C++二叉樹中葉節點的成對交換
給定一棵二叉樹。任務是成對交換葉節點,例如:
輸入:
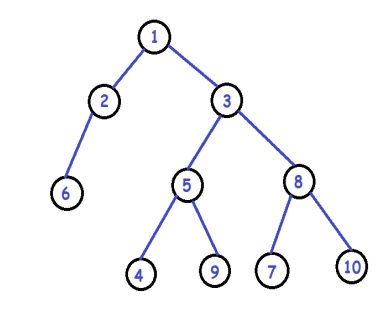
輸出:
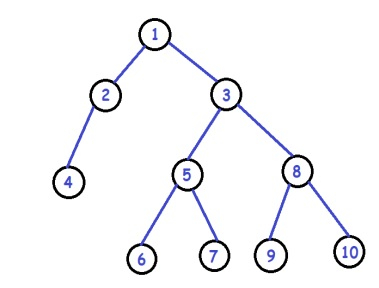
我們將跟蹤指向兩個相鄰葉節點的兩個指標,並在給定問題中交換它們的值。
尋找解決方案的方法
在這種方法中,我們遍歷樹,找到葉節點,並跟蹤計數器以檢查當前計數。主要的技巧是我們的計數器是奇數,所以我們的第一個指標現在指向該節點。當我們的計數器變為偶數時,我們交換資料,因此我們的葉節點被交換。
示例
上述方法的C++程式碼
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node{ // structure of our tree node
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
void Swap(Node **a, Node **b){ // the swapping utility function
Node * temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
/********Pointers for leaf nodes for swapping********/
Node **firstleaf;
Node **secondleaf;
void SwapTheLeafNodes(Node **root, int &count){//recursive function for
//Swapping leaf nodes
if (!(*root)) // if root is null we return
return;
if(!(*root)->left &&!(*root)->right){ // condition for leaf node
secondleaf = root; // now we firstly make our second pointer point to this node
count++; // we also increment the count
if (count%2 == 0) // now if our count is even that means we have a pair so we can swap them
Swap(firstleaf, secondleaf);
else // if count is odd so that means we only got first node yet
firstleaf = secondleaf;
}
if ((*root)->left)
SwapTheLeafNodes(&(*root)->left, count);
if ((*root)->right)
SwapTheLeafNodes(&(*root)->right, count);
}
Node* newNode(int data){ // function for initializing new node
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void printInorder(Node* node){ // inorder traversal function
if (node == NULL)
return;
printInorder(node->left);
printf("%d ", node->data);
printInorder(node->right);
}
int main(){
/* Creating binary tree*/
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->right = newNode(8);
root->right->left->left = newNode(6);
root->right->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->right->left = newNode(9);
root->right->right->right = newNode(10);
cout << "Inorder traversal before swap:\n";
printInorder(root);
cout << "\n";
int count = 0; // out counter for keeping track of leaf nodes
SwapTheLeafNodes(&root, count); // swapping the nodes
cout << "Inorder traversal after swap:\n";
printInorder(root);
cout << "\n";
return 0;
}輸出
Inorder traversal before swap: 4 2 1 6 5 7 3 9 8 10 Inorder traversal after swap: 6 2 1 4 5 9 3 7 8 10
上述程式碼的解釋
在上述方法中,我們只是建立了兩個指標,它們將跟蹤我們的葉節點。當我們遇到葉節點時,我們遍歷樹。我們首先使我們的第二個指標指向該節點,現在我們增加一個計數變數,如果我們的計數是偶數,那麼我們交換節點,如果計數是奇數,那麼這意味著我們只找到了我們對的第一個元素,所以我們將該值儲存在第一個指標中,這就是我們的函式的工作方式。
結論
在本教程中,我們解決了二叉樹中成對交換葉節點的問題。我們還學習了這個問題的C++程式以及我們解決這個問題的完整方法(普通和高效)。我們可以用C、Java、Python和其他語言編寫相同的程式。我們希望您覺得本教程有所幫助。

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統(RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統(RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP