
- F# 基礎教程
- F# - 首頁
- F# - 概述
- F# - 環境設定
- F# - 程式結構
- F# - 基本語法
- F# - 資料型別
- F# - 變數
- F# - 運算子
- F# - 決策
- F# - 迴圈
- F# - 函式
- F# - 字串
- F# - 可選項
- F# - 元組
- F# - 記錄
- F# - 列表
- F# - 序列
- F# - 集合
- F# - 對映
- F# - 判別聯合
- F# - 可變資料
- F# - 陣列
- F# - 可變列表
- F# - 可變字典
- F# - 基本輸入/輸出
- F# - 泛型
- F# - 委託
- F# - 列舉
- F# - 模式匹配
- F# - 異常處理
- F# - 類
- F# - 結構體
- F# - 運算子過載
- F# - 繼承
- F# - 介面
- F# - 事件
- F# - 模組
- F# - 名稱空間
F# 快速指南
F# - 概述
F# 是一種函數語言程式設計語言。要理解 F# 的結構,您需要閱讀幾行關於名為函數語言程式設計的程式設計正規化的介紹。
函數語言程式設計將計算機程式視為數學函式。在函數語言程式設計中,重點是常量和函式,而不是變數和狀態。因為函式和常量是不變的。
在函數語言程式設計中,您將編寫模組化程式,即程式將由將其他函式作為輸入的函式組成。
用函數語言程式設計語言編寫的程式往往簡潔。
關於 F#
以下是關於 F# 的基本資訊:
- 它於 2005 年在微軟研究院開發。
- 它是微軟 .Net 語言家族的一部分。
- 它是一種函數語言程式設計語言。
- 它基於函數語言程式設計語言 OCaml。
F# 的特性
它是 OCaml 的 .Net 實現。
它編譯 .Net CLI(公共語言介面)位元組碼或 MSIL(Microsoft 中間語言),可在 CLR(公共語言執行時)上執行。
它提供型別推斷。
它提供豐富的模式匹配結構。
它具有互動式指令碼和除錯功能。
它允許編寫高階函式。
它提供完善的物件模型。
F# 的用途
F# 通常用於以下領域:
- 建立科學模型
- 數學問題求解
- 人工智慧研究工作
- 金融建模
- 圖形設計
- CPU 設計
- 編譯器程式設計
- 電信
它也用於 CRUD 應用程式、網頁、GUI 遊戲和其他通用程式。
F# - 環境設定
本章將討論 F# 程式設計所需的工具。
F# 的整合開發環境 (IDE)
Microsoft 提供 Visual Studio 2013 用於 F# 程式設計。
免費的 Visual Studio 2013 Community 版本可從 Microsoft 的官方網站獲得。Visual Studio 2013 Community 及更高版本附帶 Visual F# 工具。安裝詳情請訪問 Asp.net 教程。Visual F# 工具包括命令列編譯器 (fsc.exe) 和 F# 互動式 (fsi.exe)。
使用這些工具,您可以編寫各種 F# 程式,從簡單的命令列應用程式到更復雜的應用程式。您還可以使用基本的文字編輯器(如記事本)編寫 F# 原始碼檔案,並使用命令列編譯器將程式碼編譯為程式集。
您可以從 Microsoft Visual Studio 下載它。它會自動安裝到您的機器上。
在 Linux 上編寫 F# 程式
請訪問 F# 官方網站,獲取有關將工具作為 Debian 包獲取或直接從原始碼編譯的最新說明:https://fsharp.org/use/linux/.
F# - 程式結構
F# 是一種函數語言程式設計語言。
在 F# 中,函式像資料型別一樣工作。您可以像任何其他變數一樣宣告和使用函式。
一般來說,F# 應用程式沒有任何特定的入口點。編譯器從上到下執行檔案中的所有頂級語句。
但是,為了遵循程序式程式設計風格,許多應用程式保留單個頂級語句來呼叫主迴圈。
以下程式碼顯示了一個簡單的 F# 程式:
open System
(* This is a multi-line comment *)
// This is a single-line comment
let sign num =
if num > 0 then "positive"
elif num < 0 then "negative"
else "zero"
let main() =
Console.WriteLine("sign 5: {0}", (sign 5))
main()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
sign 5: positive
請注意:
F# 程式碼檔案可能以多個open語句開頭,用於匯入名稱空間。
檔案的主體包含實現應用程式業務邏輯的其他函式。
主迴圈包含頂級可執行語句。
F# - 基本語法
您已經看到了 F# 程式的基本結構,因此很容易理解 F# 程式語言的其他基本構建塊。
F# 中的標記
F# 程式由各種標記組成。標記可以是關鍵字、識別符號、常量、字串文字或符號。我們可以將 F# 標記分為兩種型別:
- 關鍵字
- 符號和運算子
F# 關鍵字
下表顯示了關鍵字及其簡要說明。我們將在後續章節中討論這些關鍵字的使用。
| 關鍵字 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| abstract | 指示一種方法,該方法在其宣告的型別中沒有實現,或者該方法是虛擬的並具有預設實現。 |
| and | 用於相互遞迴繫結、屬性宣告以及泛型引數上的多個約束。 |
| as | 用於為當前類物件指定物件名稱。也用於為模式匹配中的整個模式命名。 |
| assert | 用於在除錯期間驗證程式碼。 |
| base | 用作基類物件的名稱。 |
| begin | 在詳細語法中,指示程式碼塊的開始。 |
| class | 在詳細語法中,指示類的定義的開始。 |
| default | 指示抽象方法的實現;與抽象方法宣告一起使用以建立虛擬方法。 |
| delegate | 用於宣告委託。 |
| do | 用於迴圈結構或執行命令式程式碼。 |
| done | 在詳細語法中,指示迴圈表示式中程式碼塊的結束。 |
| downcast | 用於轉換為繼承鏈中較低的型別。 |
| downto | 在for表示式中,用於反向計數。 |
| elif | 用於條件分支。else if 的簡寫形式。 |
| else | 用於條件分支。 |
| end | 在型別定義和型別擴充套件中,指示成員定義部分的結束。 在詳細語法中,用於指定以 begin 關鍵字開始的程式碼塊的結束。 |
| exception | 用於宣告異常型別。 |
| extern | 指示已宣告的程式元素是在另一個二進位制檔案或程式集中定義的。 |
| false | 用作布林文字。 |
| finally | 與 try 一起使用以引入無論是否發生異常都執行的程式碼塊。 |
| for | 用於迴圈結構。 |
| fun | 用於 lambda 表示式,也稱為匿名函式。 |
| function | 用作 fun 關鍵字和 lambda 表示式中對單個引數進行模式匹配的 match 表示式的較短替代方案。 |
| global | 用於引用頂級 .NET 名稱空間。 |
| if | 用於條件分支結構。 |
| in | 用於序列表達式,並在詳細語法中用於將表示式與繫結分開。 |
| inherit | 用於指定基類或基介面。 |
| inline | 用於指示應直接整合到呼叫者程式碼中的函式。 |
| interface | 用於宣告和實現介面。 |
| internal | 用於指定成員在程式集內可見,但在程式集外不可見。 |
| lazy | 用於指定僅在需要結果時才執行的計算。 |
| let | 用於將名稱與值或函式關聯或繫結。 |
| let! | 用於非同步工作流中將名稱繫結到非同步計算的結果,或者在其他計算表示式中用於將名稱繫結到計算型別的結果。 |
| match | 用於透過將值與模式進行比較來分支。 |
| member | 用於在物件型別中宣告屬性或方法。 |
| module | 用於將名稱與一組相關的型別、值和函式關聯,以將其與其他程式碼邏輯地分開。 |
| mutable | 用於宣告變數,即可以更改的值。 |
| namespace | 用於將名稱與一組相關的型別和模組關聯,以將其與其他程式碼邏輯地分開。 |
| new | 用於宣告、定義或呼叫建立或可以建立物件的建構函式。 還在泛型引數約束中使用,以指示型別必須具有特定的建構函式。 |
| not | 實際上不是關鍵字。但是,not struct 組合用作泛型引數約束。 |
| null | 指示物件不存在。 也用於泛型引數約束。 |
| of | 在判別聯合中用於指示值的類別型別,以及在委託和異常宣告中。 |
| open | 用於使名稱空間或模組的內容無需限定即可使用。 |
| or | 用作布林條件的布林或運算子。等同於 ||。 也用於成員約束。 |
| override | 用於實現與基版本不同的抽象或虛方法版本。 |
| private | 將成員的訪問許可權限制在同一型別或模組中的程式碼。 |
| public | 允許從型別外部訪問成員。 |
| rec | 用於指示函式是遞迴的。 |
| return | 用於指示作為計算表示式結果提供的值。 |
| return! | 用於指示計算表示式,在評估時,提供包含計算表示式的結果。 |
| select | 在查詢表示式中用於指定要提取的欄位或列。請注意,這是一個上下文關鍵字,這意味著它實際上不是保留字,它只在適當的上下文中充當關鍵字。 |
| static | 用於指示無需型別例項即可呼叫的方法或屬性,或在型別的所有例項之間共享的值成員。 |
| struct | 用於宣告結構型別。 也用於泛型引數約束。 在模組定義中用於OCaml相容性。 |
| then | 用於條件表示式。 也用於在物件構造後執行副作用。 |
| to | 在for迴圈中用於指示範圍。 |
| true | 用作布林文字。 |
| try | 用於引入可能生成異常的程式碼塊。與with或finally一起使用。 |
| type | 用於宣告類、記錄、結構、區分聯合、列舉型別、度量單位或型別縮寫。 |
| upcast | 用於轉換為繼承鏈中較高的型別。 |
| use | 用於代替let,用於需要呼叫Dispose來釋放資源的值。 |
| use! | 在非同步工作流和其他計算表示式中,用於代替let!,用於需要呼叫Dispose來釋放資源的值。 |
| val | 在簽名中用於指示值,或在型別中用於宣告成員(在有限情況下)。 |
| void | 指示.NET void型別。在與其他.NET語言互操作時使用。 |
| when | 用於模式匹配上的布林條件(when guards)以及為泛型型別引數引入約束子句。 |
| while | 引入迴圈構造。 |
| with | 與模式匹配表示式中的match關鍵字一起使用。也用於物件表示式、記錄複製表示式和型別擴充套件中,以引入成員定義和引入異常處理程式。 |
| yield | 在序列表達式中用於為序列生成值。 |
| yield! | 在計算表示式中用於將給定計算表示式的結果附加到包含計算表示式的結果集合中。 |
一些保留關鍵字來自OCaml語言:
| asr | land | lor | lsl | lsr | lxor | mod | sig |
其他一些保留關鍵字保留用於F#的未來擴充套件。
| atomic | break | checked | component | const | constraint | constructor |
| continue | eager | event | external | fixed | functor | include |
| method | mixin | object | parallel | process | protected | pure |
| sealed | tailcall | trait | virtual | volatile |
F#中的註釋
F#提供兩種型別的註釋:
- 單行註釋以//符號開頭。
- 多行註釋以(*開頭,以*)結尾。
F#中的基本程式和應用程式入口點
通常,F#程式沒有任何顯式的入口點。編譯F#應用程式時,提供給編譯器的最後一個檔案成為入口點,該檔案中所有頂級語句都從上到下執行。
一個編寫良好的程式應該只有一個頂級語句來呼叫程式的主迴圈。
一個非常簡小的F#程式,它將在螢幕上顯示“Hello World”:
(* This is a comment *) (* Sample Hello World program using F# *) printfn "Hello World!"
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Hello World!
F# - 資料型別
F#中的資料型別可以分類如下:
- 整數型別
- 浮點型別
- 文字型別
- 其他型別
整數資料型別
下表提供了F#的整數資料型別。這些基本上是整數資料型別。
| F#型別 | 大小 | 範圍 | 示例 | 備註 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sbyte | 1位元組 | -128到127 | 42y -11y |
8位有符號整數 |
| byte | 1位元組 | 0到255 | 42uy 200uy |
8位無符號整數 |
| int16 | 2位元組 | -32768到32767 | 42s -11s |
16位有符號整數 |
| uint16 | 2位元組 | 0到65,535 | 42us 200us |
16位無符號整數 |
| int/int32 | 4位元組 | -2,147,483,648到2,147,483,647 | 42 -11 |
32位有符號整數 |
| uint32 | 4位元組 | 0到4,294,967,295 | 42u 200u |
32位無符號整數 |
| int64 | 8位元組 | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808到9,223,372,036,854,775,807 | 42L -11L |
64位有符號整數 |
| uint64 | 8位元組 | 0到18,446,744,073,709,551,615 | 42UL 200UL |
64位無符號整數 |
| bigint | 至少4位元組 | 任何整數 | 42I 1499999 9999999 9999999 9999999 9999I |
任意精度整數 |
示例
(* single byte integer *) let x = 268.97f let y = 312.58f let z = x + y printfn "x: %f" x printfn "y: %f" y printfn "z: %f" z (* unsigned 8-bit natural number *) let p = 2uy let q = 4uy let r = p + q printfn "p: %i" p printfn "q: %i" q printfn "r: %i" r (* signed 16-bit integer *) let a = 12s let b = 24s let c = a + b printfn "a: %i" a printfn "b: %i" b printfn "c: %i" c (* signed 32-bit integer *) let d = 212l let e = 504l let f = d + e printfn "d: %i" d printfn "e: %i" e printfn "f: %i" f
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
x: 1 y: 2 z: 3 p: 2 q: 4 r: 6 a: 12 b: 24 c: 36 d: 212 e: 504 f: 716
浮點資料型別
下表提供了F#的浮點資料型別。
| F#型別 | 大小 | 範圍 | 示例 | 備註 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| float32 | 4位元組 | ±1.5e-45到±3.4e38 | 42.0F -11.0F |
32位有符號浮點數(7位有效數字) |
| float | 8位元組 | ±5.0e-324到±1.7e308 | 42.0 -11.0 |
64位有符號浮點數(15-16位有效數字) |
| decimal | 16位元組 | ±1.0e-28到±7.9e28 | 42.0M -11.0M |
128位有符號浮點數(28-29位有效數字) |
| BigRational | 至少4位元組 | 任何有理數。 | 42N -11N |
任意精度有理數。使用此型別需要引用FSharp.PowerPack.dll。 |
示例
(* 32-bit signed floating point number *) (* 7 significant digits *) let d = 212.098f let e = 504.768f let f = d + e printfn "d: %f" d printfn "e: %f" e printfn "f: %f" f (* 64-bit signed floating point number *) (* 15-16 significant digits *) let x = 21290.098 let y = 50446.768 let z = x + y printfn "x: %g" x printfn "y: %g" y printfn "z: %g" z
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
d: 212.098000 e: 504.768000 f: 716.866000 x: 21290.1 y: 50446.8 z: 71736.9
文字資料型別
下表提供了F#的文字資料型別。
| F#型別 | 大小 | 範圍 | 示例 | 備註 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| char | 2位元組 | U+0000到U+ffff | 'x' '\t' |
單個Unicode字元 |
| string | 20 + (2 * 字串長度)位元組 | 0到大約20億個字元 | "Hello" "World" |
Unicode文字 |
示例
let choice = 'y' let name = "Zara Ali" let org = "Tutorials Point" printfn "Choice: %c" choice printfn "Name: %s" name printfn "Organisation: %s" org
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Choice: y Name: Zara Ali Organisation: Tutorials Point
其他資料型別
下表提供了F#的其他一些資料型別。
| F#型別 | 大小 | 範圍 | 示例 | 備註 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bool | 1位元組 | 只有兩個可能的值,true或false | true false |
儲存布林值 |
示例
let trueVal = true let falseVal = false printfn "True Value: %b" (trueVal) printfn "False Value: %b" (falseVal)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
True Value: true False Value: false
F# - 變數
變數是賦予儲存區域的名稱,我們的程式可以操作它。每個變數都有一個特定的型別,它決定了變數記憶體的大小和佈局;可以儲存在該記憶體中的值的範圍;以及可以應用於變數的操作集。
F#中的變數宣告
let關鍵字用於變數宣告:
例如:
let x = 10
它宣告一個變數x並將其值賦值為10。
您還可以將表示式賦值給變數:
let x = 10 let y = 20 let z = x + y
以下示例說明了這個概念:
示例
let x = 10 let y = 20 let z = x + y printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
x: 10 y: 20 z: 30
F#中的變數是不可變的,這意味著一旦變數繫結到一個值,就不能更改它。它們實際上被編譯為靜態只讀屬性。
以下示例演示了這一點。
示例
let x = 10 let y = 20 let z = x + y printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z let x = 15 let y = 20 let z = x + y printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z
編譯並執行程式時,它會顯示以下錯誤訊息:
Duplicate definition of value 'x' Duplicate definition of value 'Y' Duplicate definition of value 'Z'
帶有型別宣告的變數定義
變數定義告訴編譯器應該在哪裡以及為變數建立多少儲存空間。變數定義可以指定資料型別,幷包含該型別的一個或多個變數的列表,如下例所示。
示例
let x:int32 = 10 let y:int32 = 20 let z:int32 = x + y printfn "x: %d" x printfn "y: %d" y printfn "z: %d" z let p:float = 15.99 let q:float = 20.78 let r:float = p + q printfn "p: %g" p printfn "q: %g" q printfn "r: %g" r
編譯並執行程式時,它會顯示以下錯誤訊息:
x: 10 y: 20 z: 30 p: 15.99 q: 20.78 r: 36.77
可變變數
有時您需要更改儲存在變數中的值。為了指定在程式的後面部分可能更改已宣告和賦值的變數的值,F#提供了mutable關鍵字。您可以使用此關鍵字宣告和賦值可變變數,其值將發生更改。
mutable關鍵字允許您宣告和賦值可變變數的值。
您可以使用let關鍵字為可變變數賦值一些初始值。但是,要為其賦值新的後續值,您需要使用←運算子。
例如:
let mutable x = 10 x ← 15
以下示例將闡明這個概念:
示例
let mutable x = 10 let y = 20 let mutable z = x + y printfn "Original Values:" printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z printfn "Let us change the value of x" printfn "Value of z will change too." x <- 15 z <- x + y printfn "New Values:" printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Original Values: x: 10 y: 20 z: 30 Let us change the value of x Value of z will change too. New Values: x: 15 y: 20 z: 35
F# - 運算子
運算子是一個符號,它告訴編譯器執行特定的數學或邏輯操作。F#富含內建運算子,並提供以下型別的運算子:
- 算術運算子
- 比較運算子
- 布林運算子
- 按位運算子
算術運算子
下表顯示了F#語言支援的所有算術運算子。假設變數A持有10,變數B持有20,則:
| 運算子 | 說明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| + | 將兩個運算元相加 | A + B 將得到 30 |
| - | 從第一個運算元中減去第二個運算元 | A - B 將得到 -10 |
| * | 將兩個運算元相乘 | A * B 將得到 200 |
| / | 將分子除以分母 | B / A 將得到 2 |
| % | 模運算子和整數除法後的餘數 | B % A 將得到 0 |
| ** | 冪運算子,將一個運算元提升到另一個運算元的冪 | B**A 將得到 2010 |
比較運算子
下表顯示了F#語言支援的所有比較運算子。這些二元比較運算子可用於整數和浮點型別。這些運算子返回bool型別的返回值。
假設變數A持有10,變數B持有20,則:
| 運算子 | 說明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| = | 檢查兩個運算元的值是否相等,如果相等,則條件為真。 | (A == B) 為假。 |
| <> | 檢查兩個運算元的值是否相等,如果不相等,則條件為真。 | (A <> B) 為真。 |
| > | 檢查左運算元的值是否大於右運算元的值,如果是,則條件為真。 | (A > B) 為假。 |
| < | 檢查左運算元的值是否小於右運算元的值,如果是,則條件為真。 | (A < B) 為真。 |
| >= | 檢查左運算元的值是否大於或等於右運算元的值,如果是,則條件為真。 | (A >= B) 為假。 |
| <= | 檢查左運算元的值是否小於或等於右運算元的值,如果是,則條件為真。 | (A <= B) 為真。 |
布林運算子
下表顯示了F#語言支援的所有布林運算子。假設變數A持有true,變數B持有false,則:
| 運算子 | 說明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| && | 稱為布林AND運算子。如果兩個運算元都非零,則條件為真。 | (A && B) 為假。 |
| || | 稱為布林OR運算子。如果兩個運算元中的任何一個非零,則條件為真。 | (A || B) 為真。 |
| not | 稱為布林NOT運算子。用於反轉其運算元的邏輯狀態。如果條件為真,則邏輯NOT運算子將變為假。 | not (A && B) 為真。 |
按位運算子
按位運算子對位進行操作,並執行逐位運算。&&&(按位AND)、|||(按位OR)和^^^(按位異或)的真值表如下:
| p | q | p &&& q | p ||| q | p ^^^ q |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
假設 A = 60;B = 13;則它們的二進位制形式如下:
A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
-----------------A&&&B = 0000 1100
A|||B = 0011 1101
A^^^B = 0011 0001
~~~A = 1100 0011
F# 語言支援的位運算子如下表所示。假設變數 A 為 60,變數 B 為 13,則:
| 運算子 | 說明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| &&& | 二進位制與運算子:如果該位同時存在於兩個運算元中,則將其複製到結果中。 | (A &&& B) 將得到 12,即 0000 1100 |
| ||| | 二進位制或運算子:如果該位存在於任一運算元中,則將其複製到結果中。 | (A ||| B) 將得到 61,即 0011 1101 |
| ^^^ | 二進位制異或運算子:如果該位僅在一個運算元中設定,則將其複製到結果中。 | (A ^^^ B) 將得到 49,即 0011 0001 |
| ~~~ | 二進位制補碼運算子:是一元運算子,作用是“反轉”位。 | (~~~A) 將得到 -61,在二進位制補碼形式下為 1100 0011。 |
| <<< | 二進位制左移運算子:左運算元的值向左移動由右運算元指定的位數。 | A <<< 2 將得到 240,即 1111 0000 |
| >>> | 二進位制右移運算子:左運算元的值向右移動由右運算元指定的位數。 | A >>> 2 將得到 15,即 0000 1111 |
運算子優先順序
下表顯示了 F# 語言中運算子和其他表示式關鍵字的優先順序順序,從最低優先順序到最高優先順序。
| 運算子 | 結合性 |
|---|---|
| as | 右結合 |
| when | 右結合 |
| | (管道) | 左結合 |
| ; | 右結合 |
| let | 非結合 |
| function, fun, match, try | 非結合 |
| if | 非結合 |
| → | 右結合 |
| := | 右結合 |
| , | 非結合 |
| or, || | 左結合 |
| &, && | 左結合 |
| < op, >op, =, |op, &op | 左結合 |
| &&& , |||, ^^^, ~~~, <<<, >>> | 左結合 |
| ^ op | 右結合 |
| :: | 右結合 |
| :?>, :? | 非結合 |
| - op, +op, (二元) | 左結合 |
| * op, /op, %op | 左結合 |
| ** op | 右結合 |
| f x (函式應用) | 左結合 |
| | (模式匹配) | 右結合 |
| 字首運算子 (+op, -op, %, %%, &, &&, !op, ~op) | 左結合 |
| . | 左結合 |
| f(x) | 左結合 |
| f<types> | 左結合 |
F# - 決策
決策結構要求程式設計師指定一個或多個條件,由程式進行評估或測試。它應該與一個或多個語句一起使用,如果條件被確定為真,則執行這些語句;如果條件被確定為假,則可以選擇執行其他語句。
以下是大多數程式語言中常見的決策結構的一般形式:
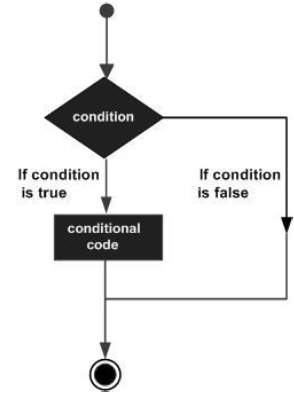
F# 程式語言提供以下型別的決策語句。
| 語句 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| if /then 語句 | 一個if/then 語句由一個布林表示式和一個或多個語句組成。 |
| if/then/else 語句 | 一個if/then 語句可以後跟一個可選的else 語句,當布林表示式為假時執行。 |
| if/then/elif/else 語句 | 一個if/then/elif/else 語句允許您擁有多個 else 分支。 |
| 巢狀 if 語句 | 您可以在另一個if 或else if 語句內使用一個if 或else if 語句。 |
F# - 迴圈
程式語言提供各種控制結構,允許更復雜的執行路徑。
迴圈語句允許我們多次執行一個語句或一組語句,以下是大多數程式語言中迴圈語句的一般形式:
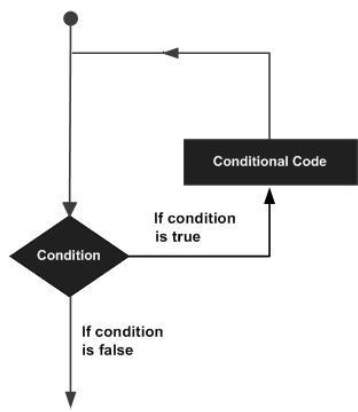
F# 提供以下型別的迴圈來處理迴圈需求。
| 迴圈型別 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| for… to 和 for… downto 表示式 | for...to 表示式用於在迴圈變數的一系列值上迭代迴圈。for… downto 表示式減少迴圈變數的值。 |
| for … in 表示式 | 這種形式的 for 迴圈用於迭代專案集合,即遍歷集合和序列。 |
| While…do 迴圈 | 當給定條件為真時重複一個語句或一組語句。它在執行迴圈體之前測試條件。 |
| 巢狀迴圈 | 您可以在任何其他 for 或 while 迴圈內使用一個或多個迴圈。 |
F# - 函式
在 F# 中,函式像資料型別一樣工作。您可以像任何其他變數一樣宣告和使用函式。
由於函式可以像其他變數一樣使用,您可以:
- 建立一個函式,併為其命名並將其名稱與型別關聯。
- 為其賦值。
- 對其值執行一些計算。
- 將其作為引數傳遞給另一個函式或子例程。
- 返回一個函式作為另一個函式的結果。
定義函式
函式使用let關鍵字定義。函式定義具有以下語法:
let [inline] function-name parameter-list [ : return-type ] = function-body
其中:
函式名是表示函式的識別符號。
引數列表給出用空格分隔的引數列表。您還可以為每個引數指定顯式型別,如果未指定,編譯器傾向於從函式體中推斷出來(像變數一樣)。
函式體由一個表示式或由多個表示式組成的複合表示式組成。函式體中的最後一個表示式是返回值。
返回型別是一個冒號後跟一個型別,是可選的。如果未指定返回型別,則編譯器從函式體中的最後一個表示式確定它。
函式的引數
您在函式名之後列出引數的名稱。您可以指定引數的型別。引數的型別應該跟在引數名稱後面,用冒號分隔。
如果沒有指定引數型別,則由編譯器推斷。
例如:
let doubleIt (x : int) = 2 * x
呼叫函式
透過指定函式名,然後是一個空格,然後是任何用空格分隔的引數來呼叫函式。
例如:
let vol = cylinderVolume 3.0 5.0
以下程式說明了這些概念。
示例 1
以下程式計算當半徑和長度作為引數給出時圓柱體的體積
// the function calculates the volume of // a cylinder with radius and length as parameters let cylinderVolume radius length : float = // function body let pi = 3.14159 length * pi * radius * radius let vol = cylinderVolume 3.0 5.0 printfn " Volume: %g " vol
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Volume: 141.372
示例 2
以下程式返回兩個給定引數中較大的值:
// the function returns the larger value between two
// arguments
let max num1 num2 : int32 =
// function body
if(num1>num2)then
num1
else
num2
let res = max 39 52
printfn " Max Value: %d " res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Max Value: 52
示例 3
let doubleIt (x : int) = 2 * x printfn "Double 19: %d" ( doubleIt(19))
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Double 19: 38
遞迴函式
遞迴函式是呼叫自身的函式。
使用let rec關鍵字組合定義遞迴。
定義遞迴函式的語法為:
//Recursive function definition let rec function-name parameter-list = recursive-function-body
例如:
let rec fib n = if n < 2 then 1 else fib (n - 1) + fib (n - 2)
示例 1
以下程式返回斐波那契數列 1 到 10:
let rec fib n = if n < 2 then 1 else fib (n - 1) + fib (n - 2) for i = 1 to 10 do printfn "Fibonacci %d: %d" i (fib i)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Fibonacci 1: 1 Fibonacci 2: 2 Fibonacci 3: 3 Fibonacci 4: 5 Fibonacci 5: 8 Fibonacci 6: 13 Fibonacci 7: 21 Fibonacci 8: 34 Fibonacci 9: 55 Fibonacci 10: 89
示例 2
以下程式返回 8 的階乘:
open System let rec fact x = if x < 1 then 1 else x * fact (x - 1) Console.WriteLine(fact 8)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
40320
F# 中的箭頭表示法
F# 使用鏈式箭頭表示法報告函式和值中的資料型別。讓我們以一個函式為例,該函式接受一個int輸入,並返回一個字串。在箭頭表示法中,它寫為:
int -> string
資料型別從左到右讀取。
讓我們再舉一個假設函式的例子,該函式接受兩個 int 資料輸入並返回一個字串。
let mydivfunction x y = (x / y).ToString();;
F# 使用鏈式箭頭表示法報告資料型別為:
val mydivfunction : x:int -> y:int -> string
返回型別由鏈式箭頭表示法中最右邊的資料型別表示。
更多示例:
| 表示法 | 含義 |
|---|---|
| float → float → float | 該函式接受兩個float輸入,返回另一個float。 |
| int → string → float | 該函式接受一個int和一個string輸入,返回一個float。 |
Lambda 表示式
Lambda 表示式是匿名函式。
讓我們舉兩個函式的例子:
let applyFunction ( f: int -> int -> int) x y = f x y let mul x y = x * y let res = applyFunction mul 5 7 printfn "%d" res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
35
現在在上面的例子中,如果不用定義函式mul,我們可以使用 lambda 表示式:
let applyFunction ( f: int -> int -> int) x y = f x y let res = applyFunction (fun x y -> x * y ) 5 7 printfn "%d" res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
35
函式組合和管道
在 F# 中,一個函式可以由其他函式組合而成。
以下示例顯示了從兩個函式 function1 和 function2 組合名為 f 的函式:
let function1 x = x + 1 let function2 x = x * 5 let f = function1 >> function2 let res = f 10 printfn "%d" res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
55
F# 還提供了一個稱為函式管道的功能。管道允許將函式呼叫連結在一起作為連續的操作。
以下示例顯示了:
let function1 x = x + 1 let function2 x = x * 5 let res = 10 |> function1 |> function2 printfn "%d" res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
55
F# - 字串
在 F# 中,字串型別表示不可變文字,作為 Unicode 字元的序列。
字串字面量
字串字面量由引號(")字元分隔。
有一些特殊字元用於特殊用途,例如換行符、製表符等。它們使用反斜槓(\)字元編碼。反斜槓字元和相關的字元構成轉義序列。下表顯示了 F# 支援的轉義序列。
| 字元 | 轉義序列 |
|---|---|
| 退格 | \b |
| 換行 | \n |
| 回車 | \r |
| 製表符 | \t |
| 反斜槓 | \\ |
| 引號 | \" |
| 撇號 | \' |
| Unicode 字元 | \uXXXX 或 \UXXXXXXXX (其中 X 表示十六進位制數字) |
忽略轉義序列的方法
以下兩種方法使編譯器忽略轉義序列:
- 使用 @ 符號。
- 用三個引號括起來。
當字串字面量前面帶有 @ 符號時,它被稱為逐字字串。這樣,字串中的所有轉義序列都被忽略,除了兩個引號字元被解釋為一個引號字元。
當字串用三個引號括起來時,所有轉義序列也被忽略,包括雙引號字元。
示例
以下示例演示了這種技術,展示瞭如何處理包含嵌入式引號的 XML 或其他結構:
// Using a verbatim string let xmldata = @"<book author=""Lewis, C.S"" title=""Narnia"">" printfn "%s" xmldata
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
<book author="Lewis, C.S" title="Narnia">
字串的基本運算子
下表顯示了字串的基本運算:
| 值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| collect : (char → string) → string → string | 建立一個新字串,其字元是將指定函式應用於輸入字串的每個字元並將結果字串連線起來的結果。 |
| concat : string → seq<string> → string | 返回一個新字串,該字串透過使用分隔符連線給定的字串。 |
| exists : (char → bool) → string → bool | 測試字串的任何字元是否滿足給定的謂詞。 |
| forall : (char → bool) → string → bool | 測試字串中所有字元是否都滿足給定的謂詞。 |
| init : int → (int → string) → string | 建立一個新的字串,其字元是由將指定函式應用於每個索引並連線結果字串生成的。 |
| iter : (char → unit) → string → unit | 將指定函式應用於字串中的每個字元。 |
| iteri : (int → char → unit) → string → unit | 將指定函式應用於字串中每個字元的索引和字元本身。 |
| length : string → int | 返回字串的長度。 |
| map : (char → char) → string → string | 建立一個新的字串,其字元是由將指定函式應用於輸入字串的每個字元生成的。 |
| mapi : (int → char → char) → string → string | 建立一個新的字串,其字元是由將指定函式應用於輸入字串的每個字元及其索引生成的。 |
| replicate : int → string → string | 透過連線指定數量的字串例項來返回一個字串。 |
以下示例演示了上述某些功能的用法:
示例 1
String.collect 函式構建一個新的字串,其字元是由將指定函式應用於輸入字串的每個字元並連線結果字串生成的。
let collectTesting inputS = String.collect (fun c -> sprintf "%c " c) inputS printfn "%s" (collectTesting "Happy New Year!")
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
H a p p y N e w Y e a r !
示例 2
String.concat 函式使用分隔符連線給定的字串序列並返回一個新字串。
let strings = [ "Tutorials Point"; "Coding Ground"; "Absolute Classes" ] let ourProducts = String.concat "\n" strings printfn "%s" ourProducts
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Tutorials Point Coding Ground Absolute Classes
示例 3
String.replicate 方法透過連線指定數量的字串例項來返回一個字串。
printfn "%s" <| String.replicate 10 "*! "
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
*! *! *! *! *! *! *! *! *! *!
F# - 可選項
F# 中的option 型別用於在計算中可能存在或不存在變數或函式值的場景。Option 型別用於表示計算中的可選值。它們可以有兩個可能的值:Some(x) 或 None。
例如,執行除法的函式在正常情況下會返回值,但在分母為零的情況下會丟擲異常。在此使用 option 可以幫助指示函式是否成功。
Option 具有底層型別,可以儲存該型別的 value,或者可能沒有 value。
使用 Options
讓我們以除法函式為例。下面的程式解釋了這一點:
讓我們編寫一個 div 函式,並向其傳送兩個引數 20 和 5:
let div x y = x / y let res = div 20 5 printfn "Result: %d" res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Result: 4
如果第二個引數為零,則程式會丟擲異常:
let div x y = x / y let res = div 20 0 printfn "Result: %d" res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Unhandled Exception: System.DivideByZeroException: Division by zero
在這種情況下,我們可以使用 option 型別,在操作成功時返回 Some(value),在操作失敗時返回 None。
以下示例演示了 option 的用法:
示例
let div x y = match y with | 0 -> None | _ -> Some(x/y) let res : int option = div 20 4 printfn "Result: %A " res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Result: Some 5
Option 屬性和方法
option 型別支援以下屬性和方法:
| 屬性或方法 | 型別 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
| None | 'T option | 一個靜態屬性,使您可以建立一個具有None 值的 option 值。 |
| IsNone | bool | 如果 option 具有None 值,則返回true。 |
| IsSome | bool | 如果 option 具有非None 值,則返回true。 |
| Some | 'T option | 一個靜態成員,建立一個具有非None 值的 option。 |
| 值 | 'T | 返回底層值,如果值為None,則丟擲 NullReferenceException。 |
示例 1
let checkPositive (a : int) =
if a > 0 then
Some(a)
else
None
let res : int option = checkPositive(-31)
printfn "Result: %A " res
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Result: <null>
示例 2
let div x y = match y with | 0 -> None | _ -> Some(x/y) let res : int option = div 20 4 printfn "Result: %A " res printfn "Result: %A " res.Value
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Result: Some 5 Result: 5
示例 3
let isHundred = function | Some(100) -> true | Some(_) | None -> false printfn "%A" (isHundred (Some(45))) printfn "%A" (isHundred (Some(100))) printfn "%A" (isHundred None)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
false true false
F# - 元組
元組是由逗號分隔的值的集合。這些用於建立臨時資料結構,將相關值組合在一起。
例如,(“Zara Ali”,“Hyderabad”,10)是一個包含兩個字串值和一個 int 值的 3 元組,其型別為 (string * string * int)。
元組可以是相同型別或不同型別的對、三元組等等。
這裡提供一些示例:
// Tuple of two integers. ( 4, 5 ) // Triple of strings. ( "one", "two", "three" ) // Tuple of unknown types. ( a, b ) // Tuple that has mixed types. ( "Absolute Classes", 1, 2.0 ) // Tuple of integer expressions. ( a * 4, b + 7)
示例
此程式有一個函式,該函式採用四個浮點值的元組並返回平均值:
let averageFour (a, b, c, d) = let sum = a + b + c + d sum / 4.0 let avg:float = averageFour (4.0, 5.1, 8.0, 12.0) printfn "Avg of four numbers: %f" avg
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Avg of four numbers: 7.275000
訪問單個元組成員
可以使用模式匹配來評估和列印元組的各個成員。
以下示例說明了這個概念:
示例
let display tuple1 =
match tuple1 with
| (a, b, c) -> printfn "Detail Info: %A %A %A" a b c
display ("Zara Ali", "Hyderabad", 10 )
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Detail Info: "Zara Ali" "Hyderabad" 10
F# 有兩個內建函式fst 和snd,它們返回 2 元組中的第一項和第二項。
以下示例說明了這個概念:
示例
printfn "First member: %A" (fst(23, 30))
printfn "Second member: %A" (snd(23, 30))
printfn "First member: %A" (fst("Hello", "World!"))
printfn "Second member: %A" (snd("Hello", "World!"))
let nameTuple = ("Zara", "Ali")
printfn "First Name: %A" (fst nameTuple)
printfn "Second Name: %A" (snd nameTuple)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
First member: 23 Second member: 30 First member: "Hello" Second member: "World!" First Name: "Zara" Second Name: "Ali"
F# - 記錄
記錄類似於元組,但它包含命名欄位。例如,
type website =
{ title : string;
url : string }
定義記錄
使用type 關鍵字定義記錄型別,並使用分號分隔的列表定義記錄的欄位。
定義記錄的語法為:
type recordName =
{ [ fieldName : dataType ] + }
建立記錄
您可以透過指定記錄的欄位來建立記錄。例如,讓我們建立一個名為homepage 的website 記錄:
let homepage = { Title = "TutorialsPoint"; Url = "www.tutorialspoint.com" }
以下示例將解釋這些概念:
示例 1
此程式定義了一個名為 website 的記錄型別。然後它建立一些 website 型別的記錄並列印這些記錄。
(* defining a record type named website *)
type website =
{ Title : string;
Url : string }
(* creating some records *)
let homepage = { Title = "TutorialsPoint"; Url = "www.tutorialspoint.com" }
let cpage = { Title = "Learn C"; Url = "www.tutorialspoint.com/cprogramming/index.htm" }
let fsharppage = { Title = "Learn F#"; Url = "www.tutorialspoint.com/fsharp/index.htm" }
let csharppage = { Title = "Learn C#"; Url = "www.tutorialspoint.com/csharp/index.htm" }
(*printing records *)
(printfn "Home Page: Title: %A \n \t URL: %A") homepage.Title homepage.Url
(printfn "C Page: Title: %A \n \t URL: %A") cpage.Title cpage.Url
(printfn "F# Page: Title: %A \n \t URL: %A") fsharppage.Title fsharppage.Url
(printfn "C# Page: Title: %A \n \t URL: %A") csharppage.Title csharppage.Url
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Home Page: Title: "TutorialsPoint"
URL: "www.tutorialspoint.com"
C Page: Title: "Learn C"
URL: "www.tutorialspoint.com/cprogramming/index.htm"
F# Page: Title: "Learn F#"
URL: "www.tutorialspoint.com/fsharp/index.htm"
C# Page: Title: "Learn C#"
URL: "www.tutorialspoint.com/csharp/index.htm"
示例 2
type student =
{ Name : string;
ID : int;
RegistrationText : string;
IsRegistered : bool }
let getStudent name id =
{ Name = name; ID = id; RegistrationText = null; IsRegistered = false }
let registerStudent st =
{ st with
RegistrationText = "Registered";
IsRegistered = true }
let printStudent msg st =
printfn "%s: %A" msg st
let main() =
let preRegisteredStudent = getStudent "Zara" 10
let postRegisteredStudent = registerStudent preRegisteredStudent
printStudent "Before Registration: " preRegisteredStudent
printStudent "After Registration: " postRegisteredStudent
main()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Before Registration: : {Name = "Zara";
ID = 10;
RegistrationText = null;
IsRegistered = false;}
After Registration: : {Name = "Zara";
ID = 10;
RegistrationText = "Registered";
IsRegistered = true;}
F# - 列表
在 F# 中,列表是相同型別元素的有序、不可變序列。它在某種程度上等同於連結串列資料結構。
F# 模組Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List 包含列表的常用操作。但是,F# 會自動匯入此模組並使其可供每個 F# 應用程式使用。
建立和初始化列表
以下是建立列表的各種方法:
使用列表字面量。
使用cons (::) 運算子。
使用 List 模組的List.init 方法。
使用一些稱為列表推導式的語法結構。
列表字面量
在這種方法中,您只需在方括號中指定分號分隔的值序列。例如:
let list1 = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10]
cons (::) 運算子
使用此方法,您可以透過使用 :: 運算子將一些值新增到現有列表的前面或cons 到現有列表中。例如:
let list2 = 1::2::3::4::5::6::7::8::9::10::[];;
[] 表示空列表。
List init 方法
List 模組的 List.init 方法通常用於建立列表。此方法的型別為:
val init : int -> (int -> 'T) -> 'T list
第一個引數是新列表的所需長度,第二個引數是初始化函式,它生成列表中的項。
例如:
let list5 = List.init 5 (fun index -> (index, index * index, index * index * index))
在這裡,索引函式生成列表。
列表推導式
列表推導式是用於生成列表的特殊語法結構。
F# 列表推導式語法有兩種形式:範圍和生成器。
範圍具有結構:[start .. end] 和 [start .. step .. end]
例如:
let list3 = [1 .. 10]
生成器具有結構:[for x in collection do ... yield expr]
例如:
let list6 = [ for a in 1 .. 10 do yield (a * a) ]
由於yield 關鍵字將單個值推入列表,因此yield! 關鍵字將值集合推入列表。
以下函式演示了上述方法:
示例
(* using list literals *) let list1 = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] printfn "The list: %A" list1 (*using cons operator *) let list2 = 1 :: 2 :: 3 :: [] printfn "The list: %A" list2 (* using range constructs*) let list3 = [1 .. 10] printfn "The list: %A" list3 (* using range constructs *) let list4 = ['a' .. 'm'] printfn "The list: %A" list4 (* using init method *) let list5 = List.init 5 (fun index -> (index, index * index, index * index * index)) printfn "The list: %A" list5 (* using yield operator *) let list6 = [ for a in 1 .. 10 do yield (a * a) ] printfn "The list: %A" list6 (* using yield operator *) let list7 = [ for a in 1 .. 100 do if a % 3 = 0 && a % 5 = 0 then yield a] printfn "The list: %A" list7 (* using yield! operator *) let list8 = [for a in 1 .. 3 do yield! [ a .. a + 3 ] ] printfn "The list: %A" list8
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The list: [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] The list: [1; 2; 3] The list: [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] The list: ['a'; 'b'; 'c'; 'd'; 'e'; 'f'; 'g'; 'h'; 'i'; 'j'; 'k'; 'l'; 'm'] The list: [(0, 0, 0); (1, 1, 1); (2, 4, 8); (3, 9, 27); (4, 16, 64)] The list: [1; 4; 9; 16; 25; 36; 49; 64; 81; 100] The list: [15; 30; 45; 60; 75; 90] The list: [1; 2; 3; 4; 2; 3; 4; 5; 3; 4; 5; 6]
列表資料型別的屬性
下表顯示了列表資料型別的各種屬性:
| 屬性 | 型別 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
| Head | 'T | 第一個元素。 |
| Empty | 'T list | 返回適當型別空列表的靜態屬性。 |
| IsEmpty | bool | 如果列表沒有元素,則為true。 |
| Item | 'T | 指定索引(基於零)處的元素。 |
| Length | int | 元素數量。 |
| Tail | 'T list | 沒有第一個元素的列表。 |
以下示例顯示了這些屬性的用法:
示例
let list1 = [ 2; 4; 6; 8; 10; 12; 14; 16 ] // Use of Properties printfn "list1.IsEmpty is %b" (list1.IsEmpty) printfn "list1.Length is %d" (list1.Length) printfn "list1.Head is %d" (list1.Head) printfn "list1.Tail.Head is %d" (list1.Tail.Head) printfn "list1.Tail.Tail.Head is %d" (list1.Tail.Tail.Head) printfn "list1.Item(1) is %d" (list1.Item(1))
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
list1.IsEmpty is false list1.Length is 8 list1.Head is 2 list1.Tail.Head is 4 list1.Tail.Tail.Head is 6 list1.Item(1) is 4
列表的基本運算子
下表顯示了列表資料型別的基本操作:
| 值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| append : 'T list → 'T list → 'T list | 返回一個新列表,其中包含第一個列表的元素,然後是第二個列表的元素。 |
| average : 'T list → ^T | 返回列表中元素的平均值。 |
| averageBy : ('T → ^U) → 'T list → ^U | 返回透過將函式應用於列表的每個元素生成的元素的平均值。 |
| choose : ('T → 'U option) → 'T list → 'U list | 將給定函式應用於列表的每個元素。返回由函式返回Some 的每個元素的結果組成的列表。 |
| collect : ('T → 'U list) → 'T list → 'U list | 對於列表的每個元素,應用給定函式。連線所有結果並返回組合列表。 |
| concat : seq<'T list> → 'T list | 返回一個新列表,其中按順序包含每個列表的元素。 |
| empty : 'T list | 返回給定型別的空列表。 |
| exists : ('T → bool) → 'T list → bool | 測試列表中的任何元素是否滿足給定的謂詞。 |
| exists2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → bool) → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → bool | 測試列表的任何一對對應元素是否滿足給定的謂詞。 |
| filter : ('T → bool) → 'T list → 'T list | 返回一個新集合,其中只包含給定謂詞返回true 的集合的元素。 |
| find : ('T → bool) → 'T list → 'T | 返回給定函式返回true 的第一個元素。 |
| findIndex : ('T → bool) → 'T list → int | 返回列表中滿足給定謂詞的第一個元素的索引。 |
| fold : ('State → 'T → 'State) → 'State → 'T list → 'State | 將函式應用於集合的每個元素,將累加器引數貫穿計算。此函式採用第二個引數,並將函式應用於它和列表的第一個元素。然後,它將此結果與第二個元素一起傳遞給函式,依此類推。最後,它返回最終結果。如果輸入函式是 f,元素是 i0...iN,則此函式計算 f (... (f s i0) i1 ...) iN。 |
| fold2 : ('State → 'T1 → 'T2 → 'State) → 'State → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → 'State | 將函式應用於兩個集合的對應元素,將累加器引數貫穿計算。集合的大小必須相同。如果輸入函式是 f,元素是 i0...iN 和 j0...jN,則此函式計算 f (... (f s i0 j0)...) iN jN。 |
| foldBack : ('T → 'State → 'State) → 'T list → 'State → 'State | 將函式應用於集合的每個元素,將累加器引數貫穿計算。如果輸入函式是 f,元素是 i0...iN,則計算 f i0 (...(f iN s))。 |
| foldBack2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → 'State → 'State) → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → 'State → 'State | 將函式應用於兩個集合的對應元素,將累加器引數貫穿計算。集合的大小必須相同。如果輸入函式是 f,元素是 i0...iN 和 j0...jN,則此函式計算 f i0 j0 (...(f iN jN s))。 |
| forall : ('T → bool) → 'T list → bool | 測試集合的所有元素是否都滿足給定的謂詞。 |
| forall2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → bool) → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → bool | 檢查集合中所有對應元素是否都滿足給定的成對謂詞。 |
| head : 'T list → 'T | 返回列表的第一個元素。 |
| init : int → (int → 'T) → 'T list | 透過對每個索引呼叫給定的生成器來建立一個列表。 |
| isEmpty : 'T list → bool | 如果列表不包含任何元素,則返回true,否則返回false。 |
| iter : ('T → unit) → 'T list → unit | 將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素。 |
| iter2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → unit) → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → unit | 同時將給定函式應用於兩個集合。這兩個集合必須大小相同。 |
| iteri : (int → 'T → unit) → 'T list → unit | 將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素。傳遞給函式的整數表示元素的索引。 |
| iteri2 : (int → 'T1 → 'T2 → unit) → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → unit | 同時將給定函式應用於兩個集合。這兩個集合必須大小相同。傳遞給函式的整數表示元素的索引。 |
| length : 'T list → int | 返回列表的長度。 |
| map : ('T → 'U) → 'T list → 'U list | 建立一個新的集合,其元素是將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素的結果。 |
| map2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → 'U) → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → 'U list | 建立一個新的集合,其元素是將給定函式成對應用於兩個集合的對應元素的結果。 |
| map3 : ('T1 → 'T2 → 'T3 → 'U) → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → 'T3 list → 'U list | 建立一個新的集合,其元素是將給定函式同時應用於三個集合的對應元素的結果。 |
| mapi : (int → 'T → 'U) → 'T list → 'U list | 建立一個新的集合,其元素是將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素的結果。傳遞給函式的整數索引表示正在轉換的元素的索引(從 0 開始)。 |
| mapi2 : (int → 'T1 → 'T2 → 'U) → 'T1 list → 'T2 list → 'U list | 類似於 List.mapi,但是對映兩個等長列表的對應元素。 |
| max : 'T list → 'T | 返回列表中所有元素中最大的元素,使用 Operators.max 進行比較。 |
| maxBy : ('T → 'U) → 'T list → 'T | 返回列表中所有元素中最大的元素,使用 Operators.max 對函式結果進行比較。 |
| min : 'T list → 'T | 返回列表中所有元素中最小的元素,使用 Operators.min 進行比較。 |
| minBy : ('T → 'U) → 'T list → 'T | 返回列表中所有元素中最小的元素,使用 Operators.min 對函式結果進行比較。 |
| nth : 'T list → int → 'T | 索引到列表中。第一個元素的索引為 0。 |
| ofArray : 'T [] → 'T list | 根據給定的陣列建立一個列表。 |
| ofSeq : seq<'T> → 'T list | 根據給定的可列舉物件建立一個新的列表。 |
| partition : ('T → bool) → 'T list * 'T list | 將集合拆分為兩個集合,分別包含給定謂詞返回true和false的元素。 |
| permute : (int → int) → 'T list → 'T list | 返回一個列表,其中所有元素都根據指定的排列進行排列。 |
| pick : ('T → 'U option) → 'T list → 'U | 將給定函式應用於連續元素,返回函式對某個值返回Some的第一個結果。 |
| reduce : ('T → 'T → 'T) → 'T list → 'T | 將函式應用於集合的每個元素,透過計算傳遞累加器引數。此函式將指定的函式應用於列表的前兩個元素。然後,它將此結果與第三個元素一起傳遞到函式中,依此類推。最後,它返回最終結果。如果輸入函式為 f,元素為 i0...iN,則此函式計算 f (... (f i0 i1) i2 ...) iN。 |
| reduceBack : ('T → 'T → 'T) → 'T list → 'T | 將函式應用於集合的每個元素,透過計算傳遞累加器引數。如果輸入函式為 f,元素為 i0...iN,則此函式計算 f i0 (...(f iN-1 iN))。 |
| replicate : (int → 'T → 'T list) | 透過對每個索引呼叫給定的生成器來建立一個列表。 |
| rev : 'T list → 'T list | 返回一個新的列表,其中元素順序相反。 |
| scan : ('State → 'T → 'State) → 'State → 'T list → 'State list | 將函式應用於集合的每個元素,透過計算傳遞累加器引數。此函式採用第二個引數,並將指定的函式應用於它和列表的第一個元素。然後,它將此結果與第二個元素一起傳遞到函式中,依此類推。最後,它返回中間結果和最終結果的列表。 |
| scanBack : ('T → 'State → 'State) → 'T list → 'State → 'State list | 類似於 foldBack,但是返回中間結果和最終結果。 |
| sort : 'T list → 'T list | 使用 Operators.compare 對給定列表進行排序。 |
| sortBy : ('T → 'Key) → 'T list → 'T list | 使用給定投影給出的鍵對給定列表進行排序。使用 Operators.compare 比較鍵。 |
| sortWith : ('T → 'T → int) → 'T list → 'T list | 使用給定的比較函式對給定列表進行排序。 |
| sum : ^T list → ^T | 返回列表中元素的總和。 |
| sumBy : ('T → ^U) → 'T list → ^U | 返回透過將函式應用於列表的每個元素生成的總和。 |
| tail : 'T list → 'T list | 返回輸入列表,但不包含第一個元素。 |
| toArray : 'T list → 'T [] | 根據給定的列表建立一個數組。 |
| toSeq : 'T list → seq<'T> | 將給定列表視為一個序列。 |
| tryFind : ('T → bool) → 'T list → 'T option | 返回給定函式返回true的第一個元素。如果不存在這樣的元素,則返回None。 |
| tryFindIndex : ('T → bool) → 'T list → int option | 返回列表中滿足給定謂詞的第一個元素的索引。如果不存在這樣的元素,則返回None。 |
| tryPick : ('T → 'U option) → 'T list → 'U option | 將給定函式應用於連續元素,返回函式對某個值返回Some的第一個結果。如果不存在這樣的元素,則返回None。 |
| unzip : ('T1 * 'T2) list → 'T1 list * 'T2 list | 將一對列表拆分為兩個列表。 |
| unzip3 : ('T1 * 'T2 * 'T3) list → 'T1 list * 'T2 list * 'T3 list | 將三元組列表拆分為三個列表。 |
| zip : 'T1 list → 'T2 list → ('T1 * 'T2) list | 將兩個列表組合成一個對列表。這兩個列表必須長度相等。 |
| zip3 : 'T1 list → 'T2 list → 'T3 list → ('T1 * 'T2 * 'T3) list | 將三個列表組合成一個三元組列表。這些列表必須長度相等。 |
以下示例演示了上述功能的用法:
示例 1
此程式演示了遞迴反轉列表:
let list1 = [ 2; 4; 6; 8; 10; 12; 14; 16 ]
printfn "The original list: %A" list1
let reverse lt =
let rec loop acc = function
| [] -> acc
| hd :: tl -> loop (hd :: acc) tl
loop [] lt
printfn "The reversed list: %A" (reverse list1)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The original list: [2; 4; 6; 8; 10; 12; 14; 16] The reversed list: [16; 14; 12; 10; 8; 6; 4; 2]
但是,您可以為此目的使用模組的rev函式:
let list1 = [ 2; 4; 6; 8; 10; 12; 14; 16 ] printfn "The original list: %A" list1 printfn "The reversed list: %A" (List.rev list1)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The original list: [2; 4; 6; 8; 10; 12; 14; 16] The reversed list: [16; 14; 12; 10; 8; 6; 4; 2]
示例 2
此程式演示了使用List.filter方法過濾列表:
let list1 = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] printfn "The list: %A" list1 let list2 = list1 |> List.filter (fun x -> x % 2 = 0);; printfn "The Filtered list: %A" list2
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The list: [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] The Filtered list: [2; 4; 6; 8; 10]
示例 3
List.map方法將列表從一種型別對映到另一種型別:
let list1 = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] printfn "The list: %A" list1 let list2 = list1 |> List.map (fun x -> (x * x).ToString());; printfn "The Mapped list: %A" list2
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The list: [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] The Mapped list: ["1"; "4"; "9"; "16"; "25"; "36"; "49"; "64"; "81"; "100"]
示例 4
List.append方法和@運算子將一個列表附加到另一個列表:
let list1 = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5 ] let list2 = [6; 7; 8; 9; 10] let list3 = List.append list1 list2 printfn "The first list: %A" list1 printfn "The second list: %A" list2 printfn "The appened list: %A" list3 let lt1 = ['a'; 'b';'c' ] let lt2 = ['e'; 'f';'g' ] let lt3 = lt1 @ lt2 printfn "The first list: %A" lt1 printfn "The second list: %A" lt2 printfn "The appened list: %A" lt3
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The first list: [1; 2; 3; 4; 5] The second list: [6; 7; 8; 9; 10] The appened list: [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] The first list: ['a'; 'b'; 'c'] The second list: ['e'; 'f'; 'g'] The appened list: ['a'; 'b'; 'c'; 'e'; 'f'; 'g']
示例 5
List.sort方法對列表進行排序。List.sum方法給出列表中元素的總和,List.average方法給出列表中元素的平均值:
let list1 = [9.0; 0.0; 2.0; -4.5; 11.2; 8.0; -10.0] printfn "The list: %A" list1 let list2 = List.sort list1 printfn "The sorted list: %A" list2 let s = List.sum list1 let avg = List.average list1 printfn "The sum: %f" s printfn "The average: %f" avg
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The list: [9.0; 0.0; 2.0; -4.5; 11.2; 8.0; -10.0] The sorted list: [-10.0; -4.5; 0.0; 2.0; 8.0; 9.0; 11.2] The sum: 15.700000 The average: 2.242857
“fold”操作將函式應用於列表中的每個元素,將函式的結果聚合到累加器變數中,並將累加器作為fold操作的結果返回。
示例 6
List.fold方法從左到右將函式應用於每個元素,而List.foldBack方法從右到左將函式應用於每個元素。
let sumList list = List.fold (fun acc elem -> acc + elem) 0 list printfn "Sum of the elements of list %A is %d." [ 1 .. 10 ] (sumList [ 1 .. 10 ])
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Sum of the elements of list [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10] is 55.
F# - 序列
序列,像列表一樣,也表示值的排序集合。但是,序列或序列表達式中的元素在需要時計算。它們不是一次性計算的,因此它們用於表示無限資料結構。
定義序列
序列使用以下語法定義:
seq { expr }
例如:
let seq1 = seq { 1 .. 10 }
建立序列和序列表達式
與列表類似,您可以使用範圍和推導式建立序列。
序列表達式是可以用來建立序列的表示式。這些可以:
- 透過指定範圍。
- 透過指定帶遞增或遞減的範圍。
- 透過使用yield關鍵字來生成成為序列一部分的值。
- 透過使用→運算子。
以下示例演示了這個概念:
示例 1
(* Sequences *)
let seq1 = seq { 1 .. 10 }
(* ascending order and increment*)
printfn "The Sequence: %A" seq1
let seq2 = seq { 1 .. 5 .. 50 }
(* descending order and decrement*)
printfn "The Sequence: %A" seq2
let seq3 = seq {50 .. -5 .. 0}
printfn "The Sequence: %A" seq3
(* using yield *)
let seq4 = seq { for a in 1 .. 10 do yield a, a*a, a*a*a }
printfn "The Sequence: %A" seq4
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The Sequence: seq [1; 2; 3; 4; ...] The Sequence: seq [1; 6; 11; 16; ...] The Sequence: seq [50; 45; 40; 35; ...] The Sequence: seq [(1, 1, 1); (2, 4, 8); (3, 9, 27); (4, 16, 64); ...]
示例 2
以下程式列印 1 到 50 之間的素數:
(* Recursive isprime function. *)
let isprime n =
let rec check i =
i > n/2 || (n % i <> 0 && check (i + 1))
check 2
let primeIn50 = seq { for n in 1..50 do if isprime n then yield n }
for x in primeIn50 do
printfn "%d" x
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
1 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 31 37 41 43 47
序列的基本操作
下表顯示了序列資料型別上的基本操作:
| 值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| append : seq<'T> → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 將兩個給定的列舉包裝為單個連線的列舉。 |
| average : seq<^T> → ^T | 返回序列中元素的平均值。 |
| averageBy : ('T → ^U) → seq<'T> → ^U | 返回透過將函式應用於序列的每個元素生成的平均值。 |
| cache : seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個與輸入序列的快取版本對應的序列。 |
| cast : IEnumerable → seq<'T> | 將鬆散型別的 System.Collections 序列包裝為型別化序列。 |
| choose : ('T → 'U option) → seq<'T> → seq<'U> | 將給定函式應用於列表的每個元素。返回由每個元素的結果組成的列表,其中函式返回Some。 |
| collect : ('T → 'Collection) → seq<'T> → seq<'U> | 將給定函式應用於序列的每個元素並連線所有結果。 |
| compareWith : ('T → 'T → int) → seq<'T> → seq<'T> → int | 使用給定的比較函式逐元素比較兩個序列。 |
| concat : seq<'Collection> → seq<'T> | 將給定的列舉-列舉組合為單個連線的列舉。 |
| countBy : ('T → 'Key) → seq<'T> → seq<'Key * int> | 將鍵生成函式應用於序列的每個元素,並返回一個序列,該序列包含唯一的鍵及其在原始序列中的出現次數。 |
| delay : (unit → seq<'T>) → seq<'T> | 返回一個根據給定的延遲序列規範構建的序列。 |
| distinct : seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個序列,該序列根據元素上的泛型雜湊和相等性比較不包含重複項。如果某個元素在序列中出現多次,則丟棄後續出現。 |
| distinctBy : ('T → 'Key) → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個序列,該序列根據給定鍵生成函式返回的鍵上的泛型雜湊和相等性比較不包含重複項。如果某個元素在序列中出現多次,則丟棄後續出現。 |
| empty : seq<'T> | 建立一個空序列。 |
| exactlyOne : seq<'T> → 'T | 返回序列中唯一的元素。 |
| exists : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → bool | 測試序列中的任何元素是否滿足給定的謂詞。 |
| exists2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → bool) → seq<'T1> → seq<'T2> → bool | 測試輸入序列的任何一對對應元素是否滿足給定的謂詞。 |
| filter : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個新集合,其中只包含給定謂詞返回true 的集合的元素。 |
| find : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → 'T | 返回給定函式返回true 的第一個元素。 |
| findIndex : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → int | 返回第一個使給定函式返回 **true** 的元素的索引。 |
| fold : ('State → 'T → 'State) → 'State → seq<'T> → 'State | 將函式應用於集合的每個元素,並將累加器引數貫穿計算。如果輸入函式為 f,元素為 i0...iN,則此函式計算 f (... (f s i0)...) iN。 |
| forall : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → bool | 測試序列中的所有元素是否滿足給定的謂詞。 |
| forall2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → bool) → seq<'T1> → seq<'T2> → bool | 測試從兩個序列中提取的所有元素對是否滿足給定的謂詞。如果一個序列比另一個序列短,則忽略較長序列的剩餘元素。 |
| groupBy : ('T → 'Key) → seq<'T> → seq<'Key * seq<'T>> | 將鍵生成函式應用於序列的每個元素,併產生唯一的鍵序列。每個唯一鍵還包含與該鍵匹配的所有元素的序列。 |
| head : seq<'T> → 'T | 返回序列的第一個元素。 |
| init : int → (int → 'T) → seq<'T> | 生成一個新的序列,當迭代時,透過呼叫給定函式返回連續的元素,直到給定的計數。呼叫函式的結果不會儲存,也就是說,函式會根據需要重新應用以重新生成元素。該函式將傳遞正在生成的專案的索引。 |
| initInfinite : (int → 'T) → seq<'T> | 生成一個新的序列,當迭代時,將透過呼叫給定函式返回連續的元素。呼叫函式的結果不會儲存,也就是說,函式將根據需要重新應用以重新生成元素。該函式將傳遞正在生成的專案的索引。 |
| isEmpty : seq<'T> → bool | 測試序列是否包含任何元素。 |
| iter : ('T → unit) → seq<'T> → unit | 將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素。 |
| iter2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → unit) → seq<'T1> → seq<'T2> → unit | 同時將給定函式應用於兩個集合。如果一個序列比另一個序列短,則忽略較長序列的剩餘元素。 |
| iteri : (int → 'T → unit) → seq<'T> → unit | 將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素。傳遞給函式的整數表示元素的索引。 |
| last : seq<'T> → 'T | 返回序列的最後一個元素。 |
| length : seq<'T> → int | 返回序列的長度。 |
| map : ('T → 'U) → seq<'T> → seq<'U> | 建立一個新的集合,其元素是將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素的結果。給定函式將在使用從物件檢索到的列舉器的MoveNext方法按需請求元素時應用。 |
| map2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → 'U) → seq<'T1> → seq<'T2> → seq<'U> | 建立一個新的集合,其元素是將給定函式應用於來自兩個序列的對應元素對的結果。如果一個輸入序列比另一個序列短,則忽略較長序列的剩餘元素。 |
| mapi : (int → 'T → 'U) → seq<'T> → seq<'U> | 建立一個新的集合,其元素是將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素的結果。傳遞給函式的整數索引表示正在轉換的元素的索引(從 0 開始)。 |
| max : seq<'T> → 'T | 返回序列中所有元素中最大的元素,使用 Operators.max 進行比較。 |
| maxBy : ('T → 'U) → seq<'T> → 'T | 返回序列中所有元素中最大的元素,使用 Operators.max 對函式結果進行比較。 |
| min : seq<'T> → 'T | 返回序列中所有元素中最小的元素,使用 Operators.min 進行比較。 |
| minBy : ('T → 'U) → seq<'T> → 'T | 返回序列中所有元素中最小的元素,使用 Operators.min 對函式結果進行比較。 |
| nth : int → seq<'T> → 'T | 計算集合中的第 n 個元素。 |
| ofArray : 'T array → seq<'T> | 將給定陣列視為序列。 |
| ofList : 'T list → seq<'T> | 將給定列表視為一個序列。 |
| pairwise : seq<'T> → seq<'T * 'T> | 返回輸入序列中每個元素及其前驅的序列,第一個元素除外,它只作為第二個元素的前驅返回。 |
| pick : ('T → 'U option) → seq<'T> → 'U | 將給定函式應用於連續元素,返回函式返回 **Some** 值的第一個值。 |
| readonly : seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 建立一個新的序列物件,該物件委託給給定的序列物件。這確保了原始序列不能透過型別轉換被重新發現和變異。例如,如果給定一個數組,返回的序列將返回陣列的元素,但不能將返回的序列物件轉換為陣列。 |
| reduce : ('T → 'T → 'T) → seq<'T> → 'T | 將函式應用於序列的每個元素,並將累加器引數貫穿計算。首先將函式應用於前兩個元素。然後將此結果與第三個元素一起輸入函式,依此類推。返回最終結果。 |
| scan : ('State → 'T → 'State) → 'State → seq<'T> → seq<'State> | 類似於 Seq.fold,但按需計算並返回中間結果和最終結果的序列。 |
| singleton : 'T → seq<'T> | 返回僅產生一個專案的序列。 |
| skip : int → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個序列,該序列跳過底層序列的指定數量的元素,然後產生序列的其餘元素。 |
| skipWhile : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個序列,當迭代時,跳過底層序列的元素,而給定的謂詞返回 **true**,然後產生序列的其餘元素。 |
| sort : seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 產生按鍵排序的序列。 |
| sortBy : ('T → 'Key) → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 將鍵生成函式應用於序列的每個元素,併產生按鍵排序的序列。使用 Operators.compare 實現的泛型比較來比較鍵。 |
| sum : seq<^T> → ^T | 返回序列中元素的總和。 |
| sumBy | 返回透過將函式應用於序列的每個元素而生成的總和。 |
| take : int → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回序列中直到指定計數的第一個元素。 |
| takeWhile : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個序列,當迭代時,產生底層序列的元素,而給定的謂詞返回 **true**,然後不返回任何其他元素。 |
| toArray : seq<'T> → 'T[] | 從給定集合建立一個數組。 |
| toList : seq<'T> → 'T list | 從給定集合建立一個列表。 |
| truncate : int → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個序列,當列舉時,返回的元素不超過指定數量。 |
| tryFind : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → 'T option | 返回第一個使給定函式返回 **true** 的元素,如果不存在這樣的元素,則返回 **None**。 |
| tryFindIndex : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → int option | 返回序列中滿足給定謂詞的第一個元素的索引,如果不存在這樣的元素,則返回 **None**。 |
| tryPick : ('T → 'U option) → seq<'T> → 'U option | 將給定函式應用於連續元素,返回函式返回 **Some** 值的第一個值。 |
| unfold : ('State → 'T * 'State option) → 'State → seq<'T> | 返回一個包含給定計算生成的元素的序列。 |
| where : ('T → bool) → seq<'T> → seq<'T> | 返回一個新集合,其中只包含給定謂詞返回 **true** 的集合的元素。Seq.filter 的同義詞。 |
| windowed : int → seq<'T> → seq<'T []> | 返回一個序列,該序列產生包含從輸入序列中提取的元素的滑動視窗。每個視窗都作為新的陣列返回。 |
| zip : seq<'T1> → seq<'T2> → seq<'T1 * 'T2> | 將兩個序列組合成一個配對列表。這兩個序列不必長度相等——當一個序列用盡時,忽略另一個序列中的任何剩餘元素。 |
| zip3 : seq<'T1> → seq<'T2> → seq<'T3> → seq<'T1 * 'T2 * 'T3> | 將三個序列組合成一個三元組列表。這些序列不必長度相等——當一個序列用盡時,忽略其他序列中的任何剩餘元素。 |
以下示例演示了上述某些功能的用法:
示例 1
此程式建立一個空序列,稍後將其填充——
(* Creating sequences *) let emptySeq = Seq.empty let seq1 = Seq.singleton 20 printfn"The singleton sequence:" printfn "%A " seq1 printfn"The init sequence:" let seq2 = Seq.init 5 (fun n -> n * 3) Seq.iter (fun i -> printf "%d " i) seq2 printfn"" (* converting an array to sequence by using cast *) printfn"The array sequence 1:" let seq3 = [| 1 .. 10 |] :> seq<int> Seq.iter (fun i -> printf "%d " i) seq3 printfn"" (* converting an array to sequence by using Seq.ofArray *) printfn"The array sequence 2:" let seq4 = [| 2..2.. 20 |] |> Seq.ofArray Seq.iter (fun i -> printf "%d " i) seq4 printfn""
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The singleton sequence: seq [20] The init sequence: 0 3 6 9 12 The array sequence 1: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 The array sequence 2: 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
請注意:
Seq.empty 方法建立一個空序列。
Seq.singleton 方法建立一個僅包含一個指定元素的序列。
Seq.init 方法建立一個序列,其元素是透過使用給定函式建立的。
Seq.ofArray 和 Seq.ofList<'T> 方法從陣列和列表建立序列。
Seq.iter 方法允許迭代序列。
示例 2
Seq.unfold 方法根據一個計算函式生成一個序列,該函式接受一個狀態並將其轉換以生成序列中的每個後續元素。
以下函式生成前 20 個自然數:
let seq1 = Seq.unfold (fun state -> if (state > 20) then None else Some(state, state + 1)) 0 printfn "The sequence seq1 contains numbers from 0 to 20." for x in seq1 do printf "%d " x printfn" "
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The sequence seq1 contains numbers from 0 to 20. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
示例 3
Seq.truncate 方法根據另一個序列建立一個序列,但將序列限制為指定數量的元素。
Seq.take 方法建立一個新序列,其中包含從序列開頭開始的指定數量的元素。
let mySeq = seq { for i in 1 .. 10 -> 3*i }
let truncatedSeq = Seq.truncate 5 mySeq
let takeSeq = Seq.take 5 mySeq
printfn"The original sequence"
Seq.iter (fun i -> printf "%d " i) mySeq
printfn""
printfn"The truncated sequence"
Seq.iter (fun i -> printf "%d " i) truncatedSeq
printfn""
printfn"The take sequence"
Seq.iter (fun i -> printf "%d " i) takeSeq
printfn""
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The original sequence 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 The truncated sequence 3 6 9 12 15 The take sequence 3 6 9 12 15
F# - 集合
F# 中的集合是一種資料結構,充當專案的集合,但不保留插入專案的順序。集合不允許將重複的條目插入集合中。
建立集合
集合可以透過以下方式建立:
- 使用 Set.empty 建立空集合,並使用 add 函式新增專案。
- 將序列和列表轉換為集合。
以下程式演示了這些技術:
(* creating sets *) let set1 = Set.empty.Add(3).Add(5).Add(7). Add(9) printfn"The new set: %A" set1 let weekdays = Set.ofList ["mon"; "tues"; "wed"; "thurs"; "fri"] printfn "The list set: %A" weekdays let set2 = Set.ofSeq [ 1 .. 2.. 10 ] printfn "The sequence set: %A" set2
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The new set: set [3; 5; 7; 9] The list set: set ["fri"; "mon"; "thurs"; "tues"; "wed"] The sequence set: set [1; 3; 5; 7; 9]
集合的基本操作
下表顯示了集合的基本操作:
| 值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| add : 'T → Set<'T> → Set<'T> | 返回一個新集合,其中添加了一個元素。如果集合已包含給定元素,則不會引發異常。 |
| contains : 'T → Set<'T> → bool | 如果給定元素在給定集合中,則評估為**true**。 |
| count : Set<'T> → int | 返回集合中元素的數量。 |
| difference : Set<'T> → Set<'T> → Set<'T> | 返回一個新集合,其中從第一個集合中刪除了第二個集合的元素。 |
| empty : Set<'T> | 指定型別的空集。 |
| exists : ('T → bool) → Set<'T> → bool | 測試集合中的任何元素是否滿足給定的謂詞。如果輸入函式是謂詞,元素是 i0...iN,則此函式計算謂詞 i0 或 ... 或謂詞 iN。 |
| filter : ('T → bool) → Set<'T> → Set<'T> | 返回一個新集合,其中只包含給定謂詞返回true 的集合的元素。 |
| fold : ('State → 'T → 'State) → 'State → Set<'T> → 'State | 將給定的累加函式應用於集合的所有元素。 |
| foldBack : ('T → 'State → 'State) → Set<'T> → 'State → 'State | 將給定的累加函式應用於集合的所有元素。 |
| forall : ('T → bool) → Set<'T> → bool | 測試集合中的所有元素是否滿足給定的謂詞。如果輸入函式是 p,元素是 i0...iN,則此函式計算 p i0 && ... && p iN。 |
| intersect : Set<'T> → Set<'T> → Set<'T> | 計算兩個集合的交集。 |
| intersectMany : seq<Set<'T>> → Set<'T> | 計算一系列集合的交集。序列必須是非空的。 |
| isEmpty : Set<'T> → bool | 如果集合為空,則返回**true**。 |
| isProperSubset : Set<'T> → Set<'T> → bool | 如果第一個集合的所有元素都在第二個集合中,並且第二個集合中至少有一個元素不在第一個集合中,則評估為**true**。 |
| isProperSuperset : Set<'T> → Set<'T> → bool | 如果第二個集合的所有元素都在第一個集合中,並且第一個集合中至少有一個元素不在第二個集合中,則評估為**true**。 |
| isSubset : Set<'T> → Set<'T> → bool | 如果第一個集合的所有元素都在第二個集合中,則評估為**true**。 |
| isSuperset : Set<'T> → Set<'T> → bool | 如果第二個集合的所有元素都在第一個集合中,則評估為**true**。 |
| iter : ('T → unit) → Set<'T> → unit | 根據比較函式,將給定函式應用於集合的每個元素。 |
| map : ('T → 'U) → Set<'T> → Set<'U> | 返回一個新集合,其中包含將給定函式應用於輸入集合的每個元素的結果。 |
| maxElement : Set<'T> → 'T | 根據集合使用的排序返回集合中最高的元素。 |
| minElement : Set<'T> → 'T | 根據集合使用的排序返回集合中最低的元素。 |
| ofArray : 'T array → Set<'T> | 建立一個包含與給定陣列相同元素的集合。 |
| ofList : 'T list → Set<'T> | 建立一個包含與給定列表相同元素的集合。 |
| ofSeq : seq<'T> → Set<'T> | 根據給定的可列舉物件建立一個新集合。 |
| partition : ('T → bool) → Set<'T> → Set<'T> * Set<'T> | 將集合拆分為兩個集合,分別包含給定謂詞返回 true 和 false 的元素。 |
| remove : 'T → Set<'T> → Set<'T> | 返回一個新集合,其中刪除了給定元素。如果集合不包含給定元素,則不會引發異常。 |
| singleton : 'T → Set<'T> | 包含給定元素的集合。 |
| toArray : Set<'T> → 'T array | 建立一個數組,其中按順序包含集合的元素。 |
| toList : Set<'T> → 'T list | 建立一個列表,其中按順序包含集合的元素。 |
| toSeq : Set<'T> → seq<'T> | 將集合的排序檢視作為可列舉物件返回。 |
| union : Set<'T> → Set<'T> → Set<'T> | 計算兩個集合的並集。 |
| unionMany : seq<Set<'T>> → Set<'T> | 計算一系列集合的並集。 |
以下示例演示了上述一些功能的用法:
示例
let a = Set.ofSeq [ 1 ..2.. 20 ] let b = Set.ofSeq [ 1 ..3 .. 20 ] let c = Set.intersect a b let d = Set.union a b let e = Set.difference a b printfn "Set a: " Set.iter (fun x -> printf "%O " x) a printfn"" printfn "Set b: " Set.iter (fun x -> printf "%O " x) b printfn"" printfn "Set c = set intersect of a and b : " Set.iter (fun x -> printf "%O " x) c printfn"" printfn "Set d = set union of a and b : " Set.iter (fun x -> printf "%O " x) d printfn"" printfn "Set e = set difference of a and b : " Set.iter (fun x -> printf "%O " x) e printfn""
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Set a: 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 Set b: 1 4 7 10 13 16 19 Set c = set intersect of a and b : 1 7 13 19 Set d = set union of a and b : 1 3 4 5 7 9 10 11 13 15 16 17 19 Set e = set difference of a and b : 3 5 9 11 15 17
F# - 對映
在 F# 中,對映是一種特殊的集合,它將值與鍵關聯。對映的建立方式與集合的建立方式類似。
建立對映
透過使用 Map.empty 建立空對映並使用 Add 函式新增專案來建立對映。以下示例演示了這一點:
示例
(* Create an empty Map *)
let students =
Map.empty. (* Creating an empty Map *)
Add("Zara Ali", "1501").
Add("Rishita Gupta", "1502").
Add("Robin Sahoo", "1503").
Add("Gillian Megan", "1504");;
printfn "Map - students: %A" students
(* Convert a list to Map *)
let capitals =
[ "Argentina", "Buenos Aires";
"France ", "Paris";
"Chili", "Santiago";
"Malaysia", " Kuala Lumpur";
"Switzerland", "Bern" ]
|> Map.ofList;;
printfn "Map capitals : %A" capitals
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Map - students: map
[("Gillian Megan", "1504"); ("Rishita Gupta", "1502"); ("Robin Sahoo", "1503
");
("Zara Ali", "1501")]
Map capitals : map
[("Argentina", "Buenos Aires"); ("Chili", "Santiago"); ("France ", "Paris");
("Malaysia", " Kuala Lumpur"); ("Switzerland", "Bern")]
可以使用鍵訪問對映中的單個元素。
示例
(* Create an empty Map *)
let students =
Map.empty. (* Creating an empty Map *)
Add("Zara Ali", "1501").
Add("Rishita Gupta", "1502").
Add("Robin Sahoo", "1503").
Add("Gillian Megan", "1504");;
printfn "Map - students: %A" students
(*Accessing an element using key *)
printfn "%A" students.["Zara Ali"]
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Map - students: map
[("Gillian Megan", "1504"); ("Rishita Gupta", "1502"); ("Robin Sahoo", "1503
");
("Zara Ali", "1501")]
"1501"
對映的基本操作
新增模組名稱
下表顯示了對映的基本操作:
| 成員 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Add | 返回一個新對映,其中將繫結新增到給定對映中。 |
| ContainsKey | 測試元素是否在對映的域中。 |
| Count | 對映中的繫結數。 |
| IsEmpty | 如果對映中沒有繫結,則返回 true。 |
| Item | 查詢對映中的元素。如果對映中不存在繫結,則引發 KeyNotFoundException。 |
| Remove | 從對映的域中刪除元素。如果元素不存在,則不會引發異常。 |
| TryFind | 查詢對映中的元素,如果元素在對映的域中則返回**Some**值,否則返回**None**。 |
以下示例演示了上述一些功能的用法:
示例
(* Create an empty Map *)
let students =
Map.empty. (* Creating an empty Map *)
Add("Zara Ali", "1501").
Add("Rishita Gupta", "1502").
Add("Robin Sahoo", "1503").
Add("Gillian Megan", "1504").
Add("Shraddha Dubey", "1505").
Add("Novonil Sarker", "1506").
Add("Joan Paul", "1507");;
printfn "Map - students: %A" students
printfn "Map - number of students: %d" students.Count
(* finding the registration number of a student*)
let found = students.TryFind "Rishita Gupta"
match found with
| Some x -> printfn "Found %s." x
| None -> printfn "Did not find the specified value."
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Map - students: map
[("Gillian Megan", "1504"); ("Joan Paul", "1507"); ("Novonil Sarker", "1506"
);
("Rishita Gupta", "1502"); ("Robin Sahoo", "1503");
("Shraddha Dubey", "1505"); ("Zara Ali", "1501")]
Map - number of students: 7
Found 1502.
F# - 判別聯合
聯合,或區分聯合允許您構建表示明確定義的選擇集的複雜資料結構。例如,您需要構建一個 *選擇* 變數的實現,該變數具有 yes 和 no 兩個值。使用聯合工具,您可以設計此變數。
語法
區分聯合使用以下語法定義:
type type-name = | case-identifier1 [of [ fieldname1 : ] type1 [ * [ fieldname2 : ] type2 ...] | case-identifier2 [of [fieldname3 : ]type3 [ * [ fieldname4 : ]type4 ...] ...
我們對 *選擇* 的簡單實現如下所示:
type choice = | Yes | No
以下示例使用 choice 型別:
type choice = | Yes | No let x = Yes (* creates an instance of choice *) let y = No (* creates another instance of choice *) let main() = printfn "x: %A" x printfn "y: %A" y main()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
x: Yes y: No
示例 1
以下示例顯示了電壓狀態的實現,該狀態設定高或低位:
type VoltageState = | High | Low let toggleSwitch = function (* pattern matching input *) | High -> Low | Low -> High let main() = let on = High let off = Low let change = toggleSwitch off printfn "Switch on state: %A" on printfn "Switch off state: %A" off printfn "Toggle off: %A" change printfn "Toggle the Changed state: %A" (toggleSwitch change) main()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Switch on state: High Switch off state: Low Toggle off: High Toggle the Changed state: Low
示例 2
type Shape = // here we store the radius of a circle | Circle of float // here we store the side length. | Square of float // here we store the height and width. | Rectangle of float * float let pi = 3.141592654 let area myShape = match myShape with | Circle radius -> pi * radius * radius | Square s -> s * s | Rectangle (h, w) -> h * w let radius = 12.0 let myCircle = Circle(radius) printfn "Area of circle with radius %g: %g" radius (area myCircle) let side = 15.0 let mySquare = Square(side) printfn "Area of square that has side %g: %g" side (area mySquare) let height, width = 5.0, 8.0 let myRectangle = Rectangle(height, width) printfn "Area of rectangle with height %g and width %g is %g" height width (area myRectangle)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Area of circle with radius 12: 452.389 Area of square that has side 15: 225 Area of rectangle with height 5 and width 8 is 40
F# - 可變資料
F#中的變數是不可變的,這意味著一旦變數繫結到一個值,就不能更改它。它們實際上被編譯為靜態只讀屬性。
以下示例演示了這一點。
示例
let x = 10 let y = 20 let z = x + y printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z let x = 15 let y = 20 let z = x + y printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z
編譯並執行程式時,它會顯示以下錯誤訊息:
Duplicate definition of value 'x' Duplicate definition of value 'Y' Duplicate definition of value 'Z'
可變變數
有時需要更改儲存在變數中的值。為了指定在程式的後面部分,宣告和賦值的變數的值可能會發生變化,F# 提供了**mutable**關鍵字。您可以使用此關鍵字宣告和賦值可變變數,其值將更改。
mutable關鍵字允許您宣告和賦值可變變數的值。
您可以使用**let**關鍵字為可變變數賦值初始值。但是,要為其賦值新的後續值,您需要使用**<-**運算子。
例如:
let mutable x = 10 x <- 15
以下示例將闡明這個概念:
示例
let mutable x = 10 let y = 20 let mutable z = x + y printfn "Original Values:" printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z printfn "Let us change the value of x" printfn "Value of z will change too." x <- 15 z <- x + y printfn "New Values:" printfn "x: %i" x printfn "y: %i" y printfn "z: %i" z
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Original Values: x: 10 y: 20 z: 30 Let us change the value of x Value of z will change too. New Values: x: 15 y: 20 z: 35
可變資料的用途
可變資料通常在資料處理中需要並使用,尤其是在記錄資料結構中。以下示例演示了這一點:
open System
type studentData =
{ ID : int;
mutable IsRegistered : bool;
mutable RegisteredText : string; }
let getStudent id =
{ ID = id;
IsRegistered = false;
RegisteredText = null; }
let registerStudents (students : studentData list) =
students |> List.iter(fun st ->
st.IsRegistered <- true
st.RegisteredText <- sprintf "Registered %s" (DateTime.Now.ToString("hh:mm:ss"))
Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000) (* Putting thread to sleep for 1 second to simulate processing overhead. *))
let printData (students : studentData list) =
students |> List.iter (fun x -> printfn "%A" x)
let main() =
let students = List.init 3 getStudent
printfn "Before Process:"
printData students
printfn "After process:"
registerStudents students
printData students
Console.ReadKey(true) |> ignore
main()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Before Process:
{ID = 0;
IsRegistered = false;
RegisteredText = null;}
{ID = 1;
IsRegistered = false;
RegisteredText = null;}
{ID = 2;
IsRegistered = false;
RegisteredText = null;}
After process:
{ID = 0;
IsRegistered = true;
RegisteredText = "Registered 05:39:15";}
{ID = 1;
IsRegistered = true;
RegisteredText = "Registered 05:39:16";}
{ID = 2;
IsRegistered = true;
RegisteredText = "Registered 05:39:17";}
F# - 陣列
陣列是固定大小、基於零的、可變的連續資料元素集合,所有元素都是同一型別。
建立陣列
您可以使用各種語法和方法,或使用 Array 模組中的函式來建立陣列。在本節中,我們將討論在不使用模組函式的情況下建立陣列。
在不使用函式的情況下,建立陣列有三種語法方式:
- 透過在 [| 和 |] 之間列出連續的值,並用分號分隔。
- 透過將每個元素放在單獨一行,在這種情況下,分號分隔符是可選的。
- 透過使用序列表達式。
您可以使用點運算子 (.) 和方括號 ([ 和 ]) 來訪問陣列元素。
以下示例演示了建立陣列:
//using semicolon separator
let array1 = [| 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6 |]
for i in 0 .. array1.Length - 1 do
printf "%d " array1.[i]
printfn" "
// without semicolon separator
let array2 =
[|
1
2
3
4
5
|]
for i in 0 .. array2.Length - 1 do
printf "%d " array2.[i]
printfn" "
//using sequence
let array3 = [| for i in 1 .. 10 -> i * i |]
for i in 0 .. array3.Length - 1 do
printf "%d " array3.[i]
printfn" "
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81 100
陣列的基本操作
庫模組 Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.Array 支援對一維陣列的操作。
下表顯示了陣列的基本操作:
| 值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| append : 'T [] → 'T [] → 'T [] | 建立一個數組,其中包含一個數組的元素,然後是另一個數組的元素。 |
| average : ^T [] → ^T | 返回陣列中元素的平均值。 |
| averageBy : ('T → ^U) → 'T [] → ^U | 返回透過將函式應用於陣列的每個元素生成的元素的平均值。 |
| blit : 'T [] → int → 'T [] → int → int → unit | 讀取一個數組中的一個元素範圍,並將它們寫入另一個數組。 |
| choose : ('T → U option) → 'T [] → 'U [] | 將提供的函式應用於陣列的每個元素。返回一個數組,其中包含每個元素的函式返回 Some(x) 的結果 x。 |
| collect : ('T → 'U []) → T [] → 'U [] | 將提供的函式應用於陣列的每個元素,連線結果,並返回組合陣列。 |
| concat : seq<'T []> → 'T [] | 建立一個數組,其中包含提供的陣列序列中每個陣列的元素。 |
| copy : 'T → 'T [] | 建立一個數組,其中包含提供的陣列的元素。 |
| create : int → 'T → 'T [] | 建立一個數組,其元素最初都是提供的 value。 |
| empty : 'T [] | 返回給定型別的空陣列。 |
| exists : ('T → bool) → 'T [] → bool | 測試陣列中的任何元素是否滿足提供的謂詞。 |
| exists2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → bool) → 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → bool | 測試兩個陣列的任何一對對應元素是否滿足提供的條件。 |
| fill : 'T [] → int → int → 'T → unit | 用提供的 value 填充陣列的元素範圍。 |
| filter : ('T → bool) → 'T [] → 'T [] | 返回一個集合,其中僅包含提供的陣列中提供的條件返回**true**的元素。 |
| find : ('T → bool) → 'T [] → 'T | 返回提供的函式返回**true**的第一個元素。如果沒有這樣的元素,則引發 KeyNotFoundException。 |
| findIndex : ('T → bool) → 'T [] → int | 返回陣列中滿足提供的條件的第一個元素的索引。如果沒有任何元素滿足該條件,則引發 KeyNotFoundException。 |
| fold : ('State → 'T → 'State) → 'State → 'T [] → 'State | 將函式應用於陣列的每個元素,將累加器引數貫穿計算。如果輸入函式是 f,陣列元素是 i0...iN,則此函式計算 f (...(f s i0)...) iN。 |
| fold2 : ('State → 'T1 → 'T2 → 'State) → 'State → 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → 'State | 將函式應用於來自兩個提供的陣列的元素對,從左到右,將累加器引數貫穿計算。兩個輸入陣列必須具有相同的長度;否則,將引發 ArgumentException。 |
| foldBack : ('T → 'State → 'State) → 'T [] → 'State → 'State | 將一個函式應用於陣列的每個元素,並將累加器引數貫穿計算過程。如果輸入函式為 f,陣列元素為 i0...iN,則此函式計算 f i0 (...(f iN s))。 |
| foldBack2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → 'State → 'State) → 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → 'State → 'State | 將一個函式應用於兩個提供的陣列中元素對,從右到左,並將累加器引數貫穿計算過程。兩個輸入陣列必須長度相同;否則,將引發 ArgumentException。 |
| forall : ('T → bool) → 'T [] → bool | 測試陣列中的所有元素是否都滿足提供的條件。 |
| forall2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → bool) → 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → bool | 測試兩個提供的陣列中所有對應元素是否都滿足提供的條件。 |
| get : 'T [] → int → 'T | 從陣列中獲取一個元素。 |
| init : int → (int → 'T) → 'T [] | 使用提供的函式建立一個指定維度的陣列。 |
| isEmpty : 'T [] → bool | 測試陣列是否包含任何元素。 |
| iter : ('T → unit) → 'T [] → unit | 將提供的函式應用於陣列的每個元素。 |
| iter2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → unit) → 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → unit | 將提供的函式應用於兩個陣列中對應索引的元素對。兩個陣列必須長度相同;否則,將引發 ArgumentException。 |
| iteri : (int → 'T → unit) → 'T [] → unit | 將提供的函式應用於陣列的每個元素。傳遞給函式的整數表示元素的索引。 |
| iteri2 : (int → 'T1 → 'T2 → unit) → 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → unit | 將提供的函式應用於兩個陣列中對應索引的元素對,並傳遞元素的索引。兩個陣列必須長度相同;否則,將引發 ArgumentException。 |
| length : 'T [] → int | 返回陣列的長度。Length 屬性具有相同的功能。 |
| map : ('T → 'U) → 'T [] → 'U [] | 建立一個數組,其元素是將提供的函式應用於提供的陣列的每個元素的結果。 |
| map2 : ('T1 → 'T2 → 'U) → 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → 'U [] | 建立一個數組,其元素是將提供的函式應用於兩個提供的陣列的對應元素的結果。兩個輸入陣列必須長度相同;否則,將引發 ArgumentException。 |
| mapi : (int → 'T → 'U) → 'T [] → 'U [] | 建立一個數組,其元素是將提供的函式應用於提供的陣列的每個元素的結果。傳遞給函式的整數索引指示正在轉換的元素的索引。 |
| mapi2 : (int → 'T1 → 'T2 → 'U) → 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → 'U [] | 建立一個數組,其元素是將提供的函式應用於兩個集合的對應元素的成對結果,並傳遞元素的索引。兩個輸入陣列必須長度相同;否則,將引發 ArgumentException。 |
| max : 'T [] → 'T | 返回陣列中所有元素的最大值。使用 Operators.max 來比較元素。 |
| maxBy : ('T → 'U) → 'T [] → 'T | 返回陣列中所有元素的最大值,透過函式結果上的 Operators.max 進行比較。 |
| min : ('T [] → 'T | 返回陣列中所有元素的最小值。使用 Operators.min 來比較元素。 |
| minBy : ('T → 'U) → 'T [] → 'T | 返回陣列中所有元素的最小值。使用 Operators.min 來比較元素。 |
| ofList : 'T list → 'T [] | 根據提供的列表建立一個數組。 |
| ofSeq : seq<'T> → 'T [] | 根據提供的可列舉物件建立一個數組。 |
| partition : ('T → bool) → 'T [] → 'T [] * 'T [] | 將陣列拆分為兩個陣列,一個包含提供的條件返回 **true** 的元素,另一個包含返回 **false** 的元素。 |
| permute : (int → int) → 'T [] → 'T [] | 根據指定的排列對陣列的元素進行排列。 |
| pick : ('T → 'U option) → 'T [] → 'U | 將提供的函式應用於提供的陣列的連續元素,返回函式對某些 x 返回 Some(x) 的第一個結果。如果函式從未返回 Some(x),則引發 KeyNotFoundException。 |
| reduce : ('T → 'T → 'T) → 'T [] → 'T | 將一個函式應用於陣列的每個元素,並將累加器引數貫穿計算過程。如果輸入函式為 f,陣列元素為 i0...iN,則此函式計算 f (...(f i0 i1)...) iN。如果陣列大小為零,則引發 ArgumentException。 |
| reduceBack : ('T → 'T → 'T) → 'T [] → 'T | 將一個函式應用於陣列的每個元素,並將累加器引數貫穿計算過程。如果輸入函式為 f,元素為 i0...iN,則此函式計算 f i0 (...(f iN-1 iN))。如果陣列大小為零,則引發 ArgumentException。 |
| rev : 'T [] → 'T [] | 反轉提供的陣列中元素的順序。 |
| scan : ('State → 'T → 'State) → 'State → 'T [] → 'State [] | 類似於 fold,但會返回中間結果以及最終結果。 |
| scanBack : ('T → 'State → 'State) → 'T [] → 'State → 'State [] | 類似於 foldBack,但會返回中間結果以及最終結果。 |
| set : 'T [] → int → 'T → unit | 設定陣列中的一個元素。 |
| sort : 'T[] → 'T [] | 對陣列的元素進行排序並返回一個新陣列。使用 Operators.compare 來比較元素。 |
| sortBy : ('T → 'Key) → 'T [] → 'T [] | 透過使用提供的函式將元素轉換為進行排序操作的型別來對陣列的元素進行排序,並返回一個新陣列。使用 Operators.compare 來比較元素。 |
| sortInPlace : 'T [] → unit | 透過就地更改陣列來對陣列的元素進行排序,使用提供的比較函式。使用 Operators.compare 來比較元素。 |
| sortInPlaceBy : ('T → 'Key) → 'T [] → unit | 透過使用提供的鍵投影就地更改陣列來對陣列的元素進行排序。使用 Operators.compare 來比較元素。 |
| sortInPlaceWith : ('T → 'T → int) → 'T [] → unit | 使用提供的比較函式對陣列的元素進行排序,並就地更改陣列。 |
| sortWith : ('T → 'T → int) → 'T [] → 'T [] | 使用提供的比較函式對陣列的元素進行排序,並返回一個新陣列。 |
| sub : 'T [] → int → int → 'T [] | 建立一個包含提供的子範圍的陣列,該子範圍由起始索引和長度指定。 |
| sum : 'T [] → ^T | 返回陣列中元素的總和。 |
| sumBy : ('T → ^U) → 'T [] → ^U | 返回透過將函式應用於陣列的每個元素生成的總和。 |
| toList : 'T [] → 'T list | 將提供的陣列轉換為列表。 |
| toSeq : 'T [] → seq<'T> | 將提供的陣列視為一個序列。 |
| tryFind : ('T → bool) → 'T [] → 'T option | 返回提供的陣列中提供的函式返回 **true** 的第一個元素。如果不存在這樣的元素,則返回 **None**。 |
| tryFindIndex : ('T → bool) → 'T [] → int option | 返回陣列中第一個滿足提供的條件的元素的索引。 |
| tryPick : ('T → 'U option) → 'T [] → 'U option | 將提供的函式應用於提供的陣列的連續元素,並返回函式對某些 x 返回 Some(x) 的第一個結果。如果函式從未返回 Some(x),則返回 **None**。 |
| unzip : ('T1 * 'T2) [] → 'T1 [] * 'T2 [] | 將元組對陣列拆分為兩個陣列的元組。 |
| unzip3 : ('T1 * 'T2 * 'T3) [] → 'T1 [] * 'T2 [] * 'T3 [] | 將三個元素的元組陣列拆分為三個陣列的元組。 |
| zeroCreate : int → 'T [] | 建立一個數組,其元素最初設定為預設值 Unchecked.defaultof<'T>。 |
| zip : 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → ('T1 * 'T2) [] | 將兩個陣列組合成一個包含兩個元素的元組陣列。兩個陣列必須長度相等;否則,將引發 ArgumentException。 |
| zip3 : 'T1 [] → 'T2 [] → 'T3 [] → ('T1 * 'T2 * 'T3) [] | 將三個陣列組合成一個包含三個元素的元組陣列。三個陣列必須長度相等;否則,將引發 ArgumentException。 |
在下一節中,我們將瞭解這些功能的一些用法。
使用函式建立陣列
Array 模組提供了一些從頭建立陣列的函式。
**Array.empty** 函式建立一個新的空陣列。
**Array.create** 函式建立一個指定大小的陣列,並將所有元素設定為給定值。
**Array.init** 函式根據維度和生成元素的函式建立一個數組。
**Array.zeroCreate** 函式建立一個所有元素都初始化為零值的陣列。
**Array.copy** 函式建立一個包含從現有陣列複製的元素的新陣列。
**Array.sub** 函式根據陣列的子範圍生成一個新陣列。
**Array.append** 函式透過組合兩個現有陣列建立一個新陣列。
**Array.choose** 函式選擇陣列中的元素以包含在新陣列中。
Array.collect 函式對現有陣列的每個陣列元素執行指定函式,然後收集函式生成的元素並將它們組合成一個新陣列。
Array.concat 函式接受一系列陣列並將它們組合成單個數組。
Array.filter 函式接受一個布林條件函式,並生成一個新陣列,該陣列僅包含輸入陣列中滿足條件的元素。
Array.rev 函式透過反轉現有陣列的順序來生成一個新陣列。
以下示例演示了這些函式:
示例 1
(* using create and set *) let array1 = Array.create 10 "" for i in 0 .. array1.Length - 1 do Array.set array1 i (i.ToString()) for i in 0 .. array1.Length - 1 do printf "%s " (Array.get array1 i) printfn " " (* empty array *) let array2 = Array.empty printfn "Length of empty array: %d" array2.Length let array3 = Array.create 10 7.0 printfn "Float Array: %A" array3 (* using the init and zeroCreate *) let array4 = Array.init 10 (fun index -> index * index) printfn "Array of squares: %A" array4 let array5 : float array = Array.zeroCreate 10 let (myZeroArray : float array) = Array.zeroCreate 10 printfn "Float Array: %A" array5
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Length of empty array: 0 Float Array: [|7.0; 7.0; 7.0; 7.0; 7.0; 7.0; 7.0; 7.0; 7.0; 7.0|] Array of squares: [|0; 1; 4; 9; 16; 25; 36; 49; 64; 81|] Float Array: [|0.0; 0.0; 0.0; 0.0; 0.0; 0.0; 0.0; 0.0; 0.0; 0.0|]
示例 2
(* creating subarray from element 5 *)
(* containing 15 elements thereon *)
let array1 = [| 0 .. 50 |]
let array2 = Array.sub array1 5 15
printfn "Sub Array:"
printfn "%A" array2
(* appending two arrays *)
let array3 = [| 1; 2; 3; 4|]
let array4 = [| 5 .. 9 |]
printfn "Appended Array:"
let array5 = Array.append array3 array4
printfn "%A" array5
(* using the Choose function *)
let array6 = [| 1 .. 20 |]
let array7 = Array.choose (fun elem -> if elem % 3 = 0 then
Some(float (elem))
else
None) array6
printfn "Array with Chosen elements:"
printfn "%A" array7
(*using the Collect function *)
let array8 = [| 2 .. 5 |]
let array9 = Array.collect (fun elem -> [| 0 .. elem - 1 |]) array8
printfn "Array with collected elements:"
printfn "%A" array9
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Sub Array: [|5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10; 11; 12; 13; 14; 15; 16; 17; 18; 19|] Appended Array: [|1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9|] Array with Chosen elements: [|3.0; 6.0; 9.0; 12.0; 15.0; 18.0|] Array with collected elements: [|0; 1; 0; 1; 2; 0; 1; 2; 3; 0; 1; 2; 3; 4|]
陣列搜尋
Array.find 函式接受一個布林函式,並返回該函式返回 true 的第一個元素,否則引發 KeyNotFoundException。
Array.findIndex 函式的工作方式類似,只是它返回元素的索引而不是元素本身。
以下示例演示了這一點。
Microsoft 提供了這個有趣的程式示例,它查詢給定數字範圍內第一個既是完全平方數又是完全立方數的元素:
let array1 = [| 2 .. 100 |] let delta = 1.0e-10 let isPerfectSquare (x:int) = let y = sqrt (float x) abs(y - round y) < delta let isPerfectCube (x:int) = let y = System.Math.Pow(float x, 1.0/3.0) abs(y - round y) < delta let element = Array.find (fun elem -> isPerfectSquare elem && isPerfectCube elem) array1 let index = Array.findIndex (fun elem -> isPerfectSquare elem && isPerfectCube elem) array1 printfn "The first element that is both a square and a cube is %d and its index is %d." element index
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
The first element that is both a square and a cube is 64 and its index is 62.
F# - 可變列表
List<'T> 類表示可以透過索引訪問的物件的強型別列表。
它是 List 類的可變對應物。它類似於陣列,因為它可以透過索引訪問,但是,與陣列不同的是,列表可以調整大小。因此,您無需在宣告期間指定大小。
建立可變列表
列表是使用 new 關鍵字並呼叫列表的建構函式建立的。以下示例演示了這一點:
(* Creating a List *)
open System.Collections.Generic
let booksList = new List<string>()
booksList.Add("Gone with the Wind")
booksList.Add("Atlas Shrugged")
booksList.Add("Fountainhead")
booksList.Add("Thornbirds")
booksList.Add("Rebecca")
booksList.Add("Narnia")
booksList |> Seq.iteri (fun index item -> printfn "%i: %s" index booksList.[index])
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
0: Gone with the Wind 1: Atlas Shrugged 2: Fountainhead 3: Thornbirds 4: Rebecca 5: Narnia
List(T) 類
List(T) 類表示可以透過索引訪問的物件的強型別列表。它提供用於搜尋、排序和操作列表的方法。
下表提供了 List(T) 類的屬性、建構函式和方法:
屬性
| 屬性 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Capacity (容量) | 獲取或設定內部資料結構在無需調整大小的情況下可以容納的元素總數。 |
| Count | 獲取 List(T) 中包含的元素數量。 |
| Item | 獲取或設定指定索引處的元素。 |
建構函式
| 建構函式 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| List(T)() | 初始化一個新的空 List(T) 類例項,並具有預設初始容量。 |
| List(T)(IEnumerable(T)) | 初始化一個新的 List(T) 類例項,其中包含從指定集合複製的元素,並且具有足夠的容量來容納複製的元素數量。 |
| List(T)(Int32) | 初始化一個新的空 List(T) 類例項,並具有指定的初始容量。 |
方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Add | 將物件新增到 List(T) 的末尾。 |
| AddRange | 將指定集合的元素新增到 List(T) 的末尾。 |
| AsReadOnly | 返回當前集合的只讀 IList(T) 包裝器。 |
| BinarySearch(T) | 使用預設比較器搜尋整個已排序的 List(T) 中的元素,並返回該元素的基於零的索引。 |
| BinarySearch(T, IComparer(T)) | 使用指定的比較器搜尋整個已排序的 List(T) 中的元素,並返回該元素的基於零的索引。 |
| BinarySearch(Int32, Int32, T, IComparer(T)) | 使用指定的比較器搜尋已排序 List(T) 中的元素範圍,並返回該元素的基於零的索引。 |
| Clear | 刪除 List(T) 中的所有元素。 |
| Contains | 確定 List(T) 中是否包含某個元素。 |
| ConvertAll(TOutput) | 將當前 List(T) 中的元素轉換為另一種型別,並返回包含已轉換元素的列表。 |
| CopyTo(T[]) | 將整個 List(T) 複製到相容的一維陣列中,從目標陣列的開頭開始。 |
| CopyTo(T[], Int32) | 將整個 List(T) 複製到相容的一維陣列中,從目標陣列的指定索引開始。 |
| CopyTo(Int32, T[], Int32, Int32) | 將 List(T) 中的元素範圍複製到相容的一維陣列中,從目標陣列的指定索引開始。 |
| Equals(Object) | 確定指定的 Object 是否等於當前 Object。(繼承自 Object。) |
| Exists | 確定 List(T) 是否包含與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素。 |
| Finalize | 允許物件在被垃圾回收之前嘗試釋放資源並執行其他清理操作(繼承自 Object)。 |
| Find | 搜尋與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素,並返回整個 List(T) 中的第一次出現。 |
| FindAll | 檢索與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的所有元素。 |
| FindIndex(Predicate(T)) | 搜尋與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素,並返回整個 List(T) 中第一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| FindIndex(Int32, Predicate(T)) | 搜尋與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素,並返回 List(T) 中從指定索引擴充套件到最後一個元素的元素範圍內第一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| FindIndex(Int32, Int32, Predicate(T)) | 搜尋與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素,並返回 List(T) 中從指定索引開始幷包含指定數量元素的元素範圍內第一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| FindLast | 搜尋與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素,並返回整個 List(T) 中的最後一次出現。 |
| FindLastIndex(Predicate(T)) | 搜尋與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素,並返回整個 List(T) 中最後一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| FindLastIndex(Int32, Predicate(T)) | 搜尋與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素,並返回 List(T) 中從第一個元素擴充套件到指定索引的元素範圍內最後一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| FindLastIndex(Int32, Int32, Predicate(T)) | 搜尋與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的元素,並返回 List(T) 中包含指定數量元素並以指定索引結尾的元素範圍內最後一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| ForEach | 對 List(T) 的每個元素執行指定的動作。 |
| GetEnumerator | 返回一個迭代 List(T) 的列舉器。 |
| GetHashCode | 用作預設雜湊函式。(繼承自 Object。) |
| GetRange | 建立源 List(T) 中的元素範圍的淺表副本。 |
| GetType | 獲取當前例項的 Type。(繼承自 Object。) |
| IndexOf(T) | 搜尋指定的 Object 並返回整個 List(T) 中第一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| IndexOf(T, Int32) | 搜尋指定的 Object 並返回 List(T) 中從指定索引擴充套件到最後一個元素的元素範圍內第一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| IndexOf(T, Int32, Int32) | 搜尋指定的 Object 並返回 List(T) 中從指定索引開始幷包含指定數量元素的元素範圍內第一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| Insert | 在 List(T) 的指定索引處插入元素。 |
| InsertRange | 在 List(T) 的指定索引處插入集合的元素。 |
| LastIndexOf(T) | 搜尋指定的 Object 並返回整個 List(T) 中最後一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| LastIndexOf(T, Int32) | 搜尋指定的 Object 並返回 List(T) 中從第一個元素擴充套件到指定索引的元素範圍內最後一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| LastIndexOf(T, Int32, Int32) | 搜尋指定的 Object 並返回 List(T) 中包含指定數量元素並以指定索引結尾的元素範圍內最後一次出現的基於零的索引。 |
| MemberwiseClone | 建立當前 Object 的淺表副本。(繼承自 Object。) |
| Remove | 從 List(T) 中刪除特定物件的第一次出現。 |
| RemoveAll | 刪除與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配的所有元素。 |
| RemoveAt | 刪除 List(T) 指定索引處的元素。 |
| RemoveRange | 從 List(T) 中刪除一系列元素。 |
| Reverse() | 反轉整個 List(T) 中元素的順序。 |
| Reverse(Int32, Int32) | 反轉指定範圍內的元素順序。 |
| Sort() | 使用預設比較器對整個 List(T) 中的元素進行排序。 |
| Sort(Comparison(T)) | 使用指定的 System.Comparison(T) 對整個 List(T) 中的元素進行排序。 |
| Sort(IComparer(T)) | 使用指定的比較器對整個 List(T) 中的元素進行排序。 |
| Sort(Int32, Int32, IComparer(T)) | 使用指定的比較器對 List(T) 中一系列元素進行排序。 |
| ToArray | 將 List(T) 的元素複製到一個新陣列中。 |
| ToString | 返回表示當前物件的字串。(繼承自 Object。) |
| TrimExcess | 如果該數字小於閾值,則將容量設定為 List(T) 中元素的實際數量。 |
| TrueForAll | 確定 List(T) 中的每個元素是否都與指定謂詞定義的條件匹配。 |
示例
(* Creating a List *)
open System.Collections.Generic
let booksList = new List<string>()
booksList.Add("Gone with the Wind")
booksList.Add("Atlas Shrugged")
booksList.Add("Fountainhead")
booksList.Add("Thornbirds")
booksList.Add("Rebecca")
booksList.Add("Narnia")
printfn"Total %d books" booksList.Count
booksList |> Seq.iteri (fun index item -> printfn "%i: %s" index booksList.[index])
booksList.Insert(2, "Roots")
printfn("after inserting at index 2")
printfn"Total %d books" booksList.Count
booksList |> Seq.iteri (fun index item -> printfn "%i: %s" index booksList.[index])
booksList.RemoveAt(3)
printfn("after removing from index 3")
printfn"Total %d books" booksList.Count
booksList |> Seq.iteri (fun index item -> printfn "%i: %s" index booksList.[index])
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Total 6 books 0: Gone with the Wind 1: Atlas Shrugged 2: Fountainhead 3: Thornbirds 4: Rebecca 5: Narnia after inserting at index 2 Total 7 books 0: Gone with the Wind 1: Atlas Shrugged 2: Roots 3: Fountainhead 4: Thornbirds 5: Rebecca 6: Narnia after removing from index 3 Total 6 books 0: Gone with the Wind 1: Atlas Shrugged 2: Roots 3: Thornbirds 4: Rebecca 5: Narnia
F# - 可變字典
Dictionary<'TKey, 'TValue> 類是 F# map 資料結構的可變模擬,幷包含許多相同的函式。
從 F# 中的 Map 章節回顧一下,map 是一種特殊的集合,它將值與鍵關聯。
建立可變字典
可變字典是使用 new 關鍵字並呼叫列表的建構函式建立的。以下示例演示了這一點:
open System.Collections.Generic
let dict = new Dictionary<string, string>()
dict.Add("1501", "Zara Ali")
dict.Add("1502","Rishita Gupta")
dict.Add("1503","Robin Sahoo")
dict.Add("1504","Gillian Megan")
printfn "Dictionary - students: %A" dict
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Dictionary - students: seq [[1501, Zara Ali]; [1502, Rishita Gupta]; [1503, Robin Sahoo]; [1504, Gillian Megan]]
Dictionary(TKey,TValue) 類
Dictionary(TKey, TValue) 類表示鍵和值的集合。
下表提供了 List(T) 類的屬性、建構函式和方法:
屬性
| 屬性 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Comparer (比較器) | 獲取用於確定字典鍵相等的 IEqualityComparer(T)。 |
| Count | 獲取 Dictionary(TKey, TValue) 中包含的鍵/值對的數量。 |
| Item | 獲取或設定與指定鍵關聯的值。 |
| Keys (鍵) | 獲取包含 Dictionary(TKey, TValue) 中鍵的集合。 |
| Values (值) | 獲取包含 Dictionary(TKey, TValue) 中值的集合。 |
建構函式
| 建構函式 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Dictionary(TKey, TValue)() | 初始化一個新的空 Dictionary(TKey, TValue) 類例項,它具有預設初始容量,並使用鍵型別的預設相等比較器。 |
| Dictionary(TKey, TValue)(IDictionary(TKey, TValue)) | 初始化一個新的 Dictionary(TKey, TValue) 類例項,其中包含從指定的 IDictionary(TKey, TValue) 複製的元素,並使用鍵型別的預設相等比較器。 |
| Dictionary(TKey, TValue)(IEqualityComparer(TKey)) | 初始化一個新的 Dictionary(TKey, TValue) 類例項,它為空,具有預設初始容量,並使用指定的 IEqualityComparer(T)。 |
| Dictionary(TKey, TValue)(Int32) | 初始化一個新的 Dictionary(TKey, TValue) 類例項,它為空,具有指定的初始容量,並使用鍵型別的預設相等比較器。 |
| Dictionary(TKey, TValue)(IDictionary(TKey, TValue), IEqualityComparer(TKey)) | 初始化一個新的Dictionary(TKey, TValue)類例項,該例項包含從指定的IDictionary(TKey, TValue)複製的元素,並使用指定的IEqualityComparer(T)。 |
| Dictionary(TKey, TValue)(Int32, IEqualityComparer(TKey)) | 初始化一個新的Dictionary(TKey, TValue)類例項,該例項為空,具有指定的初始容量,並使用指定的IEqualityComparer(T)。 |
| Dictionary(TKey, TValue)(SerializationInfo, StreamingContext) | 使用序列化資料初始化一個新的Dictionary(TKey, TValue)類例項。 |
方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Add | 將指定的鍵和值新增到字典中。 |
| Clear | 移除Dictionary(TKey, TValue)中的所有鍵和值。 |
| ContainsKey | 確定Dictionary(TKey, TValue)是否包含指定的鍵。 |
| ContainsValue | 確定Dictionary(TKey, TValue)是否包含特定的值。 |
| Equals(Object) | 確定指定的 Object 是否等於當前 Object。(繼承自 Object。) |
| Finalize | 允許物件在被垃圾回收之前嘗試釋放資源並執行其他清理操作。(繼承自Object。) |
| GetEnumerator | 返回一個迭代器,用於遍歷Dictionary(TKey, TValue)。 |
| GetHashCode | 用作預設雜湊函式。(繼承自 Object。) |
| GetObjectData | 實現System.Runtime.Serialization.ISerializable介面,並返回序列化Dictionary(TKey, TValue)例項所需的資料。 |
| GetType | 獲取當前例項的 Type。(繼承自 Object。) |
| MemberwiseClone | 建立當前 Object 的淺表副本。(繼承自 Object。) |
| OnDeserialization | 實現System.Runtime.Serialization.ISerializable介面,並在反序列化完成後引發反序列化事件。 |
| Remove | 從Dictionary(TKey, TValue)中移除具有指定鍵的值。 |
| ToString | 返回表示當前物件的字串。(繼承自 Object。) |
| TryGetValue | 獲取與指定鍵關聯的值。 |
示例
open System.Collections.Generic
let dict = new Dictionary<string, string>()
dict.Add("1501", "Zara Ali")
dict.Add("1502","Rishita Gupta")
dict.Add("1503","Robin Sahoo")
dict.Add("1504","Gillian Megan")
printfn "Dictionary - students: %A" dict
printfn "Total Number of Students: %d" dict.Count
printfn "The keys: %A" dict.Keys
printf"The Values: %A" dict.Values
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Dictionary - students: seq [[1501, Zara Ali]; [1502, Rishita Gupta]; [1503, Robin Sahoo]; [1504, Gillian Megan]] Total Number of Students: 4 The keys: seq ["1501"; "1502"; "1503"; "1504"] The Values: seq ["Zara Ali"; "Rishita Gupta"; "Robin Sahoo"; "Gillian Megan"]
F# - 基本輸入/輸出
基本的輸入輸出包括:
- 從控制檯讀取和寫入資料。
- 從檔案讀取和寫入資料。
Core.Printf 模組
我們使用了printf和printfn函式向控制檯寫入資料。在本節中,我們將詳細瞭解F#的Printf模組。
除了上述函式外,F#的Core.Printf模組還提供其他多種方法,可以使用%標記作為佔位符進行列印和格式化。下表顯示了這些方法及其簡要說明:
| 值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| bprintf : StringBuilder → BuilderFormat<'T> → 'T | 列印到StringBuilder。 |
| eprintf : TextWriterFormat<'T> → 'T | 將格式化後的輸出列印到stderr。 |
| eprintfn : TextWriterFormat<'T> → 'T | 將格式化後的輸出列印到stderr,並新增換行符。 |
| failwithf : StringFormat<'T,'Result> → 'T | 列印到字串緩衝區,並引發帶有給定結果的異常。 |
| fprintf : TextWriter → TextWriterFormat<'T> → 'T | 列印到文字寫入器。 |
| fprintfn : TextWriter → TextWriterFormat<'T> → 'T | 列印到文字寫入器,並新增換行符。 |
| kbprintf : (unit → 'Result) → StringBuilder → BuilderFormat<'T,'Result> → 'T | 類似於bprintf,但呼叫指定的函式生成結果。 |
| kfprintf : (unit → 'Result) → TextWriter → TextWriterFormat<'T,'Result> → 'T | 類似於fprintf,但呼叫指定的函式生成結果。 |
| kprintf : (string → 'Result) → StringFormat<'T,'Result> → 'T | 類似於printf,但呼叫指定的函式生成結果。例如,這些允許列印在所有輸出都已輸入通道後強制重新整理,但在此之前不會。 |
| ksprintf : (string → 'Result) → StringFormat<'T,'Result> → 'T | 類似於sprintf,但呼叫指定的函式生成結果。 |
| printf : TextWriterFormat<'T> → 'T | 將格式化後的輸出列印到stdout。 |
| printfn : TextWriterFormat<'T> → 'T | 將格式化後的輸出列印到stdout,並新增換行符。 |
| sprintf : StringFormat<'T> → 'T | 使用內部字串緩衝區列印到字串,並將結果作為字串返回。 |
格式說明符
格式說明符用於根據程式設計師的需求格式化輸入或輸出。
這些是帶有%標記的字串,表示格式佔位符。
格式佔位符的語法為:
%[flags][width][.precision][type]
型別的解釋如下:
| 型別 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| %b | 格式化一個bool值,格式化為true或false。 |
| %c | 格式化一個字元。 |
| %s | 格式化一個string值,格式化為其內容,不解釋任何跳脫字元。 |
| %d, %i | 格式化任何基本整數型別,格式化為十進位制整數,如果基本整數型別為有符號型別,則為有符號整數。 |
| %u | 格式化任何基本整數型別,格式化為無符號十進位制整數。 |
| %x | 格式化任何基本整數型別,格式化為無符號十六進位制整數,使用小寫字母a到f。 |
| %X | 格式化任何基本整數型別,格式化為無符號十六進位制整數,使用大寫字母A到F。 |
| %o | 格式化任何基本整數型別,格式化為無符號八進位制整數。 |
| %e, %E, %f, %F, %g, %G | 格式化任何基本浮點型別(float, float32),使用C風格的浮點格式說明符進行格式化。 |
| %e, %E | 格式化一個有符號值,其形式為[-]d.dddde[sign]ddd,其中d是一個十進位制數字,dddd是一個或多個十進位制數字,ddd正好是三個十進位制數字,sign是+或-。 |
| %f | 格式化一個有符號值,其形式為[-]dddd.dddd,其中dddd是一個或多個十進位制數字。小數點前的數字個數取決於數字的大小,小數點後的數字個數取決於請求的精度。 |
| %g, %G | 格式化一個有符號值,以f或e格式列印,對於給定的值和精度,哪種格式更緊湊就使用哪種格式。 |
| %M | 格式化一個Decimal值。 |
| %O | 格式化任何值,透過裝箱物件並使用其ToString方法進行列印。 |
| %A, %+A | 格式化任何值,使用預設佈局設定進行列印。使用%+A列印具有內部和私有表示的辨別聯合體的結構。 |
| %a | 一個通用格式說明符,需要兩個引數。第一個引數是一個函式,它接受兩個引數:第一個是給定格式化函式的適當型別的上下文引數(例如,TextWriter),第二個是要列印的值,並且該值要麼輸出要麼返回適當的文字。 第二個引數是要列印的特定值。 |
| %t | 一個通用格式說明符,需要一個引數:一個函式,它接受給定格式化函式的適當型別的上下文引數(aTextWriter),並且該函式要麼輸出要麼返回適當的文字。基本整數型別為byte, sbyte, int16, uint16, int32, uint32, int64, uint64, nativeint,和unativeint。基本浮點型別為float和float32。 |
寬度是一個可選引數。它是一個整數,表示結果的最小寬度。例如,%5d列印一個至少有5個字元空格的整數。
有效的標誌在下表中描述:
| 值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 指定新增零而不是空格以構成所需的寬度。 |
| - | 指定在指定的寬度內左對齊結果。 |
| + | 如果數字為正,則指定新增+字元(以匹配負數的-號)。 |
| ' ' (空格) | 如果數字為正,則指定新增一個額外的空格(以匹配負數的-號)。 |
| # | 無效。 |
示例
printf "Hello " printf "World" printfn "" printfn "Hello " printfn "World" printf "Hi, I'm %s and I'm a %s" "Rohit" "Medical Student" printfn "d: %f" 212.098f printfn "e: %f" 504.768f printfn "x: %g" 212.098f printfn "y: %g" 504.768f printfn "x: %e" 212.098f printfn "y: %e" 504.768f printfn "True: %b" true
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Hello World Hello World Hi, I'm Rohit and I'm a Medical Studentd: 212.098000 e: 504.768000 x: 212.098 y: 504.768 x: 2.120980e+002 y: 5.047680e+002 True: true
Console 類
此類是.NET框架的一部分。它表示控制檯應用程式的標準輸入、輸出和錯誤流。
它提供各種方法用於從控制檯讀取和寫入資料。下表顯示了這些方法:
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Beep() | 透過控制檯揚聲器播放蜂鳴聲。 |
| Beep(Int32, Int32) | 透過控制檯揚聲器播放指定頻率和持續時間的蜂鳴聲。 |
| Clear | 清除控制檯緩衝區和相應的控制檯視窗顯示資訊。 |
| MoveBufferArea(Int32, Int32, Int32, Int32, Int32, Int32) | 將螢幕緩衝區的指定源區域複製到指定的目標區域。 |
| MoveBufferArea(Int32, Int32, Int32, Int32, Int32, Int32, Char, ConsoleColor, ConsoleColor) | 將螢幕緩衝區的指定源區域複製到指定的目標區域。 |
| OpenStandardError() | 獲取標準錯誤流。 |
| OpenStandardError(Int32) | 獲取標準錯誤流,該流設定為指定的緩衝區大小。 |
| OpenStandardInput() | 獲取標準輸入流。 |
| OpenStandardInput(Int32) | 獲取標準輸入流,該流設定為指定的緩衝區大小。 |
| OpenStandardOutput() | 獲取標準輸出流。 |
| OpenStandardOutput(Int32) | 獲取標準輸出流,該流設定為指定的緩衝區大小。 |
| Read | 從標準輸入流讀取下一個字元。 |
| ReadKey() | 獲取使用者按下的下一個字元或功能鍵。按下的鍵將顯示在控制檯視窗中。 |
| ReadKey(Boolean) | 獲取使用者按下的下一個字元或功能鍵。按下的鍵可以選擇性地在控制檯視窗中顯示。 |
| ReadLine | 從標準輸入流讀取下一行字元。 |
| ResetColor | 將前景色和背景色控制檯顏色設定為其預設值。 |
| SetBufferSize | 將螢幕緩衝區區域的高度和寬度設定為指定的值。 |
| SetCursorPosition | 設定游標的位置。 |
| SetError | 將Error屬性設定為指定的TextWriter物件。 |
| SetIn | 將In屬性設定為指定的TextReader物件。 |
| SetOut | 將Out屬性設定為指定的TextWriter物件。 |
| SetWindowPosition | 設定控制檯視窗相對於螢幕緩衝區的位置。 |
| SetWindowSize | 將控制檯視窗的高度和寬度設定為指定的值。 |
| Write(Boolean) | 將指定布林值的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Char) | 將指定的Unicode字元值寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Char[]) | 將指定的Unicode字元陣列寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Decimal) | 將指定Decimal值的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Double) | 將指定雙精度浮點值的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Int32) | 將指定32位有符號整數值的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Int64) | 將指定64位有符號整數值的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Object) | 將指定物件的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Single) | 將指定單精度浮點值的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(String) | 將指定的字串值寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(UInt32) | 將指定32位無符號整數值的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(UInt64) | 將指定64位無符號整數值的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(String, Object) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定物件的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(String, Object[]) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定物件陣列的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(Char[], Int32, Int32) | 將指定的 Unicode 字元子陣列寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(String, Object, Object) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定物件的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(String, Object, Object, Object) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定物件的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| Write(String, Object, Object, Object, Object) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定的物件和可變長度引數列表的文字表示形式寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine() | 將當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Boolean) | 將指定布林值的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Char) | 將指定的 Unicode 字元及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Char[]) | 將指定的 Unicode 字元陣列及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Decimal) | 將指定 Decimal 值的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Double) | 將指定的雙精度浮點值的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Int32) | 將指定的 32 位有符號整數值的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Int64) | 將指定的 64 位有符號整數值的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Object) | 將指定物件的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Single) | 將指定的單精度浮點值的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(String) | 將指定的字串值及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(UInt32) | 將指定的 32 位無符號整數值的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(UInt64) | 將指定的 64 位無符號整數值的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(String, Object) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定物件的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(String, Object[]) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定物件陣列的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(Char[], Int32, Int32) | 將指定的 Unicode 字元子陣列及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(String, Object, Object) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定物件的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(String, Object, Object, Object) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定物件的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
| WriteLine(String, Object, Object, Object, Object) | 使用指定的格式資訊將指定的物件和可變長度引數列表的文字表示形式及其後的當前行終止符寫入標準輸出流。 |
以下示例演示了從控制檯讀取和寫入資料:
示例
open System
let main() =
Console.Write("What's your name? ")
let name = Console.ReadLine()
Console.Write("Hello, {0}\n", name)
Console.WriteLine(System.String.Format("Big Greetings from {0} and {1}", "TutorialsPoint", "Absoulte Classes"))
Console.WriteLine(System.String.Format("|{0:yyyy-MMM-dd}|", System.DateTime.Now))
main()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
What's your name? Kabir Hello, Kabir Big Greetings from TutorialsPoint and Absoulte Classes |2015-Jan-05|
System.IO 名稱空間
System.IO 名稱空間包含各種用於執行基本 I/O 操作的有用類。
它包含允許讀取和寫入檔案和資料流的型別或類,以及提供基本檔案和目錄支援的型別。
用於處理檔案系統的有用類:
- System.IO.File 類用於建立、追加和刪除檔案。
- System.IO.Directory 類用於建立、移動和刪除目錄。
- System.IO.Path 類對錶示檔案路徑的字串執行操作。
- System.IO.FileSystemWatcher 類允許使用者監聽目錄的更改。
用於處理流(位元組序列)的有用類:
- System.IO.StreamReader 類用於從流中讀取字元。
- System.IO.StreamWriter 類用於向流中寫入字元。
- System.IO.MemoryStream 類建立一個記憶體中的位元組流。
下表顯示了名稱空間中提供的所有類及其簡要說明:
| 類 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| BinaryReader | 以二進位制值的形式讀取特定編碼中的原始資料型別。 |
| BinaryWriter | 以二進位制形式將原始型別寫入流,並支援以特定編碼寫入字串。 |
| BufferedStream | 為另一個流上的讀取和寫入操作新增緩衝層。 |
| Directory | 公開用於建立、移動和列舉目錄和子目錄的靜態方法。 |
| DirectoryInfo | 公開用於建立、移動和列舉目錄和子目錄的例項方法。 |
| DirectoryNotFoundException | 當找不到檔案或目錄的一部分時引發的異常。 |
| DriveInfo | 提供對驅動器資訊的訪問。 |
| DriveNotFoundException | 嘗試訪問不可用的驅動器或共享時引發的異常。 |
| EndOfStreamException | 嘗試讀取超過流末尾時引發的異常。 |
| ErrorEventArgs | 為 FileSystemWatcher.Error 事件提供資料。 |
| File | 提供用於建立、複製、刪除、移動和開啟單個檔案的靜態方法,並幫助建立 FileStream 物件。 |
| FileFormatException | 當輸入檔案或應符合特定檔案格式規範的資料流格式錯誤時引發的異常。 |
| FileInfo | 提供用於建立、複製、刪除、移動和開啟檔案的屬性和例項方法,並幫助建立 FileStream 物件。 |
| FileLoadException | 當找到託管程式集但無法載入時引發的異常。 |
| FileNotFoundException | 當嘗試訪問磁碟上不存在的檔案失敗時引發的異常。 |
| FileStream | 公開圍繞檔案的流,支援同步和非同步讀取和寫入操作。 |
| FileSystemEventArgs | 為目錄事件(已更改、已建立、已刪除)提供資料。 |
| FileSystemInfo | 為 FileInfo 和 DirectoryInfo 物件提供基類。 |
| FileSystemWatcher | 偵聽檔案系統更改通知,並在目錄或目錄中的檔案更改時引發事件。 |
| InternalBufferOverflowException | 內部緩衝區溢位時引發的異常。 |
| InvalidDataException | 當資料流格式無效時引發的異常。 |
| IODescriptionAttribute | 設定引用事件、擴充套件程式或屬性時視覺設計器可以顯示的描述。 |
| IOException | 發生 I/O 錯誤時引發的異常。 |
| MemoryStream | 建立一個其後備儲存為記憶體的流。 |
| Path | 對包含檔案或目錄路徑資訊的 String 例項執行操作。這些操作以跨平臺的方式執行。 |
| PathTooLongException | 當路徑或檔名長於系統定義的最大長度時引發的異常。 |
| PipeException | 命名管道中發生錯誤時引發。 |
| RenamedEventArgs | 為 Renamed 事件提供資料。 |
| Stream | 提供位元組序列的通用檢視。這是一個抽象類。 |
| StreamReader | 實現一個 TextReader,它以特定編碼從位元組流中讀取字元。 |
| StreamWriter | 實現一個 TextWriter,用於以特定編碼向流中寫入字元。要瀏覽此型別的 .NET Framework 原始碼,請參閱參考源。 |
| StringReader | 實現一個從字串中讀取的 TextReader。 |
| StringWriter | 實現一個 TextWriter,用於將資訊寫入字串。資訊儲存在底層 StringBuilder 中。 |
| TextReader | 表示可以讀取一系列連續字元的讀取器。 |
| TextWriter | 表示可以寫入一系列連續字元的寫入器。此類是抽象的。 |
| UnmanagedMemoryAccessor | 提供對託管程式碼中非託管記憶體塊的隨機訪問。 |
| UnmanagedMemoryStream | 提供對託管程式碼中非託管記憶體塊的訪問。 |
| WindowsRuntimeStorageExtensions | 在開發 Windows 應用商店應用時,包含 Windows 執行時中 IStorageFile 和 IStorageFolder 介面的擴充套件方法。 |
| WindowsRuntimeStreamExtensions | 包含用於在 Windows 執行時中的流和 .NET 中的託管流之間進行轉換的擴充套件方法,用於 Windows 應用商店應用。 |
示例
以下示例建立一個名為 test.txt 的檔案,向其中寫入訊息,從檔案讀取文字並將其列印到控制檯。
注意 - 完成此操作所需的程式碼量出乎意料地少!
open System.IO // Name spaces can be opened just as modules
File.WriteAllText("test.txt", "Hello There\n Welcome to:\n Tutorials Point")
let msg = File.ReadAllText("test.txt")
printfn "%s" msg
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Hello There Welcome to: Tutorials Point
F# - 泛型
泛型允許您延遲指定類或方法中程式設計元素的資料型別,直到它實際在程式中使用。換句話說,泛型允許您編寫可以處理任何資料型別的類或方法。
您編寫類或方法的規範,並使用替代引數表示資料型別。當編譯器遇到類的建構函式或方法的函式呼叫時,它會生成程式碼來處理特定的資料型別。
在 F# 中,函式值、方法、屬性和聚合型別(例如類、記錄和辨別聯合)都可以是泛型的。
泛型構造至少包含一個型別引數。泛型函式和型別使您可以編寫適用於各種型別的程式碼,而無需為每種型別重複程式碼。
語法
編寫泛型構造的語法如下:
// Explicitly generic function. let function-name<type-parameters> parameter-list = function-body // Explicitly generic method. [ static ] member object-identifer.method-name<type-parameters> parameter-list [ return-type ] = method-body // Explicitly generic class, record, interface, structure, // or discriminated union. type type-name<type-parameters> type-definition
示例
(* Generic Function *) let printFunc<'T> x y = printfn "%A, %A" x y printFunc<float> 10.0 20.0
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
10.0, 20.0
您還可以使用單引號語法使函式泛型:
(* Generic Function *) let printFunction (x: 'a) (y: 'a) = printfn "%A %A" x y printFunction 10.0 20.0
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
10.0 20.0
請注意,當您使用泛型函式或方法時,您可能不必指定型別引數。但是,如果出現歧義,您可以像在第一個示例中那樣在尖括號中提供型別引數。
如果您有多個型別,則用逗號分隔多個型別引數。
泛型類
像泛型函式一樣,您也可以編寫泛型類。以下示例演示了這一點:
type genericClass<'a> (x: 'a) =
do printfn "%A" x
let gr = new genericClass<string>("zara")
let gs = genericClass( seq { for i in 1 .. 10 -> (i, i*i) } )
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
"zara" seq [(1, 1); (2, 4); (3, 9); (4, 16); ...]
F# - 委託
委託是一個引用型別變數,它儲存對方法的引用。可以在執行時更改引用。F# 委託類似於 C 或 C++ 中的函式指標。
宣告委託
委託聲明確定委託可以引用的方法。委託可以引用與委託簽名相同的方法。
委託宣告的語法如下:
type delegate-typename = delegate of type1 -> type2
例如,考慮以下委託:
// Delegate1 works with tuple arguments. type Delegate1 = delegate of (int * int) -> int // Delegate2 works with curried arguments. type Delegate2 = delegate of int * int -> int
這兩個委託都可以用來引用任何具有兩個int引數並返回int型別變數的方法。
在語法中:
type1表示引數型別。
type2表示返回型別。
請注意:
引數型別會自動柯里化。
委託可以附加到函式值以及靜態或例項方法。
F# 函式值可以直接作為引數傳遞給委託建構函式。
對於靜態方法,透過使用類名和方法名來呼叫委託。對於例項方法,則使用物件例項名和方法名。
委託型別的 Invoke 方法呼叫封裝的函式。
此外,可以透過引用 Invoke 方法名(不帶括號)將委託作為函式值傳遞。
以下示例演示了這個概念:
示例
type Myclass() =
static member add(a : int, b : int) =
a + b
static member sub (a : int) (b : int) =
a - b
member x.Add(a : int, b : int) =
a + b
member x.Sub(a : int) (b : int) =
a - b
// Delegate1 works with tuple arguments.
type Delegate1 = delegate of (int * int) -> int
// Delegate2 works with curried arguments.
type Delegate2 = delegate of int * int -> int
let InvokeDelegate1 (dlg : Delegate1) (a : int) (b: int) =
dlg.Invoke(a, b)
let InvokeDelegate2 (dlg : Delegate2) (a : int) (b: int) =
dlg.Invoke(a, b)
// For static methods, use the class name, the dot operator, and the
// name of the static method.
let del1 : Delegate1 = new Delegate1( Myclass.add )
let del2 : Delegate2 = new Delegate2( Myclass.sub )
let mc = Myclass()
// For instance methods, use the instance value name, the dot operator, and the instance method name.
let del3 : Delegate1 = new Delegate1( mc.Add )
let del4 : Delegate2 = new Delegate2( mc.Sub )
for (a, b) in [ (400, 200); (100, 45) ] do
printfn "%d + %d = %d" a b (InvokeDelegate1 del1 a b)
printfn "%d - %d = %d" a b (InvokeDelegate2 del2 a b)
printfn "%d + %d = %d" a b (InvokeDelegate1 del3 a b)
printfn "%d - %d = %d" a b (InvokeDelegate2 del4 a b)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
400 + 200 = 600 400 - 200 = 200 400 + 200 = 600 400 - 200 = 200 100 + 45 = 145 100 - 45 = 55 100 + 45 = 145 100 - 45 = 55
F# - 列舉
列舉是一組命名的整型常量。
在 F# 中,列舉(也稱為列舉)是整型型別,其中標籤分配給值的子集。您可以使用它們代替字面量,使程式碼更易讀且更易維護。
宣告列舉
宣告列舉的通用語法如下:
type enum-name = | value1 = integer-literal1 | value2 = integer-literal2 ...
以下示例演示了列舉的使用:
示例
// Declaration of an enumeration. type Days = | Sun = 0 | Mon = 1 | Tues = 2 | Wed = 3 | Thurs = 4 | Fri = 5 | Sat = 6 // Use of an enumeration. let weekend1 : Days = Days.Sat let weekend2 : Days = Days.Sun let weekDay1 : Days = Days.Mon printfn "Monday: %A" weekDay1 printfn "Saturday: %A" weekend1 printfn "Sunday: %A" weekend2
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Monday: Mon Saturday: Sat Sunday: Sun
F# - 模式匹配
模式匹配允許您“將資料與邏輯結構或結構進行比較,將資料分解成組成部分,或以各種方式從資料中提取資訊”。
換句話說,它提供了一種更靈活、更強大的方法來測試資料是否符合一系列條件,並根據滿足的條件執行一些計算。
從概念上講,它就像一系列 if… then 語句。
語法
從高階層面來看,F# 中的模式匹配遵循以下語法:
match expr with | pat1 - result1 | pat2 -> result2 | pat3 when expr2 -> result3 | _ -> defaultResult
其中:
- 每個 | 符號定義一個條件。
- -> 符號表示“如果條件為真,則返回此值…”。
- _ 符號提供預設模式,這意味著它像萬用字元一樣匹配所有其他內容。
示例 1
以下示例使用模式匹配語法計算斐波那契數:
let rec fib n = match n with | 0 -> 0 | 1 -> 1 | _ -> fib (n - 1) + fib (n - 2) for i = 1 to 10 do printfn "Fibonacci %d: %d" i (fib i)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Fibonacci 1: 1 Fibonacci 2: 1 Fibonacci 3: 2 Fibonacci 4: 3 Fibonacci 5: 5 Fibonacci 6: 8 Fibonacci 7: 13 Fibonacci 8: 21 Fibonacci 9: 34 Fibonacci 10: 55
您還可以將多個返回相同值的條件連結在一起。例如:
示例 2
let printSeason month = match month with | "December" | "January" | "February" -> printfn "Winter" | "March" | "April" -> printfn "Spring" | "May" | "June" -> printfn "Summer" | "July" | "August" -> printfn "Rainy" | "September" | "October" | "November" -> printfn "Autumn" | _ -> printfn "Season depends on month!" printSeason "February" printSeason "April" printSeason "November" printSeason "July"
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Winter Spring Autumn Rainy
模式匹配函式
F# 允許您使用function關鍵字編寫模式匹配函式:
let getRate = function | "potato" -> 10.00 | "brinjal" -> 20.50 | "cauliflower" -> 21.00 | "cabbage" -> 8.75 | "carrot" -> 15.00 | _ -> nan (* nan is a special value meaning "not a number" *) printfn "%g"(getRate "potato") printfn "%g"(getRate "brinjal") printfn "%g"(getRate "cauliflower") printfn "%g"(getRate "cabbage") printfn "%g"(getRate "carrot")
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
10 20.5 21 8.75 15
向模式新增過濾器或保護
您可以使用when關鍵字向模式新增過濾器或保護。
示例 1
let sign = function | 0 -> 0 | x when x < 0 -> -1 | x when x > 0 -> 1 printfn "%d" (sign -20) printfn "%d" (sign 20) printfn "%d" (sign 0)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
-1 1 0
示例 2
let compareInt x = match x with | (var1, var2) when var1 > var2 -> printfn "%d is greater than %d" var1 var2 | (var1, var2) when var1 < var2 -> printfn "%d is less than %d" var1 var2 | (var1, var2) -> printfn "%d equals %d" var1 var2 compareInt (11,25) compareInt (72, 10) compareInt (0, 0)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
11 is less than 25 72 is greater than 10 0 equals 0
使用元組進行模式匹配
以下示例演示了使用元組進行模式匹配:
let greeting (name, subject) =
match (name, subject) with
| ("Zara", _) -> "Hello, Zara"
| (name, "English") -> "Hello, " + name + " from the department of English"
| (name, _) when subject.StartsWith("Comp") -> "Hello, " + name + " from the department of Computer Sc."
| (_, "Accounts and Finance") -> "Welcome to the department of Accounts and Finance!"
| _ -> "You are not registered into the system"
printfn "%s" (greeting ("Zara", "English"))
printfn "%s" (greeting ("Raman", "Computer Science"))
printfn "%s" (greeting ("Ravi", "Mathematics"))
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Hello, Zara Hello, Raman from the department of Computer Sc. You are not registered into the system
使用記錄進行模式匹配
以下示例演示了使用記錄進行模式匹配:
type Point = { x: float; y: float }
let evaluatePoint (point: Point) =
match point with
| { x = 0.0; y = 0.0 } -> printfn "Point is at the origin."
| { x = xVal; y = 0.0 } -> printfn "Point is on the x-axis. Value is %f." xVal
| { x = 0.0; y = yVal } -> printfn "Point is on the y-axis. Value is %f." yVal
| { x = xVal; y = yVal } -> printfn "Point is at (%f, %f)." xVal yVal
evaluatePoint { x = 0.0; y = 0.0 }
evaluatePoint { x = 10.0; y = 0.0 }
evaluatePoint { x = 0.0; y = 10.0 }
evaluatePoint { x = 10.0; y = 10.0 }
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Point is at the origin. Point is on the x-axis. Value is 10.000000. Point is on the y-axis. Value is 10.000000. Point is at (10.000000, 10.000000).
F# - 異常處理
異常是在程式執行期間出現的錯誤。F# 異常是對程式執行期間出現的異常情況的響應,例如嘗試除以零。
異常提供了一種將控制權從程式的一個部分轉移到另一個部分的方法。F# 異常處理提供以下結構:
| 結構 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| raise expr | 引發給定的異常。 |
| failwith expr | 引發System.Exception異常。 |
| try expr with rules | 捕獲與模式規則匹配的表示式。 |
| try expr finally expr | 在計算成功和引發異常時都執行finally表示式。 |
| | :? ArgumentException | 與給定的 .NET 異常型別匹配的規則。 |
| | :? ArgumentException as e | 與給定的 .NET 異常型別匹配的規則,將名稱e繫結到異常物件值。 |
| | Failure(msg) → expr | 與給定的攜帶資料的 F# 異常匹配的規則。 |
| | exn → expr | 與任何異常匹配的規則,將名稱exn繫結到異常物件值。 |
| | exn when expr → expr | 在給定條件下與異常匹配的規則,將名稱exn繫結到異常物件值。 |
讓我們從異常處理的基本語法開始。
語法
F# 異常處理塊的基本語法如下:
exception exception-type of argument-type
其中:
exception-type是新的 F# 異常型別的名稱。
argument-type表示在引發此型別的異常時可以提供的引數的型別。
可以透過使用元組型別作為argument-type來指定多個引數。
try...with表示式用於F#語言中的異常處理。
try … with表示式的語法如下:
try expression1 with | pattern1 -> expression2 | pattern2 -> expression3 ...
try...finally表示式允許您即使程式碼塊引發異常也能執行清理程式碼。
try … finally表示式的語法如下:
try expression1 finally expression2
raise函式用於指示已發生錯誤或異常情況。它還會在異常物件中捕獲有關錯誤的資訊。
raise函式的語法如下:
raise (expression)
failwith函式生成 F# 異常。
failwith函式的語法如下:
failwith error-message-string
invalidArg函式生成引數異常。
invalidArg parameter-name error-message-string
異常處理示例
示例 1
以下程式顯示了使用簡單的 try… with 塊進行基本異常處理:
let divisionprog x y =
try
Some (x / y)
with
| :? System.DivideByZeroException -> printfn "Division by zero!"; None
let result1 = divisionprog 100 0
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Division by zero!
示例 2
F# 提供了一個exception型別來宣告異常。您可以直接在try...with表示式中的過濾器中使用異常型別。
以下示例演示了這一點:
exception Error1 of string
// Using a tuple type as the argument type.
exception Error2 of string * int
let myfunction x y =
try
if x = y then raise (Error1("Equal Number Error"))
else raise (Error2("Error Not detected", 100))
with
| Error1(str) -> printfn "Error1 %s" str
| Error2(str, i) -> printfn "Error2 %s %d" str i
myfunction 20 10
myfunction 5 5
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Error2 Error Not detected 100 Error1 Equal Number Error
示例 3
以下示例演示了巢狀異常處理:
exception InnerError of string
exception OuterError of string
let func1 x y =
try
try
if x = y then raise (InnerError("inner error"))
else raise (OuterError("outer error"))
with
| InnerError(str) -> printfn "Error:%s" str
finally
printfn "From the finally block."
let func2 x y =
try
func1 x y
with
| OuterError(str) -> printfn "Error: %s" str
func2 100 150
func2 100 100
func2 100 120
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
From the finally block. Error: outer error Error:inner error From the finally block. From the finally block. Error: outer error
示例 4
以下函式演示了failwith函式:
let divisionFunc x y =
if (y = 0) then failwith "Divisor cannot be zero."
else
x / y
let trydivisionFunc x y =
try
divisionFunc x y
with
| Failure(msg) -> printfn "%s" msg; 0
let result1 = trydivisionFunc 100 0
let result2 = trydivisionFunc 100 4
printfn "%A" result1
printfn "%A" result2
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Divisor cannot be zero. 0 25
示例 5
invalidArg函式生成引數異常。以下程式演示了這一點:
let days = [| "Sunday"; "Monday"; "Tuesday"; "Wednesday"; "Thursday"; "Friday"; "Saturday" |]
let findDay day =
if (day > 7 || day < 1)
then invalidArg "day" (sprintf "You have entered %d." day)
days.[day - 1]
printfn "%s" (findDay 1)
printfn "%s" (findDay 5)
printfn "%s" (findDay 9)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Sunday Thursday Unhandled Exception: System.ArgumentException: You have entered 9. …
根據系統不同,還會顯示有關導致系統錯誤的檔案和變數的其他資訊。
F# - 類
類是表示可以具有屬性、方法和事件的物件的型別。“它們用於對應用程式中的動作、流程和任何概念實體進行建模”。
語法
定義類型別的語法如下:
// Class definition:
type [access-modifier] type-name [type-params] [access-modifier] ( parameter-list ) [ as identifier ] =
[ class ]
[ inherit base-type-name(base-constructor-args) ]
[ let-bindings ]
[ do-bindings ]
member-list
...
[ end ]
// Mutually recursive class definitions:
type [access-modifier] type-name1 ...
and [access-modifier] type-name2 ...
...
其中:
type-name是任何有效的識別符號。預設訪問修飾符為public。
type-params描述可選的泛型型別引數。
parameter-list描述建構函式引數。主建構函式的預設訪問修飾符為public。
帶可選as關鍵字的識別符號為例項變數或self-identifier命名,它可以在型別定義中用於引用型別的例項。
inherit關鍵字允許您指定類的基類。
let繫結允許您宣告對類區域性欄位或函式值。
do-bindings部分包括在物件構造時要執行的程式碼。
member-list由附加的建構函式、例項和靜態方法宣告、介面宣告、抽象繫結以及屬性和事件宣告組成。
標記定義開始和結束的關鍵字class和end是可選的。
類的建構函式
建構函式是建立類型別例項的程式碼。
在 F# 中,建構函式的工作方式與其他 .Net 語言略有不同。在類定義中,主建構函式的引數被描述為 parameter-list。
建構函式的主體由let和do繫結組成。
您可以使用 new 關鍵字新增成員來新增其他建構函式:
new (argument-list) = constructor-body
以下示例說明了這個概念:
示例
以下程式建立了一個線類以及一個建構函式,該建構函式在建立類的物件時計算線的長度:
type Line = class
val X1 : float
val Y1 : float
val X2 : float
val Y2 : float
new (x1, y1, x2, y2) as this =
{ X1 = x1; Y1 = y1; X2 = x2; Y2 = y2;}
then
printfn " Creating Line: {(%g, %g), (%g, %g)}\nLength: %g"
this.X1 this.Y1 this.X2 this.Y2 this.Length
member x.Length =
let sqr x = x * x
sqrt(sqr(x.X1 - x.X2) + sqr(x.Y1 - x.Y2) )
end
let aLine = new Line(1.0, 1.0, 4.0, 5.0)
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Creating Line: {(1, 1), (4, 5)}
Length: 5
Let 繫結
類定義中的 let 繫結允許您為 F# 類定義私有欄位和私有函式。
type Greetings(name) as gr =
let data = name
do
gr.PrintMessage()
member this.PrintMessage() =
printf "Hello %s\n" data
let gtr = new Greetings("Zara")
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Hello Zara
請注意對 Greetings 類的 self-identifier gr 的使用。
F# - 結構體
F# 中的結構是一種值型別資料型別。它可以幫助您使單個變數儲存各種資料型別的相關資料。struct關鍵字用於建立結構。
語法
定義結構的語法如下:
[ attributes ]
type [accessibility-modifier] type-name =
struct
type-definition-elements
end
// or
[ attributes ]
[<StructAttribute>]
type [accessibility-modifier] type-name =
type-definition-elements
有兩種語法。第一種語法最常用,因為如果您使用struct和end關鍵字,則可以省略StructAttribute屬性。
結構定義元素提供:
- 成員宣告和定義。
- 建構函式以及可變和不可變欄位。
- 成員和介面實現。
與類不同,結構不能被繼承,也不能包含 let 或 do 繫結。由於結構沒有 let 繫結;您必須使用val關鍵字在結構中宣告欄位。
當您使用val關鍵字定義欄位及其型別時,無法初始化欄位值,它們將初始化為零或空。因此,對於具有隱式建構函式的結構,val宣告需要使用DefaultValue屬性進行註釋。
示例
下面的程式建立一個線結構以及一個建構函式。程式使用該結構計算線的長度:
type Line = struct
val X1 : float
val Y1 : float
val X2 : float
val Y2 : float
new (x1, y1, x2, y2) =
{X1 = x1; Y1 = y1; X2 = x2; Y2 = y2;}
end
let calcLength(a : Line)=
let sqr a = a * a
sqrt(sqr(a.X1 - a.X2) + sqr(a.Y1 - a.Y2) )
let aLine = new Line(1.0, 1.0, 4.0, 5.0)
let length = calcLength aLine
printfn "Length of the Line: %g " length
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Length of the Line: 5
F# - 運算子過載
您可以重新定義或過載F#中提供的大多數內建運算子。因此,程式設計師也可以將運算子與使用者定義型別一起使用。
運算子是用括號括起來的特殊名稱的函式。它們必須定義為靜態類成員。與任何其他函式一樣,過載運算子具有返回型別和引數列表。
以下示例顯示了複數上的 + 運算子:
//overloading + operator static member (+) (a : Complex, b: Complex) = Complex(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y)
上述函式實現了使用者定義類Complex的加法運算子(+)。它新增兩個物件的屬性並返回結果Complex物件。
運算子過載的實現
下面的程式顯示了完整的實現:
//implementing a complex class with +, and - operators
//overloaded
type Complex(x: float, y : float) =
member this.x = x
member this.y = y
//overloading + operator
static member (+) (a : Complex, b: Complex) =
Complex(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y)
//overloading - operator
static member (-) (a : Complex, b: Complex) =
Complex(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y)
// overriding the ToString method
override this.ToString() =
this.x.ToString() + " " + this.y.ToString()
//Creating two complex numbers
let c1 = Complex(7.0, 5.0)
let c2 = Complex(4.2, 3.1)
// addition and subtraction using the
//overloaded operators
let c3 = c1 + c2
let c4 = c1 - c2
//printing the complex numbers
printfn "%s" (c1.ToString())
printfn "%s" (c2.ToString())
printfn "%s" (c3.ToString())
printfn "%s" (c4.ToString())
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
7 5 4.2 3.1 11.2 8.1 2.8 1.9
F# - 繼承
面向物件程式設計中最重要概念之一是繼承。繼承允許我們根據另一個類來定義一個類,這使得建立和維護應用程式更容易。這也提供了重用程式碼功能和加快實現時間的機會。
建立類時,程式設計師可以指定新類應該繼承現有類的成員,而不是編寫全新的資料成員和成員函式。這個現有類稱為基類,新類稱為派生類。
繼承的概念實現了IS-A關係。例如,哺乳動物是一種動物,狗是一種哺乳動物,因此狗也是一種動物,依此類推。
基類和子類
子類派生自已定義的基類。子類繼承基類的成員,並擁有自己的成員。
子類使用inherit關鍵字定義,如下所示:
type MyDerived(...) = inherit MyBase(...)
在F#中,一個類最多隻能有一個直接基類。如果不使用inherit關鍵字指定基類,則該類隱式地繼承自Object。
請注意:
基類的 方法和成員對派生類的使用者可用,如同派生類的直接成員一樣。
let繫結和建構函式引數對類是私有的,因此無法從派生類訪問。
關鍵字base指的是基類例項。它像 self 識別符號一樣使用。
示例
type Person(name) =
member x.Name = name
member x.Greet() = printfn "Hi, I'm %s" x.Name
type Student(name, studentID : int) =
inherit Person(name)
let mutable _GPA = 0.0
member x.StudentID = studentID
member x.GPA
with get() = _GPA
and set value = _GPA <- value
type Teacher(name, expertise : string) =
inherit Person(name)
let mutable _salary = 0.0
member x.Salary
with get() = _salary
and set value = _salary <- value
member x.Expertise = expertise
//using the subclasses
let p = new Person("Mohan")
let st = new Student("Zara", 1234)
let tr = new Teacher("Mariam", "Java")
p.Greet()
st.Greet()
tr.Greet()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Hi, I'm Mohan Hi, I'm Zara Hi, I'm Mariam
重寫方法
您可以重寫基類方法的預設行為,並在子類或派生類中以不同的方式實現它。
預設情況下,F#中的方法不能被重寫。
要在派生類中重寫方法,必須使用abstract和default關鍵字將方法宣告為可重寫,如下所示:
type Person(name) = member x.Name = name abstract Greet : unit -> unit default x.Greet() = printfn "Hi, I'm %s" x.Name
現在,Person類的Greet方法可以在派生類中被重寫。以下示例演示了這一點:
示例
type Person(name) =
member x.Name = name
abstract Greet : unit -> unit
default x.Greet() = printfn "Hi, I'm %s" x.Name
type Student(name, studentID : int) =
inherit Person(name)
let mutable _GPA = 0.0
member x.StudentID = studentID
member x.GPA
with get() = _GPA
and set value = _GPA <- value
override x.Greet() = printfn "Student %s" x.Name
type Teacher(name, expertise : string) =
inherit Person(name)
let mutable _salary = 0.0
member x.Salary
with get() = _salary
and set value = _salary <- value
member x.Expertise = expertise
override x.Greet() = printfn "Teacher %s." x.Name
//using the subclasses
let p = new Person("Mohan")
let st = new Student("Zara", 1234)
let tr = new Teacher("Mariam", "Java")
//default Greet
p.Greet()
//Overriden Greet
st.Greet()
tr.Greet()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Hi, I'm Mohan Student Zara Teacher Mariam.
抽象類
有時,您需要提供物件的非完整實現,這在現實中不應實現。稍後,其他程式設計師應該建立抽象類的子類來完成實現。
例如,在學校管理系統中不需要Person類。但是,需要Student或Teacher類。在這種情況下,您可以將Person類宣告為抽象類。
AbstractClass屬性告訴編譯器該類有一些抽象成員。
無法建立抽象類的例項,因為該類未完全實現。
以下示例演示了這一點:
示例
[<AbstractClass>]
type Person(name) =
member x.Name = name
abstract Greet : unit -> unit
type Student(name, studentID : int) =
inherit Person(name)
let mutable _GPA = 0.0
member x.StudentID = studentID
member x.GPA
with get() = _GPA
and set value = _GPA <- value
override x.Greet() = printfn "Student %s" x.Name
type Teacher(name, expertise : string) =
inherit Person(name)
let mutable _salary = 0.0
member x.Salary
with get() = _salary
and set value = _salary <- value
member x.Expertise = expertise
override x.Greet() = printfn "Teacher %s." x.Name
let st = new Student("Zara", 1234)
let tr = new Teacher("Mariam", "Java")
//Overriden Greet
st.Greet()
tr.Greet()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Student Zara Teacher Mariam.
F# - 介面
介面提供了一種抽象的方式來編寫類的實現細節。它是一個模板,宣告類必須實現並公開的方法。
語法
介面指定其他類實現的相關成員集。它具有以下語法:
// Interface declaration:
[ attributes ]
type interface-name =
[ interface ]
[ inherit base-interface-name ...]
abstract member1 : [ argument-types1 -> ] return-type1
abstract member2 : [ argument-types2 -> ] return-type2
...
[ end ]
// Implementing, inside a class type definition:
interface interface-name with
member self-identifier.member1 argument-list = method-body1
member self-identifier.member2 argument-list = method-body2
// Implementing, by using an object expression:
[ attributes ]
let class-name (argument-list) =
{ new interface-name with
member self-identifier.member1 argument-list = method-body1
member self-identifier.member2 argument-list = method-body2
[ base-interface-definitions ]
}
member-list
請注意:
在介面宣告中,成員未實現。
成員是抽象的,由abstract關鍵字宣告。但是,您可以使用default關鍵字提供預設實現。
您可以使用物件表示式或類型別來實現介面。
在類或物件實現中,需要為介面的抽象方法提供方法體。
標記定義開始和結束的關鍵字interface和end是可選的。
例如:
type IPerson = abstract Name : string abstract Enter : unit -> unit abstract Leave : unit -> unit
呼叫介面方法
介面方法是透過介面呼叫的,而不是透過實現介面的類的例項或型別呼叫的。要呼叫介面方法,您可以使用:>運算子(向上轉型運算子)向上轉型為介面型別。
例如:
(s :> IPerson).Enter() (s :> IPerson).Leave()
以下示例說明了這個概念:
示例
type IPerson =
abstract Name : string
abstract Enter : unit -> unit
abstract Leave : unit -> unit
type Student(name : string, id : int) =
member this.ID = id
interface IPerson with
member this.Name = name
member this.Enter() = printfn "Student entering premises!"
member this.Leave() = printfn "Student leaving premises!"
type StuffMember(name : string, id : int, salary : float) =
let mutable _salary = salary
member this.Salary
with get() = _salary
and set(value) = _salary <- value
interface IPerson with
member this.Name = name
member this.Enter() = printfn "Stuff member entering premises!"
member this.Leave() = printfn "Stuff member leaving premises!"
let s = new Student("Zara", 1234)
let st = new StuffMember("Rohit", 34, 50000.0)
(s :> IPerson).Enter()
(s :> IPerson).Leave()
(st :> IPerson).Enter()
(st :> IPerson).Leave()
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Student entering premises! Student leaving premises! Stuff member entering premises! Stuff member leaving premises!
介面繼承
介面可以繼承一個或多個基介面。
以下示例顯示了該概念:
type Interface1 =
abstract member doubleIt: int -> int
type Interface2 =
abstract member tripleIt: int -> int
type Interface3 =
inherit Interface1
inherit Interface2
abstract member printIt: int -> string
type multiplierClass() =
interface Interface3 with
member this.doubleIt(a) = 2 * a
member this.tripleIt(a) = 3 * a
member this.printIt(a) = a.ToString()
let ml = multiplierClass()
printfn "%d" ((ml:>Interface3).doubleIt(5))
printfn "%d" ((ml:>Interface3).tripleIt(5))
printfn "%s" ((ml:>Interface3).printIt(5))
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
10 15 5
F# - 事件
事件允許類彼此之間傳送和接收訊息。
在GUI中,事件是使用者操作,例如按鍵、點選、滑鼠移動等,或某些事件,例如系統生成的通知。應用程式需要在事件發生時響應事件。例如,中斷。事件用於程序間通訊。
物件透過同步訊息傳遞相互通訊。
事件附加到其他函式;物件將回撥函式註冊到事件,並且當(如果)某個物件觸發事件時,將執行這些回撥。
事件類和事件模組
Control.Event<'T>類有助於建立可觀察物件或事件。
它具有以下例項成員來處理事件:
| 成員 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Publish | 將觀察結果釋出為一等值。 |
| Trigger | 使用給定引數觸發觀察結果。 |
Control.Event模組提供用於管理事件流的函式:
| 值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| add : ('T → unit) → Event<'Del,'T> → unit | 每次觸發給定事件時執行給定函式。 |
| choose : ('T → 'U option) → IEvent<'Del,'T> → IEvent<'U> | 返回一個新事件,該事件在從原始事件選擇的郵件上觸發。選擇函式將原始訊息轉換為可選的新訊息。 |
| filter : ('T → bool) → IEvent<'Del,'T> → IEvent<'T> | 返回一個新事件,該事件偵聽原始事件,並且僅當事件的引數透過給定函式時才觸發結果事件。 |
| map : ('T → 'U) → IEvent<'Del, 'T> → IEvent<'U> | 返回一個新事件,該事件傳遞由給定函式轉換的值。 |
| merge : IEvent<'Del1,'T> → IEvent<'Del2,'T> → IEvent<'T> | 當任一輸入事件觸發時觸發輸出事件。 |
| pairwise : IEvent<'Del,'T> → IEvent<'T * 'T> | 返回一個新事件,該事件在輸入事件的第二次及後續觸發時觸發。輸入事件的第 N 次觸發將第 N-1 次和第 N 次觸發的引數作為一對傳遞。傳遞給第 N-1 次觸發的引數將儲存在隱藏的內部狀態中,直到發生第 N 次觸發。 |
| partition : ('T → bool) → IEvent<'Del,'T> → IEvent<'T> * IEvent<'T> | 返回一個新事件,該事件偵聽原始事件,如果將謂詞應用於事件引數返回 true,則觸發第一個結果事件;如果返回 false,則觸發第二個事件。 |
| scan : ('U → 'T → 'U) → 'U → IEvent<'Del,'T> → IEvent<'U> | 返回一個新事件,該事件由將給定的累加函式應用於輸入事件上觸發的連續值的結果組成。內部狀態的一個專案記錄狀態引數的當前值。在累加函式執行期間不會鎖定內部狀態,因此應注意,輸入 IEvent 不應由多個執行緒同時觸發。 |
| split : ('T → Choice<'U1,'U2>) → IEvent<'Del,'T> → IEvent<'U1> * IEvent<'U2> | 返回一個新事件,該事件偵聽原始事件,如果將函式應用於事件引數返回 Choice1Of2,則觸發第一個結果事件;如果返回 Choice2Of2,則觸發第二個事件。 |
建立事件
事件是透過Event類建立和使用的。Event建構函式用於建立事件。
示例
type Worker(name : string, shift : string) =
let mutable _name = name;
let mutable _shift = shift;
let nameChanged = new Event<unit>() (* creates event *)
let shiftChanged = new Event<unit>() (* creates event *)
member this.Name
with get() = _name
and set(value) = _name <- value
member this.Shift
with get() = _shift
and set(value) = _shift <- value
之後,您需要將nameChanged欄位公開為公共成員,以便偵聽器可以掛接到事件上,為此,您可以使用事件的Publish屬性:
type Worker(name : string, shift : string) =
let mutable _name = name;
let mutable _shift = shift;
let nameChanged = new Event<unit>() (* creates event *)
let shiftChanged = new Event<unit>() (* creates event *)
member this.NameChanged = nameChanged.Publish (* exposed event handler *)
member this.ShiftChanged = shiftChanged.Publish (* exposed event handler *)
member this.Name
with get() = _name
and set(value) = _name <- value
nameChanged.Trigger() (* invokes event handler *)
member this.Shift
with get() = _shift
and set(value) = _shift <- value
shiftChanged.Trigger() (* invokes event handler *)
接下來,您將回調新增到事件處理程式。每個事件處理程式都具有型別IEvent<'T>,它提供多種方法:
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| val Add : event:('T → unit) → unit | 將偵聽器函式連線到事件。觸發事件時將呼叫偵聽器。 |
| val AddHandler : 'del → unit | 將處理程式委託物件連線到事件。稍後可以使用RemoveHandler刪除處理程式。觸發事件時將呼叫偵聽器。 |
| val RemoveHandler : 'del → unit | 從事件偵聽器儲存中刪除偵聽器委託。 |
以下部分提供完整的示例。
示例
以下示例演示了上面討論的概念和技術:
type Worker(name : string, shift : string) =
let mutable _name = name;
let mutable _shift = shift;
let nameChanged = new Event<unit>() (* creates event *)
let shiftChanged = new Event<unit>() (* creates event *)
member this.NameChanged = nameChanged.Publish (* exposed event handler *)
member this.ShiftChanged = shiftChanged.Publish (* exposed event handler *)
member this.Name
with get() = _name
and set(value) =
_name <- value
nameChanged.Trigger() (* invokes event handler *)
member this.Shift
with get() = _shift
and set(value) =
_shift <- value
shiftChanged.Trigger() (* invokes event handler *)
let wk = new Worker("Wilson", "Evening")
wk.NameChanged.Add(fun () -> printfn "Worker changed name! New name: %s" wk.Name)
wk.Name <- "William"
wk.NameChanged.Add(fun () -> printfn "-- Another handler attached to NameChanged!")
wk.Name <- "Bill"
wk.ShiftChanged.Add(fun () -> printfn "Worker changed shift! New shift: %s" wk.Shift)
wk.Shift <- "Morning"
wk.ShiftChanged.Add(fun () -> printfn "-- Another handler attached to ShiftChanged!")
wk.Shift <- "Night"
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Worker changed name! New name: William Worker changed name! New name: Bill -- Another handler attached to NameChanged! Worker changed shift! New shift: Morning Worker changed shift! New shift: Night -- Another handler attached to ShiftChanged!
F# - 模組
根據MSDN庫,F#模組是F#程式碼結構(例如型別、值、函式值和do繫結中的程式碼)的組合。它實現為公共語言執行時 (CLR) 類,該類只有靜態成員。
根據整個檔案是否包含在模組中,模組宣告有兩種型別:
- 頂級模組宣告
- 區域性模組宣告
在頂級模組宣告中,整個檔案都包含在模組中。在這種情況下,檔案中的第一個宣告是模組宣告。您不必縮排頂級模組中的宣告。
在區域性模組宣告中,只有在該模組宣告下縮排的宣告才是模組的一部分。
語法
模組宣告的語法如下:
// Top-level module declaration. module [accessibility-modifier] [qualified-namespace.]module-name declarations // Local module declaration. module [accessibility-modifier] module-name = declarations
請注意,訪問修飾符可以是以下之一:public、private、internal。預設為public。
以下示例將演示這些概念:
示例 1
模組檔案Arithmetic.fs:
module Arithmetic let add x y = x + y let sub x y = x - y let mult x y = x * y let div x y = x / y
程式檔案main.fs:
// Fully qualify the function name. open Arithmetic let addRes = Arithmetic.add 25 9 let subRes = Arithmetic.sub 25 9 let multRes = Arithmetic.mult 25 9 let divRes = Arithmetic.div 25 9 printfn "%d" addRes printfn "%d" subRes printfn "%d" multRes printfn "%d" divRes
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
34 16 225 2 110 90 1000 10
示例 2
// Module1
module module1 =
// Indent all program elements within modules that are declared with an equal sign.
let value1 = 100
let module1Function x =
x + value1
// Module2
module module2 =
let value2 = 200
// Use a qualified name to access the function.
// from module1.
let module2Function x =
x + (module1.module1Function value2)
let result = module1.module1Function 25
printfn "%d" result
let result2 = module2.module2Function 25
printfn "%d" result2
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
125 325
F# - 名稱空間
名稱空間旨在提供一種方法來使一組名稱與另一組名稱分開。在一個名稱空間中宣告的類名不會與在另一個名稱空間中宣告的相同類名衝突。
根據MSDN庫,名稱空間允許您透過將名稱附加到程式元素組來組織程式碼到相關的功能區域。
宣告名稱空間
要在名稱空間中組織程式碼,必須將名稱空間宣告為檔案中的第一個宣告。然後,整個檔案的內容都成為名稱空間的一部分。
namespace [parent-namespaces.]identifier
以下示例說明了這個概念:
示例
namespace testing
module testmodule1 =
let testFunction x y =
printfn "Values from Module1: %A %A" x y
module testmodule2 =
let testFunction x y =
printfn "Values from Module2: %A %A" x y
module usermodule =
do
testmodule1.testFunction ( "one", "two", "three" ) 150
testmodule2.testFunction (seq { for i in 1 .. 10 do yield i * i }) 200
編譯並執行程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Values from Module1: ("one", "two", "three") 150
Values from Module2: seq [1; 4; 9; 16; ...] 200