將即時輸出的程序執行到 Tkinter GUI
本教程探討了使用 Python 將即時程序輸出整合到 Tkinter GUI 中。Tkinter 有助於建立視覺上吸引人的介面,而 subprocess 模組則有助於執行外部程序。透過結合這兩者並結合線程進行並行處理,開發人員可以建立響應迅速且互動式應用程式。
本教程概述了一個實際示例,以說明在基於 Tkinter 的 Python 應用程式中無縫整合即時輸出。在深入研究程式碼之前,讓我們簡要了解在 Tkinter GUI 中實現即時輸出所涉及的關鍵元件。
Tkinter − Tkinter 是 Python 的事實上的標準 GUI(圖形使用者介面)包。它提供建立視覺上吸引人且互動式使用者介面的工具。
subprocess 模組 − Python 的 subprocess 模組允許我們生成新程序,連線到它們的輸入/輸出/錯誤管道,並獲取它們的返回碼。
示例
讓我們逐步介紹一個簡單的示例,以演示在 Tkinter GUI 中執行具有即時輸出的程序。在本例中,我們將使用一個基本場景,其中命令列程序生成連續輸出。
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import scrolledtext
import subprocess
from threading import Thread
class RealTimeOutputGUI:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("Real-time Output in Tkinter GUI")
root.geometry("720x250")
# Create a scrolled text widget for real-time output
self.output_text = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(root, wrap=tk.WORD, height=20, width=50)
self.output_text.pack(padx=10, pady=10)
# Button to start the process
self.start_button = tk.Button(root, text="Start Process", command=self.start_process)
self.start_button.pack(pady=10)
def start_process(self):
# Disable the button to prevent multiple process launches
self.start_button['state'] = tk.DISABLED
# Launch the process in a separate thread
process_thread = Thread(target=self.run_process)
process_thread.start()
def run_process(self):
# Command to simulate a process with continuous output
command = ["python", "-u", "-c", "for i in range(5): print('Output:', i); import time; time.sleep(1)"]
# Use subprocess to run the command
process = subprocess.Popen(command, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, text=True, bufsize=1)
# Read and display real-time output in the GUI
with process.stdout:
for line in iter(process.stdout.readline, ''):
self.output_text.insert(tk.END, line)
self.output_text.yview(tk.END)
self.root.update()
# Enable the button after the process completes
self.start_button['state'] = tk.NORMAL
# Create the Tkinter root window
root = tk.Tk()
# Instantiate the RealTimeOutputGUI class
real_time_output_gui = RealTimeOutputGUI(root)
root.mainloop()
理解程式碼結構
讓我們剖析程式碼結構,以理解 Python 指令碼如何協調 Tkinter、subprocess 和執行緒之間的互動。
Tkinter 設定 − 我們首先設定一個基本的 Tkinter GUI,其中包含一個滾動文字小部件用於顯示即時輸出,以及一個按鈕用於啟動程序。
start_process 方法 − 當用戶單擊“啟動程序”按鈕時,將呼叫此方法。它停用該按鈕以防止多次啟動程序,並啟動一個新執行緒來執行程序。
run_process 方法 − 此方法定義將要執行的實際程序。在本例中,我們使用 subprocess 來執行生成連續輸出的 Python 命令。即時輸出逐行讀取並在 Tkinter GUI 中顯示。
執行緒使用 − 我們使用 threading 模組中的 Thread 類在新執行緒中執行程序。這確保了在程序執行時 GUI 保持響應。
更新 GUI − 為了在 Tkinter GUI 中顯示即時輸出,我們使用 ScrolledText 小部件的 insert 方法。此外,呼叫 yview 方法以將捲軸保持在底部,確保始終可見最新的輸出。update 方法用於在程序執行期間重新整理 GUI。
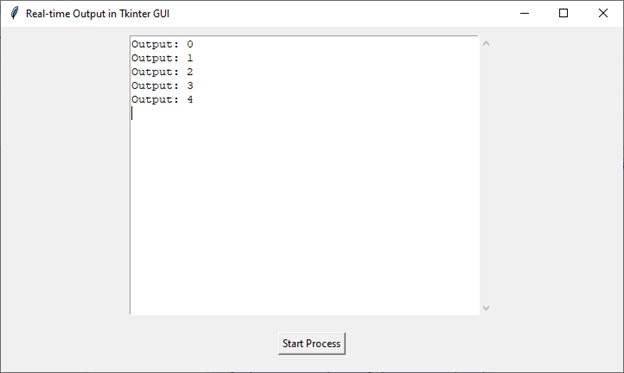
輸出
執行此程式碼後,您將獲得以下輸出視窗:
結論
總之,本教程中演示的將即時輸出整合到 Tkinter GUI 中,增強了各種 Python 應用程式的使用者體驗。透過結合用於圖形介面的 Tkinter、用於執行外部程序的subprocess 和用於並行執行的threading,開發人員可以建立響應迅速的互動式工具。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係型資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP