 | isSupported(DOMString feature, DOMString version) 此方法返回當前節點是否支援指定的 DOM 模組。如果此節點上支援指定的特性,則返回 true;否則返回 false。此方法已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| 13 | lookupNamespaceURI(DOMString prefix) 此方法獲取與名稱空間字首關聯的名稱空間的 URI。 |
| 14 | lookupPrefix(DOMString namespaceURI) 此方法返回當前名稱空間中為名稱空間 URI 定義的最接近的字首。如果找到關聯的名稱空間字首,則返回該字首;否則返回 null。 |
| 15 | normalize()
規範化新增所有文字節點,包括定義規範形式的屬性節點,其中包含元素、註釋、處理指令、CDATA 節和實體引用的節點結構將文字節點分開,即沒有相鄰的文字節點或空文字節點。 |
| 16 | removeChild(Node oldChild) 此方法用於從當前節點中移除指定的子節點。它返回被移除的節點。 |
| 17 | replaceChild(Node newChild, Node oldChild) 此方法用於將舊子節點替換為新節點。它返回被替換的節點。 |
| 18 | setUserData(DOMString key, DOMUserData data, UserDataHandler handler) 此方法將物件與此節點上的鍵關聯。稍後可以透過呼叫 getUserData 和相同的鍵從此節點檢索該物件。它返回先前與此節點上給定鍵關聯的 DOMUserData。此方法已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
DOM - 節點列表物件
NodeList 物件指定有序節點集合的抽象。NodeList 中的專案可以透過整數索引訪問,從 0 開始。
屬性
下表列出了 NodeList 物件的屬性:
| Attribute | 型別 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| length | 無符號長整數 | 它給出節點列表中節點的數量。 |
方法
以下是 NodeList 物件的唯一方法:
| 序號 | 方法和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
item()
它返回集合中的第 index 個專案。如果 index 大於或等於列表中節點的數量,則返回 null。 |
DOM - 命名節點對映物件
NamedNodeMap 物件用於表示可以透過名稱訪問的節點集合。
屬性
下表列出了 NamedNodeMap 物件的屬性:
| Attribute | 型別 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| length | 無符號長整數 | 它給出此對映中節點的數量。有效的子節點索引範圍是 0 到 length-1(包含)。 |
方法
下表列出了 NamedNodeMap 物件的方法:
| 序號 | 方法和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | getNamedItem () 檢索按名稱指定的節點。 |
| 2 | getNamedItemNS () 檢索按區域性名稱和名稱空間 URI 指定的節點。 |
| 3 | item () 返回對映中的第 index 個專案。如果 index 大於或等於此對映中節點的數量,則返回 null。 |
| 4 | removeNamedItem () 移除按名稱指定的節點。 |
| 5 | removeNamedItemNS () 移除按區域性名稱和名稱空間 URI 指定的節點。 |
| 6 | setNamedItem () 使用其 nodeName 屬性新增節點。如果此對映中已存在具有該名稱的節點,則將其替換為新的節點。 |
| 7 | setNamedItemNS () 使用其 namespaceURI 和 localName 新增節點。如果此對映中已存在具有該名稱空間 URI 和該區域性名稱的節點,則將其替換為新的節點。用自身替換節點無效。 |
DOM - DOMImplementation 物件
DOMImplementation 物件提供許多方法來執行獨立於文件物件模型任何特定例項的操作。
方法
下表列出了 DOMImplementation 物件的方法:
| 序號 | 方法和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | createDocument(namespaceURI, qualifiedName, doctype) 它建立指定型別的 DOM 文件物件及其文件元素。 |
| 2 | createDocumentType(qualifiedName, publicId, systemId) 它建立一個空的 DocumentType 節點。 |
| 3 | getFeature(feature, version) 此方法返回一個專門的物件,該物件實現指定特性和版本的專門 API。此方法已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| 4 | hasFeature(feature, version)
此方法測試 DOM 實現是否實現特定特性和版本。 |
DOM - DocumentType 物件
DocumentType 物件是訪問文件資料的關鍵,在文件中,doctype 屬性可以具有 null 值或 DocumentType 物件值。這些 DocumentType 物件充當對 XML 文件中描述的實體的介面。
屬性
下表列出了 DocumentType 物件的屬性:
| Attribute | 型別 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| name | DOMString | 它返回 DTD 的名稱,該名稱緊跟在 !DOCTYPE 關鍵字之後。 |
| entities | NamedNodeMap | 它返回一個 NamedNodeMap 物件,其中包含在 DTD 中宣告的外部和內部通用實體。 |
| notations | NamedNodeMap | 它返回一個包含在 DTD 中宣告的符號的 NamedNodeMap。 |
| internalSubset | DOMString | 它將內部子集作為字串返回,如果沒有則返回 null。此屬性已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| publicId | DOMString | 它返回外部子集的公共識別符號。 |
| systemId | DOMString | 它返回外部子集的系統識別符號。這可以是絕對 URI,也可以不是。 |
方法
DocumentType 繼承自其父節點 Node 的方法,並實現 ChildNode 介面。
DOM - ProcessingInstruction 物件
ProcessingInstruction 提供應用程式特定的資訊,這些資訊通常包含在 XML 文件的序言部分。
處理指令 (PI) 可用於將資訊傳遞給應用程式。PI 可以出現在文件中標記之外的任何位置。它們可以出現在序言中,包括文件型別定義 (DTD),在文字內容中,或文件之後。
PI 以特殊的標記 <? 開始,以 ?> 結束。在遇到字串 ?> 後,內容的處理立即結束。
屬性
下表列出了 ProcessingInstruction 物件的屬性:
DOM - 實體物件
Entity 介面表示 XML 文件中已知的實體,無論是已解析的還是未解析的。從 Node 繼承的 nodeName 屬性包含實體的名稱。
Entity 物件沒有任何父節點,並且其所有後繼節點都是隻讀的。
屬性
下表列出了 Entity 物件的屬性:
| Attribute | 型別 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| inputEncoding | DOMString | 這指定外部已解析實體使用的編碼。如果它是內部子集中的實體,或者未知,則其值為 null。 |
| notationName | DOMString | 對於未解析的實體,它給出符號的名稱,對於已解析的實體,其值為 null。 |
| publicId | DOMString | 它給出與實體關聯的公共識別符號的名稱。 |
| systemId | DOMString | 它給出與實體關聯的系統識別符號的名稱。 |
| xmlEncoding | DOMString | 它給出作為外部已解析實體文字宣告一部分包含的 xml 編碼,否則為 null。 |
| xmlVersion | DOMString | 它給出作為外部已解析實體文字宣告一部分包含的 xml 版本,否則為 null。 |
DOM - Entity Reference 物件
EntityReference 物件是插入到 XML 文件中的一般實體引用,提供替換文字的範圍。EntityReference 物件不適用於預定義實體,因為它們被認為是由 HTML 或 XML 處理器擴充套件的。
此介面本身沒有任何屬性或方法,但繼承自 Node。
DOM - 符號物件
在本章中,我們將學習 XML DOM 的 Notation 物件。notation 物件屬性提供了一個範圍來識別具有 notation 屬性的元素、特定的處理指令或非 XML 資料的格式。Node 物件的屬性和方法可以在 Notation 物件上執行,因為它也被視為一個 Node。
此物件繼承自 Node 的方法和屬性。其 nodeName 是符號名稱。沒有父節點。
屬性
下表列出了 Notation 物件的屬性:
DOM - 元素物件
XML 元素可以定義為 XML 的構建塊。元素可以充當容器,用於儲存文字、元素、屬性、媒體物件或所有這些。每當解析器根據良構性解析 XML 文件時,解析器都會遍歷元素節點。元素節點包含其中的文字,稱為文字節點。
元素物件繼承節點物件的屬性和方法,因為元素物件也被視為節點。除了節點物件的屬性和方法外,它還具有以下屬性和方法。
屬性
下表列出了Element 物件的屬性:
| Attribute | 型別 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| tagName | DOMString | 它給出指定元素的標籤名稱。 |
| schemaTypeInfo | TypeInfo | 它表示與此元素關聯的型別資訊。此項已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
方法
下表列出了 Element 物件的方法:
| 方法 | 型別 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| getAttribute() | DOMString | 如果指定元素存在屬性,則檢索該屬性的值。 |
| getAttributeNS() | DOMString | 透過區域性名稱和名稱空間 URI 檢索屬性值。 |
| getAttributeNode() | Attr | 從當前元素檢索屬性節點的名稱。 |
| getAttributeNodeNS() | Attr | 透過區域性名稱和名稱空間 URI 檢索 Attr 節點。 |
| getElementsByTagName() | NodeList | 返回所有具有給定標籤名稱的子代元素的 NodeList,按文件順序排列。 |
| getElementsByTagNameNS() | NodeList | 返回所有具有給定區域性名稱和名稱空間 URI 的子代元素的 NodeList,按文件順序排列。 |
| hasAttribute() | 布林值 | 當在此元素上指定了具有給定名稱的屬性或具有預設值時返回 true,否則返回 false。 |
| hasAttributeNS() | 布林值 | 當在此元素上指定了具有給定區域性名稱和名稱空間 URI 的屬性或具有預設值時返回 true,否則返回 false。 |
| removeAttribute() | 無返回值 | 按名稱移除屬性。 |
| removeAttributeNS | 無返回值 | 按區域性名稱和名稱空間 URI 移除屬性。 |
| removeAttributeNode() | Attr | 從元素中移除指定的屬性節點。 |
| setAttribute() | 無返回值 | 將新的屬性值設定為現有元素。 |
| setAttributeNS() | 無返回值 | 新增新的屬性。如果元素上已經存在具有相同區域性名稱和名稱空間 URI 的屬性,則其字首將更改為 qualifiedName 的字首部分,其值將更改為 value 引數。 |
| setAttributeNode() | Attr | 將新的屬性節點設定為現有元素。 |
| setAttributeNodeNS | Attr | 新增新的屬性。如果元素中已經存在具有該區域性名稱和該名稱空間 URI 的屬性,則將其替換為新的屬性。 |
| setIdAttribute | 無返回值 | 如果引數 isId 為 true,則此方法宣告指定的屬性為使用者確定的 ID 屬性。此項已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
| setIdAttributeNS | 無返回值 | 如果引數 isId 為 true,則此方法宣告指定的屬性為使用者確定的 ID 屬性。此項已被移除。請參考 規範。 |
DOM - 屬性物件
Attr 介面表示 Element 物件中的屬性。通常,屬性的允許值在與文件關聯的模式中定義。Attr 物件不被視為文件樹的一部分,因為它們實際上並不是其描述的元素的子節點。因此,對於子節點parentNode、previousSibling 和nextSibling,屬性值為null。
屬性
下表列出了Attribute 物件的屬性:
| Attribute | 型別 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| name | DOMString | 它給出屬性的名稱。 |
| specified | 布林值 | 這是一個布林值,如果屬性值存在於文件中,則返回 true。 |
| value | DOMString | 返回屬性的值。 |
| ownerElement | Element | 它給出與屬性關聯的節點,如果屬性未被使用則為 null。 |
| isId | 布林值 | 它返回屬性是否已知為 ID 型別(即包含其所有者元素的識別符號)。 |
DOM - CDATASection 物件
在本章中,我們將學習 XML DOM CDATASection 物件。XML 文件中存在的文字根據其宣告方式進行解析或未解析。如果文字宣告為解析字元資料 (PCDATA),則解析器會對其進行解析,以將 XML 文件轉換為 XML DOM 物件。另一方面,如果文字宣告為未解析字元資料 (CDATA),則 XML 解析器不會解析其中的文字。這些不被視為標記,也不會擴充套件實體。
使用 CDATASection 物件的目的是轉義包含字元的文字塊,否則這些字元將被視為標記。"]]>",這是 CDATA 部分中唯一識別的分隔符,它結束 CDATA 部分。
CharacterData.data 屬性儲存 CDATA 部分包含的文字。此介面透過 Text 介面繼承CharatcterData 介面。
CDATASection 物件沒有定義方法和屬性。它只直接實現Text 介面。
DOM - 註釋物件
在本章中,我們將學習Comment 物件。註釋作為筆記或行新增到 XML 程式碼中,以理解其用途。註釋可用於包含相關連結、資訊和術語。這些註釋可能出現在 XML 程式碼的任何位置。
comment 介面繼承CharacterData 介面,表示註釋的內容。
語法
XML 註釋具有以下語法:
<!-------Your comment----->
註釋以 <!-- 開頭,以 --> 結尾。您可以在字元之間新增文字註釋作為註釋。您不能將一個註釋巢狀在另一個註釋內。
Comment 物件沒有定義方法和屬性。它繼承其父級CharacterData 的方法和屬性,並間接繼承Node 的方法和屬性。
DOM - XMLHttpRequest 物件
XMLHttpRequest 物件在網頁的客戶端和伺服器端之間建立了一種媒介,許多指令碼語言(如 JavaScript、JScript、VBScript 和其他 Web 瀏覽器)可以使用它來傳輸和操作 XML 資料。
使用 XMLHttpRequest 物件,可以更新網頁的一部分而無需重新載入整個頁面,在頁面載入後請求和接收來自伺服器的資料,以及向伺服器傳送資料。
語法
可以如下例項化 XMLHttpRequest 物件:
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
為了處理所有瀏覽器,包括 IE5 和 IE6,請檢查瀏覽器是否支援 XMLHttpRequest 物件,如下所示:
if(window.XMLHttpRequest) // for Firefox, IE7+, Opera, Safari, ... {
xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else if(window.ActiveXObject) // for Internet Explorer 5 or 6 {
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
有關使用 XMLHttpRequest 物件載入 XML 檔案的示例,請參見 此處
方法
下表列出了 XMLHttpRequest 物件的方法:
| 序號 | 方法和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | abort() 終止當前發出的請求。 |
| 2 | getAllResponseHeaders() 返回所有響應標頭作為字串,如果尚未收到響應則返回 null。 |
| 3 | getResponseHeader() 返回包含指定標頭文字的字串,如果尚未收到響應或響應中不存在該標頭,則返回 null。 |
| 4 | open(method,url,async,uname,pswd) 它與 Send 方法結合使用,將請求傳送到伺服器。open 方法指定以下引數:
|
| 5 | send(string) 它用於傳送與 Open 方法一起工作的請求。 |
| 6 | setRequestHeader() 標頭包含傳送請求的標籤/值對。 |
屬性
下表列出了 XMLHttpRequest 物件的屬性:
| 序號 | 屬性 & 說明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | onreadystatechange 這是一個基於事件的屬性,在每次狀態更改時都會設定。 |
| 2 | readyState 這描述了 XMLHttpRequest 物件的當前狀態。readyState 屬性有五種可能的狀態:
|
| 3 | responseText 當伺服器的響應是文字檔案時,使用此屬性。 |
| 4 | responseXML 當伺服器的響應是 XML 檔案時,使用此屬性。 |
| 5 | status 將 Http 請求物件的狀體作為數字給出。例如,“404”或“200”。 |
| 6 | statusText 將 Http 請求物件的狀體作為字串給出。例如,“未找到”或“確定”。 |
示例
node.xml 內容如下:
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<Company>
<Employee category = "Technical">
<FirstName>Tanmay</FirstName>
<LastName>Patil</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>
<Email>tanmaypatil@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Non-Technical">
<FirstName>Taniya</FirstName>
<LastName>Mishra</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234667898</ContactNo>
<Email>taniyamishra@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Management">
<FirstName>Tanisha</FirstName>
<LastName>Sharma</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234562350</ContactNo>
<Email>tanishasharma@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
</Company>
檢索資原始檔的特定資訊
以下示例演示如何使用 getResponseHeader() 方法和 readState 屬性檢索資原始檔的特定資訊。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv = "content-type" content = "text/html; charset = iso-8859-2" />
<script>
function loadXMLDoc() {
var xmlHttp = null;
if(window.XMLHttpRequest) // for Firefox, IE7+, Opera, Safari, ... {
xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else if(window.ActiveXObject) // for Internet Explorer 5 or 6 {
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
return xmlHttp;
}
function makerequest(serverPage, myDiv) {
var request = loadXMLDoc();
request.open("GET", serverPage);
request.send(null);
request.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (request.readyState == 4) {
document.getElementById(myDiv).innerHTML = request.getResponseHeader("Content-length");
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button type = "button" onclick="makerequest('/dom/node.xml', 'ID')">Click me to get the specific ResponseHeader</button>
<div id = "ID">Specific header information is returned.</div>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案另存為伺服器路徑上的elementattribute_removeAttributeNS.htm(此檔案和 node_ns.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。我們將得到如下所示的輸出:
Before removing the attributeNS: en After removing the attributeNS: null
檢索資原始檔的標頭資訊
以下示例演示如何使用 getAllResponseHeaders() 方法和 readyState 屬性檢索資原始檔的標頭資訊。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-2" />
<script>
function loadXMLDoc() {
var xmlHttp = null;
if(window.XMLHttpRequest) // for Firefox, IE7+, Opera, Safari, ... {
xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else if(window.ActiveXObject) // for Internet Explorer 5 or 6 {
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
return xmlHttp;
}
function makerequest(serverPage, myDiv) {
var request = loadXMLDoc();
request.open("GET", serverPage);
request.send(null);
request.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (request.readyState == 4) {
document.getElementById(myDiv).innerHTML = request.getAllResponseHeaders();
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button type = "button" onclick = "makerequest('/dom/node.xml', 'ID')">
Click me to load the AllResponseHeaders</button>
<div id = "ID"></div>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案另存為伺服器路徑上的http_allheader.html(此檔案和 node.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。我們將得到如下所示的輸出(取決於瀏覽器):
Date: Sat, 27 Sep 2014 07:48:07 GMT Server: Apache Last-Modified:
Wed, 03 Sep 2014 06:35:30 GMT Etag: "464bf9-2af-50223713b8a60" Accept-Ranges: bytes Vary: Accept-Encoding,User-Agent
Content-Encoding: gzip Content-Length: 256 Content-Type: text/xml
DOM - DOMException 物件
DOMException 表示在使用方法或屬性時發生的異常事件。
屬性
下表列出了 DOMException 物件的屬性
| 序號 | 屬性 & 說明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | name 返回一個 DOMString,其中包含與錯誤常量關聯的字串之一(如下表所示)。 |
錯誤型別
| 序號 | 型別 & 說明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | IndexSizeError 索引不在允許的範圍內。例如,這可以由 Range 物件引發。(舊程式碼值:1 和舊常量名稱:INDEX_SIZE_ERR) |
| 2 | HierarchyRequestError 節點樹層次結構不正確。(舊程式碼值:3 和舊常量名稱:HIERARCHY_REQUEST_ERR) |
| 3 | WrongDocumentError 物件在錯誤的文件中。(舊程式碼值:4 和舊常量名稱:WRONG_DOCUMENT_ERR) |
| 4 | InvalidCharacterError 字串包含無效字元。(舊程式碼值:5 和舊常量名稱:INVALID_CHARACTER_ERR) |
| 5 | NoModificationAllowedError 無法修改物件。(舊程式碼值:7 和舊常量名稱:NO_MODIFICATION_ALLOWED_ERR) |
| 6 | NotFoundError 在此找不到物件。(舊程式碼值:8 和舊常量名稱:NOT_FOUND_ERR) |
| 7 | NotSupportedError 不支援此操作。(舊程式碼值:9 和舊常量名稱:NOT_SUPPORTED_ERR) |
| 8 | InvalidStateError 物件處於無效狀態。(舊程式碼值:11 和舊常量名稱:INVALID_STATE_ERR) |
| 9 | SyntaxError 字串與預期模式不匹配。(舊程式碼值:12 和舊常量名稱:SYNTAX_ERR) |
| 10 | InvalidModificationError 無法以這種方式修改物件。(舊程式碼值:13 和舊常量名稱:INVALID_MODIFICATION_ERR) |
| 11 | 名稱空間錯誤 XML 的名稱空間不允許此操作。(舊程式碼值:14,舊常量名稱:NAMESPACE_ERR) |
| 12 | 無效訪問錯誤 物件不支援此操作或引數。(舊程式碼值:15,舊常量名稱:INVALID_ACCESS_ERR) |
| 13 | 型別不匹配錯誤 物件的型別與預期型別不匹配。(舊程式碼值:17,舊常量名稱:TYPE_MISMATCH_ERR)此值已棄用,現在會引發 JavaScript TypeError 異常,而不是帶有此值的 DOMException。 |
| 14 | 安全錯誤 此操作不安全。(舊程式碼值:18,舊常量名稱:SECURITY_ERR) |
| 15 | 網路錯誤 發生網路錯誤。(舊程式碼值:19,舊常量名稱:NETWORK_ERR) |
| 16 | 中止錯誤 操作已中止。(舊程式碼值:20,舊常量名稱:ABORT_ERR) |
| 17 | URL 不匹配錯誤 給定的 URL 與另一個 URL 不匹配。(舊程式碼值:21,舊常量名稱:URL_MISMATCH_ERR) |
| 18 | 配額超出錯誤 配額已超出。(舊程式碼值:22,舊常量名稱:QUOTA_EXCEEDED_ERR) |
| 19 | 超時錯誤 操作超時。(舊程式碼值:23,舊常量名稱:TIMEOUT_ERR) |
| 20 | 無效節點型別錯誤 此節點不正確,或其祖先節點對於此操作不正確。(舊程式碼值:24,舊常量名稱:INVALID_NODE_TYPE_ERR) |
| 21 | 資料克隆錯誤 無法克隆物件。(舊程式碼值:25,舊常量名稱:DATA_CLONE_ERR) |
| 22 | 編碼錯誤 編碼或解碼操作失敗(無舊程式碼值和常量名稱)。 |
| 23 | 不可讀錯誤 輸入/輸出讀取操作失敗(無舊程式碼值和常量名稱)。 |
示例
以下示例演示了使用格式不正確的 XML 文件如何導致 DOMException。
error.xml 內容如下:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" standalone = "no" ?>
<Company id = "companyid">
<Employee category = "Technical" id = "firstelement" type = "text/html">
<FirstName>Tanmay</first>
<LastName>Patil</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>
<Email>tanmaypatil@xyz.com</Email>
</Employee>
</Company>
以下示例演示了name 屬性的用法:
<html>
<head>
<script>
function loadXMLDoc(filename) {
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else // code for IE5 and IE6 {
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xhttp.open("GET",filename,false);
xhttp.send();
return xhttp.responseXML;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
try {
xmlDoc = loadXMLDoc("/dom/error.xml");
var node = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("to").item(0);
var refnode = node.nextSibling;
var newnode = xmlDoc.createTextNode('That is why you fail.');
node.insertBefore(newnode, refnode);
} catch(err) {
document.write(err.name);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
執行
將此檔案另存為伺服器路徑上的domexcption_name.html(此檔案和 error.xml 應位於伺服器上的同一路徑)。我們將獲得如下所示的輸出:
TypeError