如何在JavaScript的React Native中安裝Yup?
Yup是一個NPM包,我們可以將其安裝在React Native應用中。它用於驗證儲存在單個物件中的表單值。此外,我們可以使用Yup為不同的表單欄位新增不同型別的驗證。
使用者可以在專案目錄中執行以下命令來安裝Yup到React Native。
npm i Yup
如果使用者使用Yarn,可以使用以下命令。
yarn i Yup
語法
使用者可以按照以下語法在React Native應用程式中使用Yup進行表單驗證。
const schema = Yup.object().shape({
key1: Yup.string().required("Required"),
});
await schema.validate(values);
在上面的語法中,我們使用Yup建立了模式,並使用validate()方法根據模式中定義的規則驗證值。這裡,values是一個包含表單屬性名稱和值對的物件。
步驟
步驟1 - 首先,開發者需要從Yup匯入所需的內容。
步驟2 - 在App()元件中,使用Yup建立一個'userFormSchema',它定義了student_id、age和portfolio欄位的規則。這裡,student_id是字串且必填欄位,age是正整數且必填欄位,portfolio是網站的URL。
步驟3 - 現在,使用'useState'鉤子定義學生資訊和驗證訊息的狀態。
步驟4 - 定義handleChange()函式,它以鍵和值作為引數,並在'initialValue'狀態物件中更新值。
步驟5 - 接下來,定義validateValues()函式,它使用validate()方法,以userFormSchema作為參考,並以studentInfo物件作為引數來驗證表單值。
步驟6 - 根據表單值的驗證結果,將訊息設定為'message'狀態。
示例1
在下面的示例中,我們建立了一個表單來收集學生資訊。我們添加了三個輸入欄位來獲取學生的ID、年齡和作品集網站的URL。此外,我們還建立了提交按鈕。
每當使用者點選提交按鈕時,它都會呼叫validateValues()函式,該函式會在螢幕上顯示驗證訊息。
import React, { useState } from "react";
import * as Yup from "yup";
import { TouchableOpacity, View, TextInput, Text, Button } from "react-native";
const App = () => {
// creating the user form schema using Yup to validate student_id, age, and portfolio
const userFormSchema = Yup.object().shape({
student_id: Yup.string().required("Required"),
age: Yup.number().required("Required").positive().integer(),
portfolio: Yup.string().url().nullable(),
});
const [studentInfo, setStudentInfo] = useState({
student_id: "",
age: 13,
portfolio: "",
});
const [message, setMessage] = useState("");
function handleChange(key, val) {
setStudentInfo({ ...studentInfo, [key]: val });
}
// creating the handleFormSubmit function to handle the form submission
async function validateValues() {
try {
await userFormSchema.validate(studentInfo);
setMessage("Form is successfully submitted with no errors!");
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
setMessage("Form is not submitted due to errors!");
}
}
return (
// rendering the form
<View style = {{ width: "70%" }}>
{/* text inputs */}
<TextInput
placeholder = "student_id"
value = {studentInfo.student_id}
onChangeText = {(value) => handleChange("student_id", value)}
/>
<TextInput
placeholder = "age"
value = {studentInfo.age}
onChangeText = {(value) => handleChange("age", value)}
/>
<TextInput
placeholder = "portfolio"
value = {studentInfo.portfolio}
onChangeText = {(value) => handleChange("portfolio", value)}
/>
{/* submit button */}
<TouchableOpacity onPress = {validateValues}>
<Text> Submit Form </Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
<Text> {message} </Text>
</View>
);
};
export default App;
輸出
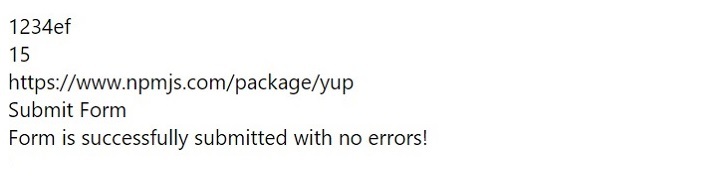
示例2
下面的示例是上面示例的進階版本。這裡,我們有三個輸入欄位,分別用於獲取使用者的姓名、電子郵件和密碼。
此外,我們還使用Yup建立了userFormSchema來驗證表單。在這裡,我們定義了規則,以便姓名至少三個字元長且必填。電子郵件應符合格式且必填,密碼應至少六個字元長。
此外,我們還為輸入欄位和錯誤訊息設定了一些樣式。當用戶點選提交按鈕時,它會呼叫handleFormSubmit()函式,該函式透過呼叫validateValues()函式來獲取驗證結果。它根據表單驗證顯示輸出訊息。
import React, { useState } from "react";
import * as Yup from "yup";
import {
StyleSheet,
TouchableOpacity,
View,
TextInput,
Text,
} from "react-native";
const App = () => {
// creating the user form schema using Yup to validate name, email and password
const userFormSchema = Yup.object().shape({
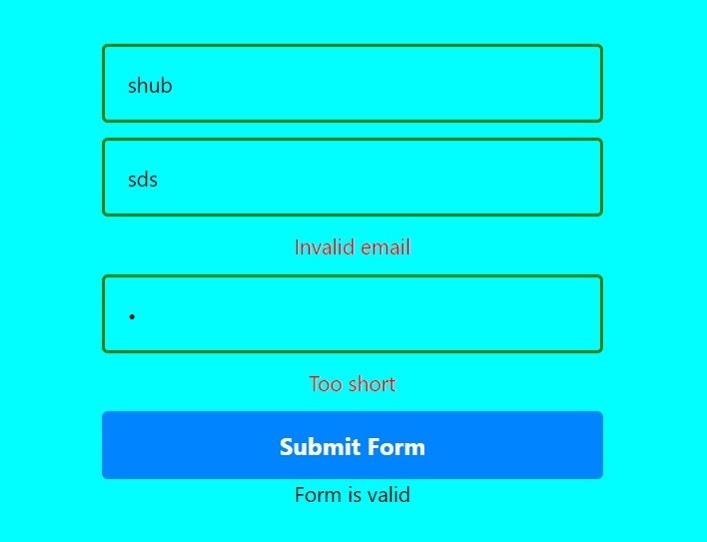
name: Yup.string().min(3, "Too short").required("Required"),
email: Yup.string().email("Invalid email").required("Required"),
password: Yup.string().min(6, "Too short").required("Required"),
});
// creating the styles for the elements
const elementStyles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
backgroundColor: "aqua",
justifyContent: "center",
},
error: {
marginBottom: 10,
color: "red",
},
button: {
backgroundColor: "#0084ff",
width: "70%",
borderRadius: 4,
alignItems: "center",
padding: 12,
},
input: {
borderWidth: 2,
padding: 15,
marginBottom: 10,
width: "70%",
borderColor: "green",
borderRadius: 4,
},
buttonText: {
color: "#fff",
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: "bold",
},
});
// creating the state for the form
const [initialValues, setInitialValues] = useState({
name: "",
email: "",
password: "",
});
// creating the state for the errors
const [errors, setErrors] = useState({});
const [message, setMessage] = useState("");
// creating the handleChange function to handle the change in the input fields
function handleChange(key, val) {
setInitialValues({ ...initialValues, [key]: val });
}
// creating the validateValues function to validate the form
async function validateValues() {
try {
// validating the form using the userFormSchema
await userFormSchema.validate(initialValues, { abortEarly: false });
setErrors({});
} catch (error) {
// if the form is invalid, then the errors are set to the state
const newErrors = error.inner.reduce((acc, cur) => {
acc[cur.path] = cur.message;
return acc;
}, {});
setErrors(newErrors);
}
}
// creating the handleFormSubmit function to handle the form submission
function handleFormSubmit() {
// validating the form values
validateValues().then(() => {
// set message based on the form is valid or invalid.
if (Object.keys(errors).length === 0) {
setMessage("Form is valid");
} else {
setMessage("Form is invalid");
}
});
}
return (
// rendering the form
<View style = {elementStyles.container}>
{/* text inputs */}
<TextInput
style = {elementStyles.input}
placeholder = "Name"
value = {initialValues.name}
onChangeText = {(value) => handleChange("name", value)}
/>
{errors.name && <Text style = {elementStyles.error}> {errors.name} </Text>}
<TextInput
style = {elementStyles.input}
placeholder = "Email"
value = {initialValues.email}
onChangeText = {(value) => handleChange("email", value)}
/>
{errors.email && <Text style= {elementStyles.error}> {errors.email} </Text>}
<TextInput
style = {elementStyles.input}
placeholder = "Password"
value = {initialValues.password}
onChangeText = {(value) => handleChange("password", value)}
secureTextEntry
/>
{errors.password && (
<Text style = {elementStyles.error}> {errors.password} </Text>
)}
{/* submit button */}
<TouchableOpacity style = {elementStyles.button} onPress = {handleFormSubmit}>
<Text style = {elementStyles.buttonText}> Submit Form </Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
<Text> {message} </Text>
</View>
);
};
export default App;
輸出
使用者學習瞭如何在React Native中使用Yup進行表單驗證。與編寫自定義表單驗證程式碼相比,開發者可以使用Yup等庫,這使程式碼更易讀且更簡單。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP