
- C++ 基礎
- C++ 首頁
- C++ 概述
- C++ 環境設定
- C++ 基本語法
- C++ 註釋
- C++ Hello World
- C++ 省略名稱空間
- C++ 常量/字面量
- C++ 關鍵字
- C++ 識別符號
- C++ 資料型別
- C++ 數值資料型別
- C++ 字元資料型別
- C++ 布林資料型別
- C++ 變數型別
- C++ 變數作用域
- C++ 多個變數
- C++ 基本輸入/輸出
- C++ 修飾符型別
- C++ 儲存類
- C++ 運算子
- C++ 數字
- C++ 列舉
- C++ 引用
- C++ 日期和時間
- C++ 控制語句
- C++ 決策
- C++ if 語句
- C++ if else 語句
- C++ 巢狀 if 語句
- C++ switch 語句
- C++ 巢狀 switch 語句
- C++ 迴圈型別
- C++ while 迴圈
- C++ for 迴圈
- C++ do while 迴圈
- C++ foreach 迴圈
- C++ 巢狀迴圈
- C++ break 語句
- C++ continue 語句
- C++ goto 語句
- C++ 建構函式
- C++ 建構函式和解構函式
- C++ 複製建構函式
C++ 字串
C++ 提供以下兩種型別的字串表示:
- C 風格字串。
- 標準 C++ 中引入的 string 類型別。
C 風格字串
C 風格字串起源於 C 語言,並在 C++ 中繼續得到支援。這個字串實際上是一個字元的一維陣列,以空字元 '\0' 結尾。因此,一個空終止字串包含構成字串的字元,後面跟著一個空字元。
以下宣告和初始化建立一個包含單詞“Hello”的字串。為了在陣列末尾儲存空字元,包含字串的字元陣列的大小比單詞“Hello”中的字元數多一個。
char greeting[6] = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\0'};
如果您遵循陣列初始化規則,則可以按如下方式編寫上述語句:
char greeting[] = "Hello";
以下是 C/C++ 中上述定義的字串的記憶體表示:
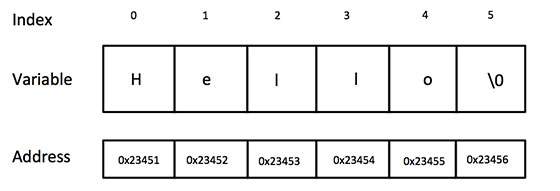
實際上,您不會在字串常量的末尾放置空字元。C++ 編譯器在初始化陣列時會自動在字串末尾放置 '\0'。讓我們嘗試列印上述字串:
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
char greeting[6] = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\0'};
cout << "Greeting message: ";
cout << greeting << endl;
return 0;
}
編譯並執行上述程式碼時,將產生以下結果:
Greeting message: Hello
C 風格字串函式
C++ 支援廣泛的函式來操作以 null 結尾的字串。這些函式在<string.h> 標頭檔案中定義。
| 序號 | 函式和用途 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
將字串 s2 複製到字串 s1。 |
| 2 |
將字串 s2 連線到字串 s1 的末尾。 |
| 3 |
返回字串 s1 的長度。 |
| 4 |
如果 s1 和 s2 相同,則返回 0;如果 s1<s2,則返回小於 0 的值;如果 s1>s2,則返回大於 0 的值。 |
| 5 |
返回指向字串 s1 中字元 ch 的第一次出現的指標。 |
| 6 |
返回指向字串 s1 中字串 s2 的第一次出現的指標。 |
示例
以下示例使用了上述幾個函式:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main () {
char str1[10] = "Hello";
char str2[10] = "World";
char str3[10];
int len ;
// copy str1 into str3
strcpy( str3, str1);
cout << "strcpy( str3, str1) : " << str3 << endl;
// concatenates str1 and str2
strcat( str1, str2);
cout << "strcat( str1, str2): " << str1 << endl;
// total lenghth of str1 after concatenation
len = strlen(str1);
cout << "strlen(str1) : " << len << endl;
return 0;
}
編譯並執行上述程式碼時,將產生如下結果:
strcpy( str3, str1) : Hello strcat( str1, str2): HelloWorld strlen(str1) : 10
C++ 中的 String 類
標準 C++ 庫提供一個string 類型別,它支援上面提到的所有操作,以及更多功能。
String 類的示例
讓我們檢查以下示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main () {
string str1 = "Hello";
string str2 = "World";
string str3;
int len ;
// copy str1 into str3
str3 = str1;
cout << "str3 : " << str3 << endl;
// concatenates str1 and str2
str3 = str1 + str2;
cout << "str1 + str2 : " << str3 << endl;
// total length of str3 after concatenation
len = str3.size();
cout << "str3.size() : " << len << endl;
return 0;
}
編譯並執行上述程式碼時,將產生如下結果:
str3 : Hello str1 + str2 : HelloWorld str3.size() : 10
建立字串
我們可以透過以下兩種方法之一建立字串變數:
使用字元陣列建立字串
我們可以使用C 型別陣列以字元格式宣告字串。這可以透過以下語法完成:
語法
char variable_name[len_value] ;
這裡,len_value 是字元陣列的長度。
使用字元陣列建立字串的示例
在下面的示例中,我們宣告一個字元陣列,併為其賦值。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char s[5]={'h','e','l','l','o'};
cout<<s<<endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
hello
使用<string>建立字串
我們可以使用 'string' 關鍵字宣告字串變數。這包含在<string> 標頭檔案中。宣告字串的語法解釋如下:
語法
string variable_name = [value];
這裡,[value] 是可選的,可以在宣告期間使用它來賦值。
示例
在下面的示例中,我們宣告一個字串變數,併為其賦值。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s="a merry tale";
cout<<s;
return 0;
}
輸出
a merry tale
遍歷字串(迭代字串)
我們可以透過兩種方式迭代字串:
使用迴圈語句
我們可以使用 for 迴圈、while 迴圈和 do while 迴圈,使用指向字串中第一個和最後一個索引的指標來遍歷字串。
使用迭代器
使用基於範圍的迴圈,我們可以使用迭代器迭代字串。這是透過在執行基於範圍的迴圈時使用 ":" 運算子實現的。
迭代字串的示例
以下示例程式碼展示了使用這兩種方法遍歷字串:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s="Hey, I am at TP.";
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
cout<<s[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
for(char c:s){
cout<<c<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
輸出
H e y , I a m a t T P . H e y , I a m a t T P .
訪問字串的字元
我們可以使用迭代器和指向字串索引的指標來訪問字串的字元。
示例
以下示例程式碼展示瞭如何訪問字串中的字元:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s="Hey, I am at TP.";
cout<<s<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
s[i]='A';
}
cout<<s<<endl;
for(char &c:s){
c='B';
}
cout<<s<<endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
Hey, I am at TP. AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
字串函式
String 是<string>類的物件,因此它具有各種函式,使用者可以利用這些函式執行各種操作。其中一些函式如下:
| 函式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| length() | 此函式返回字串的長度。 |
| swap() | 此函式用於交換兩個字串的值。 |
| size() | 用於查詢字串的大小 |
| resize() | 此函式用於將字串的長度調整到給定數量的字元。 |
| find() | 用於查詢引數中傳遞的字串 |
| push_back() | 此函式用於將字元推送到字串的末尾 |
| pop_back() | 此函式用於從字串中彈出最後一個字元 |
| clear() | 此函式用於刪除字串的所有元素。 |
| find() | 此函式用於搜尋字串內的某個子字串,並返回子字串的第一個字元的位置。 |
| replace() | 此函式用於將範圍 [first, last) 中等於舊值的每個元素替換為新值。 |
| substr() | 此函式用於從給定字串建立子字串。 |
| compare() | 此函式用於比較兩個字串,並以整數的形式返回結果。 |
| erase() | 此函式用於刪除字串的某個部分。 |
字串長度
字串的長度是字串中存在的字元數。因此,字串“apple”的長度為 5 個字元,字串“hello son”的長度為 9 個字元(包括空格)。這可以使用<string> 標頭檔案中的 length() 方法訪問。
語法
語法解釋如下:
int len = string_1.length();
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string x="hey boy";
cout<<x.length()<<endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
7
字串連線
字串連線是將兩個字串組合在一起的一種方法。這可以透過兩種方式完成:
加法運算子
加法運算子用於新增兩個元素。對於字串,加法運算子會連線兩個字串。這在以下示例中清楚地解釋:
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string x = "10";
string y = "20";
cout<<x+y<<endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
1020
這與整數加法不同。當我們取兩個整數並使用加法運算子將它們相加時,我們得到這兩個數字的和。
這在以下示例中清楚地解釋:
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
cout<<x+y<<endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
30
使用 string append() 方法
C++ 是一種面向物件的程式語言,因此字串實際上是一個物件,它包含可以對字串執行某些操作的函式。我們可以使用string append() 方法將一個字串附加到另一個字串。
此操作的語法如下:
語法
string_1.append(string_2);
此方法的使用在以下示例中清晰地顯示:
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string x="hey boy";
string y=" now";
x.append(y);
cout<<x<<endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
hey boy now
C++ 中的字串輸入
字串可以作為程式的輸入,最常見的方法是使用 cin 方法。
有三種方法可以將字串作為輸入,這些方法如下所示:
- cin
- getline()
- stringstream
使用 cin 方法
這是將字串作為輸入的最簡單方法。語法如下:
語法
cin>>string_name;
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
cout << "Enter custom string : "<<endl;
//enter the string here
cin>>s;
cout<<"The string is : "<<s;
}
使用 getline() 方法
getline() 方法可用於從輸入流讀取字串。這在 <string> 標頭檔案中定義。上述方法的語法如下:
語法
getline(cin, string_name);
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
cout << "Enter String as input : " << endl;
getline(cin, s);
//enter the string here
cout << "Printed string is : " << s << endl;
return 0;
}
使用 stringstream
stringstream 類用於一次性接收多個字串作為輸入。上述方法的語法如下:
語法
Stringstream object_name(string_name);
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s = "Hey, I am at TP";
stringstream object(s);
string newstr;
// >> operator will read from the stringstream object
while (object >> newstr) {
cout << newstr << " ";
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Hey, I am at TP