
- IndexedDB 教程
- IndexedDB - 首頁
- IndexedDB - 簡介
- IndexedDB - 安裝
- IndexedDB - 連線
- IndexedDB - 物件儲存
- IndexedDB - 建立資料
- IndexedDB - 讀取資料
- IndexedDB - 更新資料
- IndexedDB - 刪除資料
- 使用 getAll() 函式
- IndexedDB - 索引
- IndexedDB - 範圍
- IndexedDB - 事務
- IndexedDB - 錯誤處理
- IndexedDB - 搜尋
- IndexedDB - 遊標
- IndexedDB - Promise 包裝器
- IndexedDB - ECMAScript 繫結
- IndexedDB 有用資源
- IndexedDB 快速指南
- IndexedDB - 有用資源
- IndexedDB - 討論
IndexedDB 快速指南
IndexedDB - 簡介
資料庫管理系統提供了一種儲存和檢索資料的機制。其中,最常用的資料庫型別包括:
- 層次資料庫
- 網路資料庫
- 面向物件資料庫
- 關係資料庫
- NoSQL 資料庫
NoSQL 資料庫
NoSQL 資料庫(有時稱為 Not Only SQL)是一種資料庫,它提供了一種儲存和檢索資料的機制,不同於關係資料庫中使用的表格關係。這些資料庫是無模式的,支援輕鬆複製,具有簡單的 API,最終一致,並且可以處理海量資料(大資料)。
NoSQL 資料庫也有不同的型別,例如:
- 文件資料庫。
鍵值儲存。
列式資料庫。
圖資料庫。
什麼是 IndexedDB
Indexed Database 是一種 NoSQL 資料庫或非關係型結構化查詢語言資料庫。它是一個事務型資料庫系統,類似於基於 SQL 的 RDBMS。但是,與使用固定列表的基於 SQL 的 RDBMS 不同,IndexedDB 是一個基於 JavaScript 的面向物件資料庫。
當我們需要在伺服器端儲存大量資料並且速度比本地儲存更快時,可以使用它。因為它將資料儲存在瀏覽器中,所以它也可以線上和離線使用。使用它,您可以建立一個(具有豐富的查詢功能)能夠線上和離線執行的 Web 應用程式。
IndexedDB 的關鍵特性
以下是 IndexedDB 資料庫的關鍵特性:
IndexedDB 是一個 NoSQL 資料庫,它儲存鍵值對。它可以透過鍵或多種鍵型別儲存幾乎任何型別的鍵值。
如前所述,IndexedDB 遵循事務型資料庫模型 - 事務是圍繞操作或操作組的包裝類,以便維護資料完整性。您不希望資料被更改或丟失,因此如果事務失敗,則會回滾。
IndexedDB 不使用結構化查詢語言 - 由於 IndexedDB 使用 NoSQL 資料庫,因此它不使用 SQL,而是使用索引上的查詢透過遊標或getAll() 方法來迭代不同的集合。
IndexedDB 使用大量請求 - 請求是接收 DOM 事件成功或失敗的物件(DOM - HTML DOM 事件允許 JavaScript 在 HTML 文件中的元素上註冊不同的事件處理程式)。DOM 事件是成功或錯誤,它有一個 target 屬性,指示請求的流程。
成功事件無法取消,但錯誤事件可以取消。IndexedDB 中有很多請求,例如 onsuccess、onerror 和addEventListener()、removeEventListener()。為了瞭解請求的狀態,我們還有 readyState、result 和錯誤程式碼屬性。
IndexedDB 需要遵循同源策略 - 原點是編寫指令碼的文件的 URL,每個原點在其下有一些資料庫,每個資料庫都有其名稱來標識原點。對 IndexedDB 實施的安全邊界阻止應用程式訪問不同原點的資料。
例如,如果我們採用一個 URL 並採用其不同的子目錄,它可以檢索資料;但是,如果我們將位置更改為埠 8080 並嘗試從常規 URL 和更改的埠檢索資料,則無法檢索資料。
術語
以下是您在繼續學習之前應該瞭解的 IndexedDB 中各種重要的術語:
資料庫 - 在 IndexedDB 中,資料庫是最高級別,它包含包含資料的物件儲存。
物件儲存 - 物件儲存是 IndexedDB 的資料儲存實體。可以將其視為 RDBMS 中的表,我們根據要儲存的資料型別(例如:id、名稱、學號等)儲存資料。
事務 - 對於任何資料庫操作,我們執行以下過程。
- 獲取資料庫物件
- 在資料庫上開啟事務
- 在事務上開啟物件儲存,然後對物件儲存進行操作。
基本上,事務是一個連線到每個資料庫的包裝函式,它確保資料完整性,這樣如果事務被取消或發生任何錯誤,它將回調到事務尚未開始的地方。
索引 - 將物件儲存視為一個表,我們使用索引從表中檢索單個屬性的資料。例如:名稱、年齡等。
遊標 - 在資料庫中,如果我們需要遍歷物件儲存中的多個記錄,我們使用遊標。
IndexedDB 的支援
IndexedDB 是瀏覽器中的資料庫,因此我們需要檢查當前/現有瀏覽器是否支援它。為此,請將以下程式碼貼上到文字編輯器中,將其另存為test.html並在瀏覽器中執行它。
const indexedDB =
window.indexedDB ||
window.mozIndexedDB ||
window.webkitIndexedDB ||
window.msIndexedDB ||
window.shimIndexedDB;
if (!indexedDB) {
document.write("IndexedDB could not be found in this browser.");
}
const request = indexedDB.open("MyDatabase", 1);
如果您的瀏覽器支援 IndexedDB,則此程式將成功執行,並且將建立一個數據庫。
IndexedDB - 安裝
Visual Studio Code 是一個重新定義和最佳化用於構建和除錯現代 Web 和雲應用程式的程式碼編輯器。
您可以從其官方網站下載 Visual Studio Code - https://vscode.com.tw
根據您的 PC 配置和作業系統選擇您想要的版本。
下載完成後,您可以直接將其安裝到您的計算機上。
在 Windows 上安裝 Visual Studio Code 安裝程式
首先,如上所述下載適用於 Windows 的 Visual Studio Code 安裝程式:
- 下載完成後,執行安裝程式。

- 然後,接受協議並單擊下一步。

- 現在,單擊“建立桌面圖示”,以便可以從桌面上訪問它,然後單擊下一步。
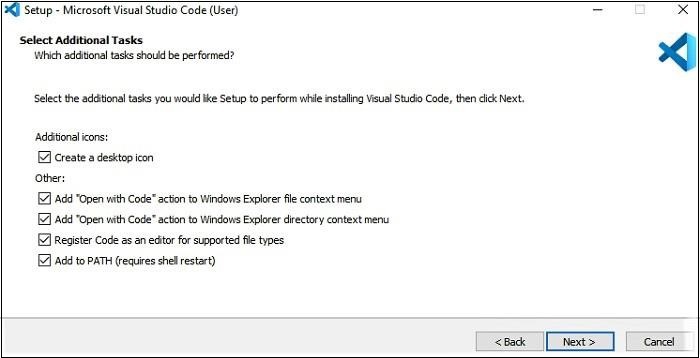
- 然後,單擊安裝按鈕。

最後,安裝完成後,單擊完成按鈕,Visual Studio Code 將開啟。

- 現在 Visual Studio Code 已成功安裝在您的裝置上,開始在此程式碼編輯器中編寫程式碼。
下載、安裝和建立 Node.js 專案(可選)
現在安裝 Visual Studio Code 後,我們需要安裝 Node.js
下載 Node.JS
您可以從其官方網站下載 Node.js,網址為 https://nodejs.com.tw/en/。
根據您的計算機配置選擇您選擇的版本。
LTS 版本是首選版本,因為它是一個更穩定的版本,它代表長期支援。
安裝 Node.js
按照以下步驟在您的系統中安裝 Node.js:
步驟 1 - 現在 Node.js 已開啟。您會看到此視窗彈出,單擊下一步。

步驟 2 - 您將被重定向到“終端使用者許可協議”視窗。接受協議並單擊下一步。

步驟 3 - 在下一個視窗中,您需要選擇“目標資料夾”。更改現有資料夾,或使用提到的預設資料夾,然後單擊下一步。

步驟 4 - 在“自定義安裝”和“原生模組工具”視窗中單擊下一步。
步驟 5 - 現在,設定已準備好,單擊安裝以安裝所選模組。

IndexedDB - 連線
資料庫是有組織的結構化資料集合,儲存在計算機系統中。要對資料執行操作,我們需要連線到資料庫。在本章中,我們將討論如何建立/連線到資料庫、開啟資料庫和刪除資料庫。
建立資料庫 - 您可以使用open() 函式在 IndexedDB 中建立資料庫。以下是此函式的語法。
let openRequest = indexedDB.open(name, version);
其中,
- name 是您需要建立的資料庫的名稱。
- version 是要建立的資料庫的版本。此引數的預設值為 1。如果您省略此值,則版本被認為是 1。
傳遞給此函式的版本值不應小於當前版本(IndexedDB)。如果資料庫建立成功,此函式返回 1;如果失敗,則返回 0。
示例
以下是如何在 IndexedDB 中建立資料庫的示例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Indexed db</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Creating a database
const request = indexedDB.open("myDatabase", 1);
if(indexedDB){
document.write("Database Created......");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
如果將上述程式碼儲存在“test.html”檔案中並執行它,則瀏覽器上將顯示以下訊息:
Database Created......
驗證
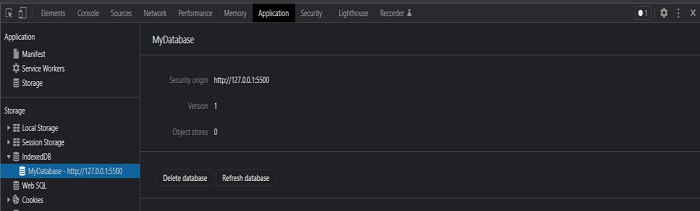
由於 IndexedDB 是瀏覽器的內建資料庫,因此您可以在瀏覽器本身中觀察建立的資料庫。
右鍵單擊結果頁面,單擊檢查元素並選擇應用程式選項卡。如果展開它,您可以在那裡看到 IndexedDB 資料庫,您可以看到如下所示的已建立資料庫檔案:

生成處理程式
事件是在 HTML 元素上執行的操作。使用 JavaScript,我們可以處理這些事件。從現在開始,我們使用 JavaScript 處理程式(為了更清楚起見)。
如果請求成功,我們使用onsuccess 事件。
request.onerror = event => {
// Do something (ex: document.write("error");
};
如果請求失敗,我們使用onerror 事件。
request.onsuccess = event => {
// Do something (ex : document.write("success");
};
當您建立資料庫或增加現有資料庫的版本號時,我們使用onupgradeneeded 事件。
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
};
示例
以下示例顯示訊息“資料庫建立成功”。如果資料庫建立成功。在這裡,我們使用onsuccess 和onerror 處理程式來顯示這些訊息。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Handlers</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("DATABASE", 1);
request.onsuccess = function (){
document.write("Database created successfully...")
}
request.onerror = function(){
document.write("database creation error");
}
request.onupgradeneeded = function(event){
var db = event.target.result;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
如果將上述程式碼儲存在“test.html”檔案中並執行它,則瀏覽器上將顯示以下訊息:
Database created successfully...
連線到現有資料庫
要與 IndexedDB 互動,我們使用 JavaScript。我們在 JavaScript 中編寫的程式碼不會直接與資料庫互動。我們需要使用連線物件連線到資料庫才能操作資料庫的物件。
直接開啟資料庫會建立一個連線。可以有多個連線到資料庫。當最初建立連線時,它處於開啟狀態。
您可以使用open() 函式(我們用來建立資料庫的函式)連線到 IndexedDB 資料庫。
語法
以下是連線到現有資料庫的語法。
let openRequest = indexedDB.open(name, version);
示例
下面給出了一個使用連線物件與現有資料庫互動的 JavaScript 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>OPENING A DATABASE</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("DATABASE", 1);
request.onsuccess = function (){
document.write("<br> Database created successfully")
}
const requestone = indexedDB.open("Database1",2);
requestone.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("<br> Database created successfully");
}
const requesttwo = indexedDB.open("DATABASE",1);
requesttwo.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("<br> Database opened successfully");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
上述程式在瀏覽器上列印以下輸出:
Database created successfully Database opened successfully Database created successfully
如果請求成功,則將呼叫名為 onsuccess 的事件。
另一種在瀏覽器中檢查資料庫的方法
除了檢查元素之外,還有一種方法可以在瀏覽器中檢查 IndexedDB 資料庫。
在右上角,將有一個自定義和控制按鈕,單擊它。
在列表中選擇更多工具選項,然後選擇開發者工具。

在下一頁中選擇應用程式選項卡,您可以在其中看到 IndexedDB 資料庫。

刪除資料庫
如果存在任何不需要的資料庫或其不必要地佔用空間,我們可以將其刪除。要刪除資料庫,可以使用deleteDatabase()函式。
以下是deleteDatabase()函式的語法:
let deleteRequest = indexedDB.deleteDatabase(name)
這裡,name引數是要刪除的資料庫的名稱。
示例
以下示例建立一個名為TestDatabase的資料庫,並使用deleteDatabase()函式將其刪除。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Indexed db</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("TestDatabase", 1);
request.onsuccess = function () {
document.write("Database Created Successfully");
};
var req = indexedDB.deleteDatabase("TestDatabase");
req.onsuccess = function () {
document.write("Database Deleted Successfully");
};
req.onerror = function () {
document.write("Couldn't delete the database");
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
直接從瀏覽器刪除資料庫
建立資料庫後,可以直接從瀏覽器中刪除它。為此,請按照以下步驟操作:
步驟1 - 使用以下一種方法開啟可以在瀏覽器中檢視 IndexedDB 資料庫(儲存)的頁面
檢查選項 - 右鍵點選 → 檢查 → 應用程式 或,
開發者工具 - 自定義和控制選項 → 更多工具 → 開發者工具 → 應用程式
步驟2 - 如果展開IndexedDB儲存,您可以看到如下所示建立的資料庫列表。

步驟3 - 點選要刪除的資料庫。在右側,您將找到刪除資料庫按鈕。如果單擊它,則將刪除此資料庫。

關閉資料庫
要關閉資料庫,我們需要使用函式IDBDatabase.close()
語法
IDBDatabase.close();
IDBDatabase 介面的close()方法立即返回並關閉連線。
在所有事務完成之前,連線不會關閉,但是,不能為此連線建立新事務,如果關閉操作正在進行中,則方法將丟擲異常。
IndexedDB - 物件儲存
物件儲存是 IndexedDB 的資料儲存。資料儲存在此處。一個數據庫可以有多個物件儲存。可以將其視為 RDBMS 中的表,我們根據要儲存的資料型別儲存資料。
為確保資料庫完整性,只能使用回撥函式idb.open()建立和刪除物件儲存。它包含一個名為createObjectStore()的方法,用於建立物件儲存。
建立物件儲存
您可以使用createObjectStore()方法建立物件儲存。以下是此方法的語法:
IDBDatabase.createObjectStore(name); Or, IDBDatabase.createObjectStore(name, options);
其中,
- name是物件儲存的名稱。
- options物件允許我們定義各種配置屬性。
示例
以下示例建立一個新的資料庫並在其中建立一個物件儲存:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Creating Object Store</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var request = indexedDB.open("myDatabase", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("customers");
document.write("Object store Created Successfully...");
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
執行後,上述程式會在瀏覽器上顯示以下訊息。
Object store Created Successfully...
驗證
如果成功執行上述程式,展開“myDatabase”,您可以看到新建立的物件儲存。

定義主鍵
類似於 RDBMS,我們需要主鍵來唯一地定義物件儲存中的某些資料。可以使用鍵路徑或鍵生成器兩種方式來完成。
鍵路徑和鍵生成器
鍵路徑是一個始終存在且包含唯一值的屬性。例如,我們可以選擇一個唯一值,例如電子郵件地址。
鍵生成器為新增到物件儲存的每個物件建立一個唯一值。預設情況下,如果我們不提及鍵生成器,它就會出現。例如,自動遞增。
語法
以下是建立物件儲存鍵路徑的語法。
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("ObjectStoreName", { keyPath: "primary key, autoincrement/autoDecrement : true" });
示例
在下面的示例中,我們使用 JavaScript 為物件儲存建立一個鍵路徑:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>keypath</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var request = indexedDB.open("myDtabase", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("customers",{keyPath:"id", autoIncrement:true});
document.write("Object store Created Successfully...");
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
執行上述示例後,它將在瀏覽器上顯示以下文字:
Object store Created Successfully...
驗證
如果成功執行上述程式,展開“myDatabase”,您可以看到新建立的物件儲存,如果單擊它,您可以觀察到為“id”建立了鍵路徑。

建立新的物件儲存時,它們會像上面一樣在 IndexedDB 資料夾中提到。
您可以同時使用鍵路徑和鍵生成器。如果資料始終唯一,我們可以使用鍵路徑;如果值發生更改,可以使用鍵生成器;如果要為每個值更改值,但要提供唯一表示儲存的值,則可以使用兩者。
定義索引
索引是一種物件儲存。它們用於從由指定屬性儲存的引用物件檢索資料。索引使用指定的屬性作為其鍵路徑,而不是引用儲存的主鍵。
要建立索引,需要在物件儲存例項上呼叫createIndex()方法。
語法
以下是createIndex()方法的語法:
var myIDBIndex = objectStore.createIndex(indexName, keyPath); var myIDBIndex = objectStore.createIndex(indexName, keyPath, Parameters);
其中,
indexName是建立的索引的名稱。
Keypath是在建立物件儲存時的主鍵定義
最後一個引數的值可以是unique或multi-entry
如果您“傳遞 unique: true”。索引不允許單個鍵出現重複值。
如果您傳遞“multi-entry: true”。當 keyPath 解析為陣列時,索引將為每個陣列元素新增一個條目。如果為 false,它將新增一個包含陣列的單個條目。
示例
以下 JavaScript 示例演示如何建立索引。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>OPENING A DATABASE</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const dbName = "myDB";
const studentdata = [
{name : "jason" , rollno: "160218737028" , branch : "IT"},
{name : "lokesh" , rollno: "160218735020" , branch : "CSE"},
{name : "tarun" , rollno: "160218733057" , branch : "EEE"},
{name : "pranith" , rollno: "160218737029" , branch : "IT"}
];
var request = indexedDB.open("myDB", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("student",{ keyPath :"rollno" });
objectStore.createIndex("name", "name", { unique: false });
objectStore.createIndex("branch", "branch", { unique: false });
objectStore.transaction.oncomplete = event => {
var objectStore = db.transaction("student", "readwrite").objectStore("student");
studentdata.forEach(function(student) {
objectStore.add(student);
});
};
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
如果您轉到並驗證 IndexedDB 資料庫myDB的內容並展開它,您可以看到建立的表如下:
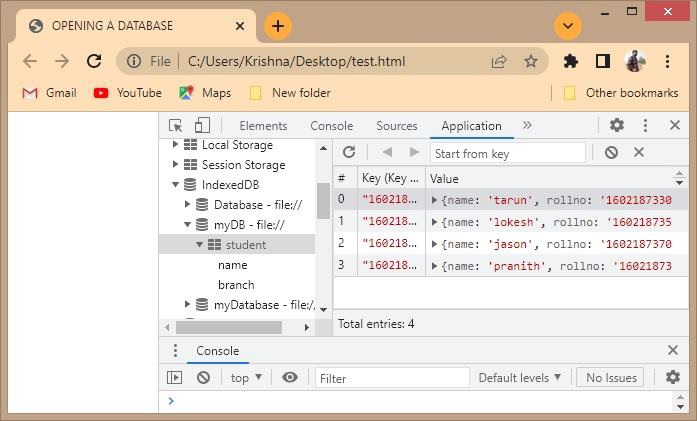
如果您單擊名稱和學生值,您可以看到索引值如下:
名稱索引
| # | 鍵(鍵路徑:“name”) | 主鍵(鍵路徑:“rollno”) | 值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | "jason" | "160218737028" | {name: 'jason', rollno: '160218737028', branch 1. branch: "IT" 2. name: "jason" 3. rollno: "160218737028" |
| 1 | "lokesh" | "160218735020" | {name: 'lokesh', rollno: '160218735020', branch: 'CSE'} 1. branch: "CSE" 2. name: "lokesh" 3. rollno: "160218735020" |
| 2 | "pranith" | "160218737029" | {name: 'pranith', rollno: '160218737029', branch: 'IT'} 1. branch: "IT" 2. name: "pranith" 3. rollno: "160218737029" |
| 3 | "tarun" | "160218733057" | {name: 'tarun', rollno: '160218733057', branch: 'EEE'} 1. branch: "EEE" 2. name: "tarun" 3. rollno: "160218733057" |
分支索引
| # | 鍵(鍵路徑:“branch”) | 主鍵(鍵路徑:“rollno”) | 值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | "CSE" | "160218735020" | {name:'lokesh', rollno:'160218735020', branch: 'CSE'} 1. branch: "CSE" 2. name: "lokesh" 3. rollno: "160218735020" |
| 1 | "EEE" | "160218733057" | {name:'tarun', rollno: '160218733057', branch: 'EEE'} 1. branch: "EEE" 2. name: "tarun" 3. rollno: "160218733057" |
| 2 | "IT" | "160218737028" | {name:'jason', rollno: '160218737028', branch: 'IT'} 1. branch: "IT" 2. name: "jason" 3. rollno: "160218737028" |
| 3 | "IT" | "160218737029" | {name:'pranith', rollno: '160218737029', branch: 'IT'} 1. branch: "IT" 2. name: "pranith" 3. rollno: "160218737029" |
刪除物件儲存
物件儲存類似於資料庫中的表,當不需要表時,我們會將其刪除。類似地,如果不再使用物件儲存,您可以將其刪除。要刪除物件儲存,需要呼叫deleteObjectStore()函式。
語法
以下是deleteObjectStore()函式的語法:
db.deleteObjectStore("store_name");
其中,store_name是要刪除的物件儲存的名稱。
示例
讓我們來看一個 JavaScript 示例,該示例刪除不再需要的物件儲存:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>OPENING A DATABASE</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const dbName = "Database";
var request = indexedDB.open("Database", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("student",{ keyPath :"rollno" } );
var objstore = db.createObjectStore("college",{autoIncrement : true});
db.deleteObjectStore("college");
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
在瀏覽器中刪除 IndexedDB 資料夾中的物件儲存之前和之後。
Database
College − object store
Student − object store
Name − index
Branch − index
Database
Student − object store
Name − index
Branch − index
IndexedDB - 建立資料
在建立資料之前,我們需要了解資料是如何傳輸的。IndexedDB 開啟事務,其每個資料操作都在每個事務內執行。每個操作都有四個步驟:
- 獲取資料庫物件
- 在資料庫上開啟事務
- 在事務上開啟物件儲存
- 對物件儲存進行操作
IndexedDB 中的操作:
- 建立
- 讀取
- 更新
- 刪除
首先,要在我們的資料庫中執行任何操作,我們需要開啟一個事務。開啟事務後,我們需要獲取所需的物件儲存。這些物件儲存僅根據建立事務時提到的要求提供。然後,可以稍後新增任何所需的資料。
函式用於執行給定的操作(如果有)。例如,我們使用 add() 函式將資料新增到資料庫或新增新條目。
語法
以下是將資料建立到資料庫中的語法:
ar request = objectStore.add(data);
我們可以使用add()或put()函式將資料新增到物件儲存中。
示例
在下面的示例中,我們使用 JavaScript 中的 add() 方法將資料插入物件儲存中:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>creating data</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const dbName = "Database";
var request = indexedDB.open("Database", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("student",{ keyPath :"rollno" } );
};
request.onsuccess = event => {
document.write("Database opened successfully");
var db = event.target.result;
var transaction = db.transaction("student", "readwrite");
var objectStore = transaction.objectStore("student");
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218737028, name: "jason", branch: "IT" });
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218733028, name: "tarun", branch: "EEE" });
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218732028, name: "lokesh", branch: "CSE" });
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218737025, name: "abdul", branch: "IT" });
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218736055, name: "palli", branch: "MECH" });
}
transaction.oncomplete = function () {
db.close();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
0 160218732028
{rollno: 160218732028, name: 'lokesh', branch: 'CSE'}
1 160218733028
{rollno: 160218733028, name: 'tarun', branch: 'EEE'}
2 160218736055
{rollno: 160218736055, name: 'palli', branch: 'CSE'}
3 160218737025
{rollno: 160218737025, name: 'abdul', branch: 'IT'}
4 160218737028
{rollno: 160218737028, name: 'jason', branch: 'IT'}
IndexedDB - 讀取資料
我們將資料輸入資料庫,我們需要呼叫資料以檢視更改,以及用於各種其他目的。
我們必須在物件儲存上呼叫get()方法來讀取此資料。get 方法獲取要從儲存中檢索的物件的主鍵。
語法
var request = objectstore.get(data);
在這裡,我們請求物件儲存使用 get() 函式獲取資料。
示例
以下示例是請求物件儲存獲取資料的實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
const idquery = store.get(4);
idquery.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("idquery",idquery.result);
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
database opened successfully
idquery {id: 4, name: 'abdul', branch: 'IT'}
IndexedDB - 更新資料
建立資料後,下一步是對其執行各種操作;因此,我們需要定期更新資料。如果我們將資料錯誤地輸入到資料庫中,我們還需要更新資料。在這裡,我們必須指定一個讀寫事務,因為我們要寫入資料庫,而不僅僅是從資料庫讀取。
如果我們想修改它或做一個已經存在於資料庫中的條目,我們使用put()函式。
語法
var requestUpdate = objectStore.put(data);
我們對發生事務的物件儲存使用put()函式,我們需要更新資料。
示例
讓我們來看下面的指令碼,瞭解如何使用 put() 函式更新或修改物件儲存中的資料:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const idquery = store.get(4);
idquery.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("idquery",idquery.result);
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
database opened successfully
idquery {id: 4, name: 'deevana', branch: 'CSE'}
Previously the data stored in id: 4 was
Name: abdul Branch : IT
But as we updated the entry the values are changed.
IndexedDB - 刪除資料
在許多情況下,我們需要從資料庫中刪除資料;無論是出於儲存目的,還是僅僅是為了刪除不需要的資料以釋放空間。如果我們想從資料庫中刪除這些不需要的資料,我們可以使用 .delete() 函式
語法
const request = objectStore.delete(data);
我們使用delete()函式刪除資料庫中不需要的欄位。
示例
讓我們來看一個刪除資料的示例指令碼:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE
const deletename = store.delete(1);
deletename.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("id : 1 has been deleted");
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
database opened successfully id : 1 has been deleted
刪除 id:1 後的資料庫:
0 2
{id: 2, name: 'praneeth', branch: 'CSE'}
1 3
{id: 3, name: 'palli', branch: 'EEE'}
2 4
{id: 4, name: 'deevana', branch: 'CSE'}
IndexedDB - 使用 getAll() 函式
在前面的部分中,我們一次只從儲存中檢索一個物件。現在我們可以檢索物件儲存的所有資料或子集。getAll 方法使用 getAll() 函式返回物件儲存中的所有物件
語法
ObjectStore.getAll(optionalConstraint);
我們可以直接呼叫 getAll() 來返回物件儲存中儲存的所有物件,或者我們可以指定可選約束,例如汽車資料庫中的紅色汽車
示例
在下面的示例指令碼中,我們呼叫 getAll() 方法一次返回物件儲存中儲存的所有物件:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const query = branchIndex.getAll(["IT"]);
query.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("query",query.result);
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
database opened successfully
query (1) [{...}]
arg1:(1) [{...}]
0:{id: 1, name: 'jason', branch: 'IT'}
length:1
[[Prototype]]:Array(0)
[[Prototype]]:Object
IndexedDB - 索引
索引是一種物件儲存,用於從由指定屬性儲存的引用物件檢索資料。即使索引位於引用物件儲存內幷包含相同的資料,它也使用指定的屬性作為其鍵路徑,而不是引用儲存的主鍵。
索引用於定義資料的唯一約束,並在建立物件儲存時建立。要建立索引,請在物件儲存例項上呼叫 createIndex 方法:
語法
var myIDBIndex = objectStore.createIndex(indexName, keyPath); var myIDBIndex = objectStore.createIndex(indexName, keyPath, objectParameters);
此方法建立並返回索引物件。該方法建立一個包含以下引數的索引:
索引名稱 - 索引的名稱。
鍵路徑 - 我們在這裡提到主鍵。
物件引數 - 存在兩個物件引數。
唯一 − 不允許新增重複值。
多值條目 − 如果為 true,則當 keyPath 解析為陣列時,索引將為索引中的每個陣列元素新增一個條目。如果為 false,則將新增一個包含陣列的單個條目。
示例
以下示例演示了在物件儲存中實現索引的方法:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
branchIndex:
1
['CSE']
0: "CSE"
length: 1
4
{id: 4, name: 'deevana', branch: 'CSE'}
branch: "CSE"
id: 4
name: "deevana"
2
['EEE']
0: "EEE"
length: 1
3
{id: 3, name: 'palli', branch: 'EEE'}
branch: "EEE"
id: 3
name: "palli"
3
['IT']
0: "IT"
length: 1
1
{id: 1, name: 'jason', branch: 'IT'}
branch: "IT"
id: 1
name: "jason"
IndexedDB - 範圍
當我們不想一次獲取所有資料時,我們使用範圍。當我們只想獲取特定範圍內的資料時,我們使用範圍。我們使用IDBKeyRange物件定義範圍。此物件有4個方法:
- upperBound()
- lowerBound()
- bound()
- only()
語法
IDBKeyRange.lowerBound(indexKey); IDBKeyRange.upperBound(indexKey); IDBKeyRange.bound(lowerIndexKey, upperIndexKey);
以下是各種範圍程式碼的列表:
| 序號 | 範圍程式碼和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 所有鍵 ≥ a DBKeyRange.lowerBound(a) |
| 2 | 所有鍵 > a IDBKeyRange.lowerBound(a, true) |
| 3 | 所有鍵 ≤ b IDBKeyRange.upperBound(b) |
| 4 | 所有鍵 < b IDBKeyRange.upperBound(b, true) |
| 5 | 所有鍵 ≥ a && ≤ b IDBKeyRange.bound(a, b) |
| 6 | 所有鍵 > a && < b IDBKeyRange.bound(a, b, true, true) |
| 7 | 所有鍵 > a && ≤ b IDBKeyRange.bound(a, b, true, false) |
| 8 | 所有鍵 ≥ a && < b IDBKeyRange.bound(a, b, false, true) |
| 9 | 鍵 = c IDBKeyRange.only(c) |
我們通常使用索引來使用範圍,在語法中,索引鍵表示索引的 keypath 值。
示例
以下是使用 get() 和 getAll() 方法檢索範圍程式碼的各種示例:
class.get(‘student’) class.getAll(IDBKeyRange.bound(‘science’,’math’) class.getAll(IDBKeyRange.upperbound(‘science’,true) class.getAll() class.getAllKeys(IDBKeyRange.lowerbound(‘student’,true))
HTML 示例
考慮以下 HTML 示例以獲取範圍程式碼:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const upperquery =store.getAll(IDBKeyRange.upperBound('2', true));
upperquery.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("upperquery",upperquery.result);
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
database opened successfully
upperquery (4) [{...}, {...}, {...}, {...}]
arg1: (4) [{...}, {...}, {...}, {...}]
0: {id: 1, name: 'jason', branch: 'IT'}
1: {id: 2, name: 'praneeth', branch: 'CSE'}
2: {id: 3, name: 'palli', branch: 'EEE'}
3: {id: 4, name: 'deevana', branch: 'CSE'}
length: 4
[[Prototype]]: Array(0)
[[Prototype]]: Object
IndexedDB - 事務
事務是一組操作,這些操作應該全部成功或全部失敗。例如,如果我們透過 UPI 向商家付款並且交易失敗,則資金必須退回到傳送方的賬戶。事務保持這種完整性。
以下是開啟事務的語法:
db.transaction(store[, type]);
這裡的 store 是我們想要進行事務的物件儲存。事務的型別有兩種:
只讀 − 只能讀取,預設情況下提供。
讀寫 − 我們既可以讀取也可以寫入資料,但不能在物件儲存中建立、刪除或更改它。
事務生命週期
事務是物件儲存之間執行任何操作的連線。每個事務都有一個狀態,可以是:
活動 − 當事務首次建立時,或當請求與事務關聯時。當事務處於此狀態時,可以針對事務發出新的請求。
非活動 − 在其建立後的事件返回控制之後,事務處於此狀態。當事務處於此狀態時,不能針對事務發出任何請求。
提交中 − 一旦與事務關聯的所有請求完成,它就會嘗試提交。在提交狀態期間,不能發出新的請求。
已完成 − 事務提交或中止後,它處於已完成狀態。在已完成狀態期間,不能發出新的請求。
事務的生命週期
形成具有作用域和模式的事務。事務的狀態最初在其生成時為活動狀態。
要開始事務,實現必須排隊一個任務。
處理與事務關聯的每個請求時,將觸發成功或錯誤事件。傳送事件時,事務狀態設定為活動狀態,允許針對事務發出後續請求。事件分派完成後,事務的狀態設定為非活動狀態。
可以在完成之前隨時取消事務,即使它當前未處於活動狀態或尚未開始。
當針對資料庫的所有請求都成功時,實現必須嘗試提交事務。
當事務提交或中止時,其狀態將設定為完成。
事務排程
當可以啟動事務時,有一些限制。
當沒有讀或寫事務時:a. 在事務 tx 之前建立;b. 與 tx 具有重疊的作用域;c. 不處於最終狀態,只讀事務 tx 可以開始。
當沒有其他事務時,可以開始讀/寫事務 tx:
- 在 tx 之前形成,
- 與 tx 具有重疊的作用域,或
- 未處於已完成狀態。
升級事務
具有模式“versionchange”的事務是升級事務。
可以使用升級操作建立、重新命名和刪除資料庫中的物件儲存和索引。
如果給定大於當前版本的版本,則在開啟資料庫連線後完成執行升級事務的步驟時,將自動生成升級事務。在此事務在upgradeneeded事件處理程式中處於活動狀態。
提交事務
必須完成以下步驟才能提交事務:
- 事務狀態首先設定為提交中。
- 等待列表中所有事務請求都已處理。
- 如果發生錯誤,則中止事務。
- 如果事務是升級事務,則將資料庫升級事務的事務連線設定為 NULL。
- 將事務狀態更改為完成。
- 觸發事務的完整事件
- 如果事務是升級事務,則將請求的事務設定為 null 併發出與事務關聯的請求。
語法
transaction.commit()
嘗試提交事務。所有掛起的請求都將被允許完成,但不會接受新的請求。
如果掛起的請求失敗,則事務將中止。成功請求的成功事件仍將觸發,但在事件處理程式中引發異常不會中止事務,呼叫preventDefault()不會阻止事務中止。
事件處理程式
以下是各種事件處理程式屬性:
attribute EventHandler onabort; attribute EventHandler oncomplete; attribute EventHandler onerror;
事務示例
以下是一個簡單的 JavaScript 程式,用於演示事務的使用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
document.write("transaction complete");
db.close;
};
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
database opened successfully transaction complete
此處僅在建立事務時才能將資料新增到物件儲存中,最後在事務完成後,我們關閉資料庫。
示例
以下示例顯示了事務屬性 oncomplete 的用法:
function student(db, names) {
let transaction = db.transaction(['names'], 'readwrite');
let store = transaction.objectStore('names');
for (let i = 0; i < messages.length; i++) {
store.add({text: names[i]});
}
transaction.oncomplete = function()
{document.write('transaction complete')};
}
中止事務
要中止事務,請按照以下步驟操作:
撤消對資料庫的所有與事務相關的修改。
在升級事務期間,物件儲存、索引和版本的更改也會被還原。
完成事務狀態。
如果錯誤不為空,則將事務錯誤設定為錯誤。
將請求已處理標誌設定為事務請求列表中每個請求的 true。
將請求完成標誌設定為 true,並將結果設定為定義。
如果事務是升級事務,則將與事務連線關聯的升級事務設定為 null。
建立一個帶有 bubbles 屬性設定為 true 的中止事務事件。
如果事務是升級事務,則假定請求是事務的開啟請求。
IndexedDB - 錯誤處理
並非我們編寫的全部請求都會返回輸出。這可能是由於:
- 編寫程式碼時可能出錯。
- 如果已超過儲存限制。
- 如果事務失敗等。
在失敗的請求中,事務被取消,所有更改都被還原。但有時我們希望在不還原所有更改的情況下處理失敗,為此我們使用request.onerror處理程式。它可以透過呼叫event.preventDefault()來阻止事務中止。
示例
以下是一個示例,用於演示 IndexedDB 中的錯誤處理:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>IndexedDB</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("DATABASE", 1);
request.onsuccess = function (){
document.write("database creation success")
}
request.onerror = function(event){
document.write("Database not created " + event.target.errorCode);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
Database not created undefined
我們可以使用 db.onerror 處理程式來捕獲錯誤。
db.onerror = function(event) {
let request = event.target;
document.write("Error is found", request.error);
};
當具有相同 ID 的物件已存在時,會發生約束錯誤。但有時如果任何錯誤都被完全處理,並且我們不想報告它,我們可以使用event.stopPropagation()在 request.onerror 中停止冒泡。
request.onerror = function(event) {
if (request.error.name == "ConstraintError") {
document.write("id already exists");
event.preventDefault();
event.stopPropagation();
}
}
IndexedDB - 搜尋
我們會遇到許多需要在物件儲存中搜索值的情況。物件儲存在內部排序。可以透過以下方式完成:
- 按鍵值或鍵範圍搜尋。
- 根據其他物件欄位搜尋。
按鍵搜尋
我們可以使用具有可接受鍵範圍的 IDBKeyRange 物件搜尋精確的鍵值或鍵值範圍。IDBKeyRange 物件具有以下呼叫:
IDBKeyRange.lowerBound(lower, [open]) 用於 >=lower
IDBKeyRange.upperBound(upper, [open]) 用於 >=upper
IDBKeyRange.bound(lower, upper, [lowerOpen] , [upperOpen]) 在 lower 和 upper 之間
IDBKeyRange.only(key) 如果範圍僅包含一個鍵。
要執行實際搜尋,我們使用物件儲存上的查詢引數。執行這些操作的不同型別的方法是
store.get(query) − 按鍵或範圍搜尋儲存中的第一個值
store.getAll([query],[count]) − 搜尋儲存中的所有值,直到達到提到的計數限制。
store.getKey(query) − 搜尋滿足查詢的第一個鍵。
store.getAllKeys([query],[count]) − 搜尋滿足查詢的所有鍵,直到完成計數限制。
store.count([query]) − 獲取滿足查詢的鍵的總數。
示例
在此示例中,我們使用 getAll() 方法檢索所有物件,並按其鍵搜尋物件:
class.get(‘student’) class.getAll(IDBKeyRange.bound(‘science’,’math’) class.getAll(IDBKeyRange.upperbound(‘science’,true) class.getAll() class.getAllKeys(IDBKeyRange.lowerbound(‘student’,true))
按欄位或索引搜尋
要根據其他物件欄位進行搜尋,我們需要使用索引。索引儲存具有所需值的物件的鍵列表。索引也像物件儲存一樣在內部排序。
語法
objectStore.createIndex(name, keyPath, [options]);
名稱 − 索引名稱
keyPath − 將對物件欄位的路徑進行搜尋
選項 − 選項有兩種型別
唯一 − 儲存中具有唯一值的物體將在 key path 中存在,並且不能建立它們的副本。
多值條目 − 如果 keypath 上的值是陣列,則預設情況下,索引將把整個陣列視為鍵,但如果我們使用多值條目,則陣列成員將成為索引鍵。
示例
如果我們想根據價格搜尋手機,示例程式如下:
openRequest.onupgradeneeded = function() {
let books = db.createObjectStore('phone', {keyPath: 'id'});
let index = books.createIndex('pricephone', 'price');
};
要建立索引,我們需要使用升級所需。
- 索引將跟蹤價格欄位。
- 如果價格不是唯一的,我們不能設定唯一選項。
- 如果價格不是陣列,則多值條目不適用。
示例
在以下示例中,我們建立了一個事務並使用 getAll() 函式檢索所有物件。檢索後,我們在該事務中搜索物件值。如果找到,則返回物件;否則,返回 false。
let transaction = db.transaction("phones");
let books = transaction.objectStore("phones");
let priceIndex = books.index("price_index");
let request = priceIndex.getAll(7);
request.onsuccess = function() {
if (request.result !== undefined) {
document.write("Phones", request.result);
} else {
document.write("There are no such phones");
}
};
HTML 示例
以下是在物件儲存中搜索值的 HTML 指令碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const req = branchIndex.getAll(["CSE"]);
req.onsuccess = function(){
if(req.result!==undefined){
document.write("bots",req.result);
} else{
document.write("There are no such bots");
}
};
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
database opened successfully
bots (2) [{...}, {...}]
arg1:(2) [{...}, {...}]
0:{id: 2, name: 'praneeth', branch: 'CSE'}
1:{id: 4, name: 'deevana', branch: 'CSE'}
length:2
[[Prototype]]:Array(0)
[[Prototype]]:Object
IndexedDB - 遊標
在檢索資料時,當我們知道要檢索哪個鍵時,我們使用了get()函式,但如果我們想遍歷物件儲存的所有值,我們可以使用遊標。
首先,我們使用 open cursor 函式,然後我們可以向其中新增引數。我們可以在openCursor()函式中插入的引數是:
- 使用鍵範圍限制物件的範圍
- 我們想要迭代的方向
以下是遊標的語法
語法
ObjectStore.openCursor(optionalKeyRange, optionalDirection);
對於物件儲存,我們使用openCursor()
optionalKeyRange − 我們可以限制需要檢索的物件數量的範圍。
optionalDirection − 我們可以指定我們想要迭代的方向。
示例 1
在此示例中,我們將學習如何使用 JavaScript 開啟遊標函式:
var objectStore = db.transaction("student").objectStore("student”);
objectStore.openCursor().onsuccess = event => {
var cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
document.write("Name" + cursor.key + cursor.value.name);
cursor.continue();
} else {
document.write("entries closed");
}
};
示例 2
當我們想要檢索物件儲存中的所有物件並將它們放入陣列中時。
var student = [];
objectStore.openCursor().onsuccess = event => {
var cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
student.push(cursor.value);
cursor.continue();
} else {
document.write(student);
}
};
示例 3
下面是另一個在 JavaScript 中實現 openCursor() 函式的示例:
var singleKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.only("Jason");
var lowerBoundKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.lowerBound("Praneeth");
var lowerBoundOpenKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.lowerBound("jason", true);
var upperBoundOpenKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.upperBound("praneeth", true);
var boundKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.bound("jason", "praneeth", false, true);
index.openCursor(boundKeyRange).onsuccess = event => {
var cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
cursor.continue();
}
};
或者如果我們想指定方向:
objectStore.openCursor(boundKeyRange, "prev").onsuccess = event => {
var cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
cursor.continue();
}
};
HTML 示例
實現遊標函式用法的 HTML 指令碼如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const req = store.openCursor();
req.onsuccess = function(){
const cursor = req.result;
if(cursor){
const key = cursor.key;
const value = cursor.value;
document.write(key,value);
cursor.continue();
} else {
document.write("bots completed");
}
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
database opened successfully
1 {id: 1, name: 'jason', branch: 'IT'}
2 {id: 2, name: 'praneeth', branch: 'CSE'}
3 {id: 3, name: 'palli', branch: 'EEE'}
4 {id: 4, name: 'deevana', branch: 'CSE'}
bots completed
IndexedDB - Promise 包裝器
Promise(承諾)就像回撥函式一樣,是一種在非同步操作完成時告訴你的程式碼要執行什麼操作的技術,而不會停止 JavaScript 執行時的執行緒。
可以使用 Promise 來代替向非同步函式提供回撥函式,以便在非同步函式完成後執行。
Promise 庫由 Jake Archibald 建立,它使用 Promise 而不是事件。
它比傳統的 IndexedDB 更易於使用。它簡化了 API,同時仍然保持其結構。
這裡我們只展示了增強功能,至於為什麼我們可以使用 Promise 庫,您可以訪問以下網站了解更多資訊:
它有一些增強功能:
- IDBDatabase
- IDBTransaction
- IDBCursor
IDBDatabase
從物件儲存中獲取或設定的快捷方式
const value = await db.get(storeName, key); await db.put(storeName, value, key);
從索引中獲取的快捷方式
const value = await db.getFromIndex(storeName, indexName, key);
IDBTransaction
tx.store
如果事務只有一個儲存區,則 store 屬性引用該儲存區;否則為 undefined,這時我們使用
const tx = db.transaction('any transaction');
const store = tx.store;
tx.objectStore(storeName);
tx.done
當事務成功完成時,.done Promise 解析;否則,它會拒絕並返回事務錯誤。
const tx = db.transaction(storeName, 'readwrite');
await Promise.all([
tx.store.add('one', 'two'),
tx.store.put('three', 'four'),
tx.done,
]);
IDBCursor
遊標前進方法有:
- Advance
- Continue
- ContinuePrimaryKey
它們返回一個指向遊標的 Promise,否則返回 null。
let cursor = await db.transaction(storeName).store.openCursor();
while (cursor) {
document.write(cursor.key, cursor.value);
cursor = await cursor.continue();
}
IndexedDB - ECMAScript 繫結
首先,什麼是 ECMAScript?
ECMAScript(歐洲計算機制造商協會指令碼)是一種基於 JavaScript 的指令碼語言。
JavaScript ES6 添加了新的語法和功能,使程式碼更易於閱讀,並且我們可以為相同的功能編寫更少的程式碼。ES6 具有許多新特性,例如箭頭函式、模板字串、類解構等。
繫結 - 將物件繫結到函式並使用“this”關鍵字引用它。
ECMAScript 處理鍵、值和鍵路徑。
它定義了本規範中定義的鍵值如何轉換為和從 ECMAScript 值轉換。
從值中提取鍵
要使用具有值、鍵路徑和可選多條目標誌的鍵路徑從值中提取鍵,我們需要遵循以下步驟。結果可能是鍵、無效、失敗,甚至是異常。
其中 r 是使用值和鍵路徑對值評估鍵路徑的結果。重新丟擲任何異常。如果 r 是失敗,則返回失敗。
如果多條目標誌為假,則 key 為使用 r 將值轉換為鍵的結果;否則,key 為使用 r 將值轉換為多條目鍵的結果。重新丟擲任何異常。
如果鍵無效,則返回無效。
返回鍵。