- Rust 教程
- Rust - 首頁
- Rust - 簡介
- Rust - 環境設定
- Rust - HelloWorld 示例
- Rust - 資料型別
- Rust - 變數
- Rust - 常量
- Rust - 字串
- Rust - 運算子
- Rust - 決策
- Rust - 迴圈
- Rust - 函式
- Rust - 元組
- Rust - 陣列
- Rust - 所有權
- Rust - 借用
- Rust - 切片
- Rust - 結構體
- Rust - 列舉
- Rust - 模組
- Rust - 集合
- Rust - 錯誤處理
- Rust - 泛型
- Rust - 輸入輸出
- Rust - 檔案輸入/輸出
- Rust - 包管理器
- Rust - 迭代器和閉包
- Rust - 智慧指標
- Rust - 併發
- Rust 有用資源
- Rust - 快速指南
- Rust - 有用資源
- Rust - 討論
Rust - 模組
一個邏輯程式碼組稱為模組。多個模組編譯成一個稱為包的單元。Rust 程式可能包含一個二進位制包或一個庫包。二進位制包是一個具有main()方法的可執行專案。庫包是可以重用於其他專案的元件組。與二進位制包不同,庫包沒有入口點(main() 方法)。Cargo 工具用於管理 Rust 中的包。例如,network模組包含網路相關函式,graphics模組包含繪圖相關函式。模組類似於其他程式語言中的名稱空間。可以使用 cargo 從crates.io下載第三方包。
| 序號 | 術語和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 包 是 Rust 中的編譯單元;包編譯為二進位制檔案或庫。 |
| 2 | cargo 用於包的官方 Rust 包管理工具。 |
| 3 | 模組 在包內邏輯地對程式碼進行分組。 |
| 4 |
官方的 Rust 包登錄檔。 |
語法
//public module
pub mod a_public_module {
pub fn a_public_function() {
//public function
}
fn a_private_function() {
//private function
}
}
//private module
mod a_private_module {
fn a_private_function() {
}
}
模組可以是公有的或私有的。私有模組中的元件無法被其他模組訪問。Rust 中的模組預設是私有的。相反,公共模組中的函式可以被其他模組訪問。模組應該以pub關鍵字為字首以使其成為公共的。公共模組中的函式也必須設為公共的。
示例:定義模組
此示例定義了一個公共模組 - movies。該模組包含一個接受引數並列印其值的函式play()。
pub mod movies {
pub fn play(name:String) {
println!("Playing movie {}",name);
}
}
fn main(){
movies::play("Herold and Kumar".to_string());
}
輸出
Playing movie Herold and Kumar
使用關鍵字
use關鍵字有助於匯入公共模組。
語法
use public_module_name::function_name;
示例
pub mod movies {
pub fn play(name:String) {
println!("Playing movie {}",name);
}
}
use movies::play;
fn main(){
play("Herold and Kumar ".to_string());
}
輸出
Playing movie Herold and Kumar
巢狀模組
模組也可以巢狀。comedy模組巢狀在english模組中,english模組進一步巢狀在movies模組中。下面給出的示例在movies/english/comedy模組內定義了一個函式play。
pub mod movies {
pub mod english {
pub mod comedy {
pub fn play(name:String) {
println!("Playing comedy movie {}",name);
}
}
}
}
use movies::english::comedy::play;
// importing a public module
fn main() {
// short path syntax
play("Herold and Kumar".to_string());
play("The Hangover".to_string());
//full path syntax
movies::english::comedy::play("Airplane!".to_string());
}
輸出
Playing comedy movie Herold and Kumar Playing comedy movie The Hangover Playing comedy movie Airplane!
示例 - 建立庫包並在二進位制包中使用
讓我們建立一個名為movie_lib的庫包,其中包含一個模組movies。要構建movie_lib庫包,我們將使用cargo工具。
步驟 1 - 建立專案資料夾
建立一個名為movie-app的資料夾,然後建立一個子資料夾movie-lib。建立資料夾和子資料夾後,在此目錄中建立一個src資料夾和一個Cargo.toml檔案。原始碼應放在src資料夾中。在src資料夾中建立lib.rs和movies.rs檔案。Cargo.toml檔案將包含專案的元資料,如版本號、作者姓名等。
專案目錄結構如下所示 -
movie-app
movie-lib/
-->Cargo.toml
-->src/
lib.rs
movies.rs
步驟 2 - 編輯Cargo.toml檔案以新增專案元資料
[package] name = "movies_lib" version = "0.1.0" authors = ["Mohtashim"]
步驟 3 - 編輯lib.rs檔案。
在此檔案中新增以下模組定義。
pub mod movies;
以上程式碼建立了一個公共模組 - movies。
步驟 4 - 編輯movies.rs檔案
此檔案將定義movies模組的所有函式。
pub fn play(name:String){
println!("Playing movie {} :movies-app",name);
}
以上程式碼定義了一個函式play(),它接受一個引數並將其列印到控制檯。
步驟 5 - 構建庫包
使用cargo build命令構建應用程式,以驗證庫包的結構是否正確。確保您位於專案的根目錄 - movie-app資料夾。如果構建成功,終端將顯示以下訊息。
D:\Rust\movie-lib> cargo build Compiling movies_lib v0.1.0 (file:///D:/Rust/movie-lib) Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.67s
步驟 6 - 建立測試應用程式
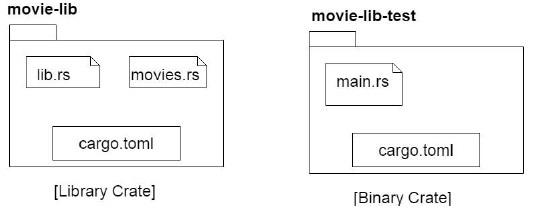
在movie-app資料夾中建立另一個資料夾movie-lib-test,然後建立一個Cargo.toml檔案和src資料夾。此專案應該有main方法,因為這是一個二進位制包,它將使用前面建立的庫包。在src資料夾中建立一個main.rs檔案。資料夾結構將如下所示。
movie-app
movie-lib
// already completed
movie-lib-test/
-->Cargo.toml
-->src/
main.rs
步驟 7 - 在Cargo.toml檔案中新增以下內容
[package]
name = "test_for_movie_lib"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Mohtashim"]
[dependencies]
movies_lib = { path = "../movie-lib" }
注意 - 庫資料夾的路徑設定為依賴項。下圖顯示了這兩個專案的內容。
步驟 8 - 將以下內容新增到main.rs檔案中
extern crate movies_lib;
use movies_lib::movies::play;
fn main() {
println!("inside main of test ");
play("Tutorialspoint".to_string())
}
以上程式碼匯入了一個名為movies_lib的外部包。檢查當前專案的Cargo.toml以驗證包名稱。
步驟 9 - 使用cargo build和cargo run
我們將使用cargo build和cargo run來構建二進位制專案並執行它,如下所示 -