辛普森 1/3 規則用於定積分
辛普森 1/3 規則與梯形規則相似,也用於求解 a 到 b 區間上的積分值。梯形規則和辛普森 1/3 規則的主要區別在於,梯形規則中將整個部分劃分為一些梯形,而此方法中每個梯形又分為兩部分。
對於此規則,我們將採用以下公式
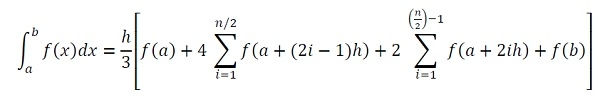
其中 h是間隔寬度,n 是間隔數量。我們可以使用
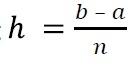
輸入和輸出
Input: The function f(x): (x+(1/x). The lower and upper limit: 1, 2. The number of intervals: 20. Output: The answer is: 2.19315
演算法
integrateSimpson(a, b, n)
輸入 − 積分的下限和上限以及間隔數量 n。
輸出 − 積分後的結果。
Begin h := (b - a)/n res := f(a) + f(b) lim := n/2 for i := 1 to lim, do oddSum := oddSum + f(a + (2i - 1)h) done oddSum := oddSum * 4 for i := 1 to lim-1, do evenSum := evenSum + f(a + 2ih) done evenSum := evenSum * 2 res := res + oddSum + evenSum res := res * (h/3) return res End
示例
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
float mathFunc(float x) {
return (x+(1/x)); //function 1 + 1/x
}
float integrate(float a, float b, int n) {
float h, res = 0.0, oddSum = 0.0, evenSum = 0.0, lim;
int i;
h = (b-a)/n; //calculate the distance between two interval
res = (mathFunc(a)+mathFunc(b)); //initial sum using f(a) and f(b)
lim = n/2;
for(i = 1; i<=lim; i++)
oddSum += mathFunc(a+(2*i-1)*h); //sum of numbers, placed at odd number
oddSum *= 4; //odd sum are multiplied by 4
for(i = 1; i<lim; i++)
evenSum += mathFunc(a+(2*i)*h); //sum of numbers, placed at even number
evenSum *= 2; //even sum are multiplied by 2
res += oddSum+evenSum;
res *= (h/3);
return res; //The result of integration
}
main() {
float result, lowLim, upLim;
int interval;
cout << "Enter Lower Limit, Upper Limit and interval: ";
cin >>lowLim >>upLim >>interval;
result = integrate(lowLim, upLim, interval);
cout << "The answer is: " << result;
}輸出
Enter Lower Limit, Upper Limit and interval: 1 2 20 The answer is: 2.19315

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統
關係型資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS 安卓
安卓 Python
Python C 語言
C 語言 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP