如何在 OpenCV Python 中找到影像輪廓的邊界矩形?
物體的邊界矩形是在影像中圍繞物體繪製的矩形。在OpenCV中有兩種方法可以找到邊界矩形 -
直邊界矩形
它是一個直線矩形,因為它不考慮物體的旋轉。可以使用函式cv2.boundingRect()計算。其語法如下 -
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
這裡,“cnt”是輪廓點的陣列。它返回邊界矩形的左上角座標(x,y)以及寬度和高度(w,h)。
旋轉矩形
它考慮了物體的旋轉,並繪製一個面積最小的矩形。旋轉矩形是使用函式cv2.minAreaRect()找到的。它返回左上角座標(x,y),(width,height),旋轉角度。矩形的4個角可以使用函式cv2.boxPoints()獲得。
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt) box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) box = np.int0(box) img = cv2.drawContours(img,[box],0,(0,255,255),2)
步驟
您可以使用以下步驟來計算給定函式的雅可比矩陣 -
匯入所需的庫。所需的庫是OpenCV和NumPy。
載入輸入影像。將輸入影像轉換為灰度影像。
對灰度影像應用閾值處理以建立二值影像。
找到影像中物體的輪廓。
使用上述輪廓計算直邊界矩形。在影像上繪製矩形。
計算旋轉邊界矩形並在影像上繪製它。
顯示帶有繪製的直線和旋轉邊界矩形的影像。
我們將在以下示例中使用以下影像作為輸入檔案。

示例 1
在下面的 Python 程式碼中,我們計算直邊界矩形。
# import required libraries import cv2 # read the input image img = cv2.imread('approx.png') # convert the image to grayscale gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # apply thresholding on the gray image to create a binary image ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,0) # find the contours contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # take the first contour cnt = contours[0] # compute the bounding rectangle of the contour x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) # draw contour img = cv2.drawContours(img,[cnt],0,(0,255,255),2) # draw the bounding rectangle img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2) # display the image with bounding rectangle drawn on it cv2.imshow("Bounding Rectangle", img) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
輸出
執行上述程式碼時,它將生成以下輸出視窗。
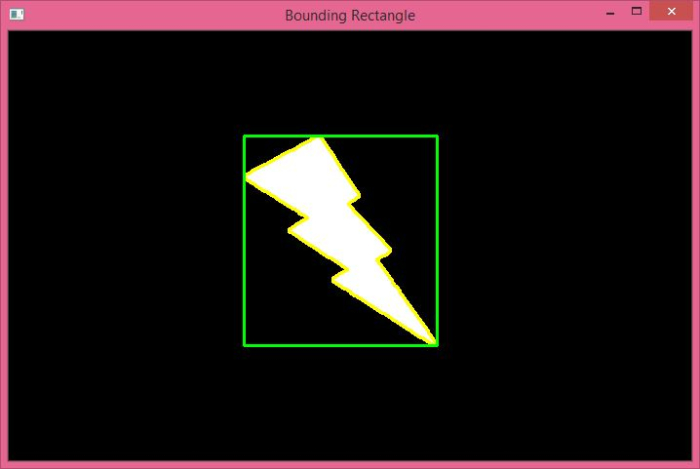
在上面的輸出中,綠色矩形顯示直邊界矩形。
現在,讓我們計算包含最小面積的旋轉邊界矩形。請參閱以下示例。
示例 2
在下面的 Python 程式碼中,我們計算直邊界矩形和旋轉邊界矩形。比較輸出視窗以清楚地瞭解兩種邊界矩形之間的區別。
import cv2 import numpy as np img = cv2.imread('approx.png') img1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img1,127,255,0) contours,_ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # print("Number of contours detected:", len(contours)) cnt = contours[0] # compute straight bounding rectangle x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) img = cv2.drawContours(img,[cnt],0,(255,255,0),2) img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2) # compute rotated rectangle (minimum area) rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt) box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) box = np.int0(box) # draw minimum area rectangle (rotated rectangle) img = cv2.drawContours(img,[box],0,(0,255,255),2) cv2.imshow("Bounding Rectangles", img) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
輸出
執行上述程式碼時,它將生成以下輸出視窗。
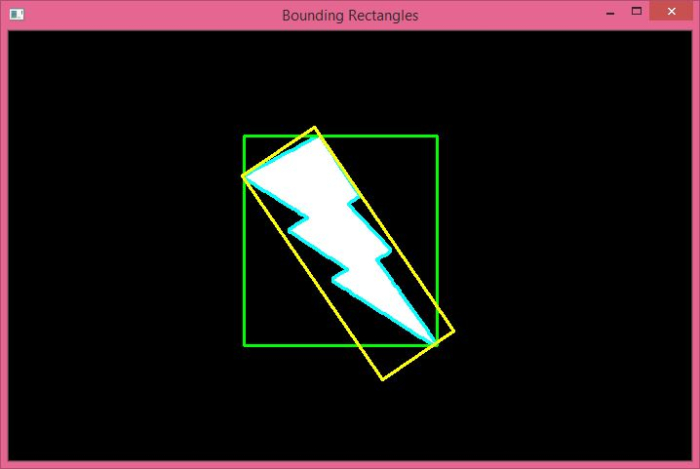
在上面的輸出中,綠色矩形是直邊界矩形,黃色矩形是最小面積的旋轉矩形。注意這兩個矩形之間的區別。

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP