如何在 Tkinter 應用程式中監聽終端?
將終端的功能與 Tkinter 應用程式結合起來可以增強其功能和多功能性。在本教程中,我們將探討如何使用 Python 的subprocess 模組將終端功能整合到 Tkinter 應用程式中,並提供一個實際示例。
要理解整合過程,必須清楚地瞭解所涉及的核心元件:
Tkinter − Tkinter 是 Python 事實上的 GUI 工具包,它為開發人員提供了構建圖形應用程式的全面工具和元件。
subprocess 模組 − Python 的 subprocess 模組對於建立附加程序、管理其輸入/輸出/錯誤管道以及檢索返回碼至關重要。此模組構成了在 Python 指令碼中執行終端命令的基礎。
實現示例
讓我們檢查一個 Python 指令碼,該指令碼舉例說明了將終端功能整合到 Tkinter 應用程式中的方法。此指令碼建立一個基本的應用程式,該應用程式執行“help”命令並在 Tkinter 視窗中顯示其輸出。
指令碼的分步實現如下:
步驟 1:類初始化
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("Terminal App")
__init__ 方法初始化 Tkinter 視窗並設定其標題,從而建立應用程式的入口點。
步驟 2:用於輸出的文字小部件
self.output_text = tk.Text(self.root, wrap="word", height=20, width=50) self.output_text.pack(padx=10, pady=10)
建立一個 Tkinter Text 小部件來顯示終端輸出。wrap="word" 選項確保在單詞邊界處正確換行,從而提高視覺清晰度。然後將小部件打包到視窗中,並指定填充。
步驟 3:用於命令執行的按鈕
self.execute_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="Run Command", command=self.run_command) self.execute_button.pack(pady=10)
向視窗新增一個標記為“執行命令”的 Tkinter Button。按下此按鈕時,將呼叫 run_command 方法。
步驟 4:執行命令
def run_command(self):
command = "help"
result = subprocess.run(command, shell=True, capture_output=True, text=True)
self.output_text.delete("1.0", tk.END)
self.output_text.insert(tk.END, result.stdout)
self.output_text.insert(tk.END, result.stderr)
run_command 方法定義終端命令(在本例中為“help”),並使用 subprocess.run() 執行它。捕獲標準輸出 (stdout) 和標準錯誤 (stderr),並在 Tkinter Text 小部件中顯示它們。
完整程式碼
讓我們結合這些步驟並檢查完整的實現示例:
示例
import tkinter as tk
import subprocess
class TerminalApp:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("Listening to Terminal on Tkinter App")
root.geometry("720x400")
# Create a Text widget to display the terminal output
self.output_text = tk.Text(self.root, wrap="word", height=20, width=50)
self.output_text.pack(padx=10, pady=10)
# Create a button to execute a command
self.execute_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="Run Command", command=self.run_command)
self.execute_button.pack(pady=10)
def run_command(self):
# The command you want to execute
command = "help"
# Use subprocess to run the command and capture the output
result = subprocess.run(command, shell=True, capture_output=True, text=True)
# Display the output in the Text widget
self.output_text.delete("1.0", tk.END) # Clear previous output
self.output_text.insert(tk.END, result.stdout)
self.output_text.insert(tk.END, result.stderr)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = TerminalApp(root)
root.mainloop()
輸出
執行上述示例後,您將看到一個帶有“執行命令”按鈕的 Tkinter 視窗。單擊按鈕後,它將執行特定命令並在 Tkinter 視窗中顯示結果。(在我們的示例中,它將執行“help”命令)。
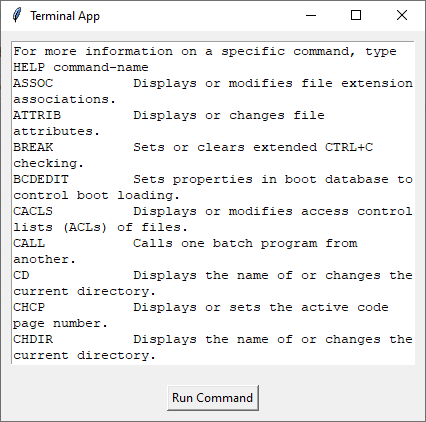
結論
將終端功能整合到 Tkinter 應用程式中,透過在應用程式介面中啟用直接系統互動來擴充套件使用者體驗。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP