如何在 Python Tkinter 中使按鈕和標籤中的文字自動調整大小?
Tkinter 是 Python 中一個強大的圖形使用者介面庫,它提供了各種用於桌面應用程式的小部件。但是,在處理動態內容(例如長度可變的文字)時,處理按鈕和標籤的自動調整大小是一個常見的挑戰。
在本文中,我們將探討如何使用 Tkinter 和 Python 來實現這一點。在深入研究之前,讓我們首先更詳細地瞭解這個挑戰。
理解挑戰
預設情況下,Tkinter 中的按鈕和標籤具有固定尺寸。當它們內部的內容動態變化時,小部件可能不會自行調整大小以適應新內容,從而導致文字不完整或隱藏。在處理可變長度文字或在執行時生成文字時,這尤其成問題。
解決方案:Tkinter Text 小部件
為了解決這個挑戰,我們可以利用 Tkinter Text 小部件。與 Label 和 Button 小部件不同,Text 小部件可以自動調整自身大小以適應其內容。我們將建立一個簡單的應用程式,其中包含一個按鈕、一個標籤和一個文字小部件。按鈕將觸發一個函式來更新標籤和按鈕文字。
實現
讓我們深入探討逐步實現的示例:
步驟 1:匯入 Tkinter 模組
import tkinter as tk
匯入 Tkinter 模組並將其簡寫為 tk。
步驟 2:定義更新函式
def revise_content():
new_text = text_widget.get("1.0", "end-1c")
label.config(text=f"Updated Label: {new_text}")
button.config(text=f"Updated Button: {new_text}")
建立一個函式 `revise_content`,該函式從 Text 小部件檢索文字,更新標籤和按鈕文字,並相應地配置它們。
步驟 3:建立主應用程式視窗
app = tk.Tk()
app.title("Text Automatically Resize in Buttons and Lables")
app.geometry("720x250")
建立主應用程式視窗並設定其標題和大小。
步驟 4:建立 Text 小部件
text_widget = tk.Text(app, height=3, width=30, wrap="word")
text_widget.insert("1.0", "Type here...")
建立一個具有指定高度、寬度和自動換行的 Text 小部件。在小部件中插入一些初始文字。
步驟 5:建立 Label 小部件
label = tk.Label(app, text="Initial Label")
步驟 6:建立 Button 小部件
button = tk.Button(app, text="Update Content", command=revise_content)
建立一個帶有標籤“更新內容”的 Button 小部件,並將其與 `update_content` 函式關聯。
步驟 7:打包小部件
text_widget.pack(pady=10) label.pack(pady=10) button.pack(pady=10)
使用一些填充將小部件打包到主視窗中。
步驟 8:執行 Tkinter 事件迴圈
app.mainloop()
啟動 Tkinter 事件迴圈以使應用程式保持執行。
示例
以下是按鈕和標籤中文字自動調整大小的完整實現程式碼:
import tkinter as tk
# Function to update the label and button text based on the content of the Text widget
def revise_content():
# Get the text from the Text widget (from the first character to the end, excluding the last character)
new_text = text_widget.get("1.0", "end-1c")
# Update the label text with the new content
label.config(text=f"Updated Label: {new_text}")
# Update the button text with the new content
button.config(text=f"Updated Button: {new_text}")
# Create the main application window
app = tk.Tk()
app.title("Text Automatically Resize in Buttons and Lables")
app.geometry("720x250")
# Create a Text widget with a specified height, width, and word wrapping
text_widget = tk.Text(app, height=3, width=30, wrap="word")
text_widget.insert("1.0", "Type here...") # Insert initial text into the Text widget
# Create a Label widget with an initial text
label = tk.Label(app, text="Initial Label")
# Create a Button widget with the label "Update Content" and associate it with the update_content function
button = tk.Button(app, text="Update Content", command=revise_content)
# Pack the widgets into the main window with some padding
text_widget.pack(pady=10)
label.pack(pady=10)
button.pack(pady=10)
# Run the Tkinter event loop to keep the application running
app.mainloop()
執行此程式碼後,將出現一個視窗,其中包含一個文字框、一個標籤和一個標有“更新內容”的按鈕。在文字框中寫一些內容,然後單擊按鈕即可自動調整按鈕和標籤的大小。
輸出
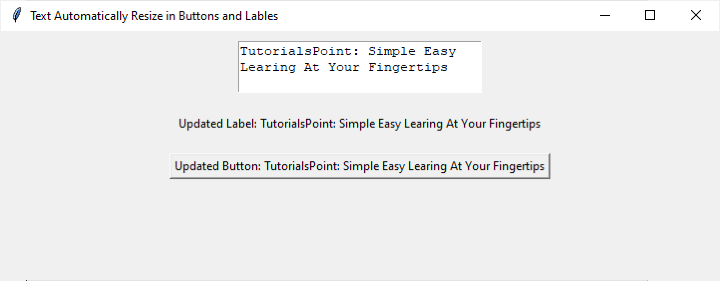
我在文字框中寫了一些文字,然後點選了“更新內容”按鈕。標籤和按鈕文字已自動調整大小。
結論
在使用 Python 進行 Tkinter GUI 開發的領域中,解決小部件的自動調整大小被證明是一個至關重要的方面,尤其是在處理動態內容時。透過利用 Tkinter Text 小部件的靈活性,我們已經展示了針對此挑戰的簡單解決方案。提供的示例展示了建立具有可調整大小的文字小部件、標籤和按鈕的響應式應用程式。
透過實現由按鈕觸發的函式,標籤和按鈕文字可以無縫地適應文字小部件不斷變化的內容。這種方法確保了 Tkinter 應用程式更友好的使用者介面和更好的適應性,為增強的使用者體驗和簡化的互動打開了大門。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP