
- Rust 教程
- Rust - 首頁
- Rust - 簡介
- Rust - 環境搭建
- Rust - HelloWorld 示例
- Rust - 資料型別
- Rust - 變數
- Rust - 常量
- Rust - 字串
- Rust - 運算子
- Rust - 決策語句
- Rust - 迴圈
- Rust - 函式
- Rust - 元組
- Rust - 陣列
- Rust - 所有權
- Rust - 借用
- Rust - 切片
- Rust - 結構體
- Rust - 列舉
- Rust - 模組
- Rust - 集合
- Rust - 錯誤處理
- Rust - 泛型
- Rust - 輸入輸出
- Rust - 檔案輸入/輸出
- Rust - 包管理器
- Rust - 迭代器和閉包
- Rust - 智慧指標
- Rust - 併發
- Rust 有用資源
- Rust - 快速指南
- Rust - 有用資源
- Rust - 討論
Rust - 包管理器
Cargo 是 Rust 的包管理器。它像一個工具,用於管理 Rust 專案。
下面表格列出了一些常用的 Cargo 命令:
| 序號 | 命令及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | cargo build 編譯當前專案。 |
| 2 | cargo check 分析當前專案並報告錯誤,但不生成目標檔案。 |
| 3 | cargo run 構建並執行 src/main.rs。 |
| 4 | cargo clean 刪除 target 目錄。 |
| 5 | cargo update 更新 Cargo.lock 中列出的依賴項。 |
| 6 | cargo new 建立一個新的 Cargo 專案。 |
Cargo 幫助下載第三方庫。因此,它充當包管理器。您還可以構建自己的庫。安裝 Rust 時預設安裝 Cargo。
要建立一個新的 Cargo 專案,我們可以使用以下命令。
建立二進位制 crate
cargo new project_name --bin
建立庫 crate
cargo new project_name --lib
要檢查 Cargo 的當前版本,請執行以下命令:
cargo --version
示例 - 建立一個二進位制 Cargo 專案
遊戲生成一個隨機數並提示使用者猜測該數字。
步驟 1 - 建立專案資料夾
開啟終端並輸入以下命令 cargo new guess-game-app --bin。
這將建立以下資料夾結構。
guess-game-app/
-->Cargo.toml
-->src/
main.rs
cargo new 命令用於建立 crate。--bin 標誌表示正在建立的 crate 是一個二進位制 crate。公共 crate 儲存在名為 crates.io 的中央儲存庫中 https://crates.io/。
步驟 2 - 包含對外部庫的引用
此示例需要生成一個隨機數。由於內部標準庫不提供隨機數生成邏輯,因此我們需要檢視外部庫或 crate。讓我們使用 rand crate,它可在 crates.io 網站上找到 crates.io
rand 是一個用於隨機數生成的 Rust 庫。Rand 提供實用程式來生成隨機數,將它們轉換為有用的型別和分佈,以及一些與隨機性相關的演算法。
下圖顯示了 crates.io 網站和 rand crate 的搜尋結果。
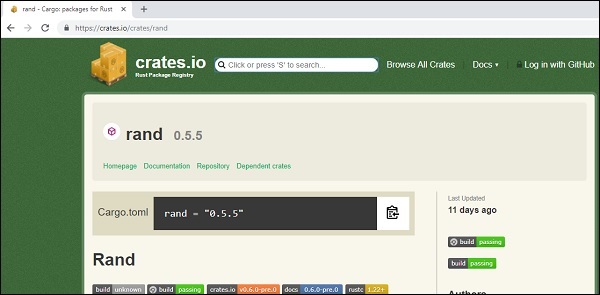
將 rand crate 的版本複製到 Cargo.toml 檔案中 rand = "0.5.5"。
[package] name = "guess-game-app" version = "0.1.0" authors = ["Mohtashim"] [dependencies] rand = "0.5.5"
步驟 3:編譯專案
導航到專案資料夾。在終端視窗中執行命令 cargo build:
Updating registry `https://github.com/rust-lang/crates.io-index` Downloading rand v0.5.5 Downloading rand_core v0.2.2 Downloading winapi v0.3.6 Downloading rand_core v0.3.0 Compiling winapi v0.3.6 Compiling rand_core v0.3.0 Compiling rand_core v0.2.2 Compiling rand v0.5.5 Compiling guess-game-app v0.1.0 (file:///E:/RustWorks/RustRepo/Code_Snippets/cargo-projects/guess-game-app) Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 1m 07s
rand crate 和所有傳遞依賴項(rand 的內部依賴項)將自動下載。
步驟 4 - 理解業務邏輯
現在讓我們看看數字猜測遊戲的業務邏輯是如何工作的:
遊戲最初生成一個隨機數。
提示使用者輸入並猜測該數字。
如果數字小於生成的數字,則列印訊息“太低”。
如果數字大於生成的數字,則列印訊息“太高”。
如果使用者輸入了程式生成的數字,則遊戲退出。
步驟 5 - 編輯 main.rs 檔案
將業務邏輯新增到 main.rs 檔案中。
use std::io;
extern crate rand;
//importing external crate
use rand::random;
fn get_guess() -> u8 {
loop {
println!("Input guess") ;
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("could not read from stdin");
match guess.trim().parse::<u8>(){ //remember to trim input to avoid enter spaces
Ok(v) => return v,
Err(e) => println!("could not understand input {}",e)
}
}
}
fn handle_guess(guess:u8,correct:u8)-> bool {
if guess < correct {
println!("Too low");
false
} else if guess> correct {
println!("Too high");
false
} else {
println!("You go it ..");
true
}
}
fn main() {
println!("Welcome to no guessing game");
let correct:u8 = random();
println!("correct value is {}",correct);
loop {
let guess = get_guess();
if handle_guess(guess,correct){
break;
}
}
}
步驟 6 - 編譯並執行專案
在終端上執行命令 cargo run。確保終端指向專案目錄。
Welcome to no guessing game correct value is 97 Input guess 20 Too low Input guess 100 Too high Input guess 97 You got it ..