如何在 Android 中將 HashMap 儲存到 Shared Preferences?
此示例演示瞭如何在 Android 中將 HashMap 儲存到 Shared Preferences。
步驟 1 − 在 Android Studio 中建立一個新專案,轉到檔案 ⇒ 新建專案,並填寫所有必需的詳細資訊以建立新專案。
步驟 2 − 將以下程式碼新增到 res/layout/activity_main.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/rlMain" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_margin="16dp" android:orientation="vertical"> <EditText android:id="@+id/etName" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="Name" android:inputType="text" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/etAge" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="Age" android:inputType="number" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/etGame" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="Favourite game" android:inputType="text" /> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="16dp" android:onClick="saveLocal" android:text="save local" /> </LinearLayout>
步驟 3 − 將以下程式碼新增到 src/MainActivity.java
package app.com.sample;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
final String mapKey = "map";
EditText etName, etAge, etGame;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
etName = findViewById(R.id.etName);
etAge = findViewById(R.id.etAge);
etGame = findViewById(R.id.etGame);
Map<String, Object> outputMap = loadMap();
if (outputMap.containsKey("name"))
etName.setText(Objects.requireNonNull(outputMap.get("name")).toString());
if (outputMap.containsKey("age"))
etAge.setText(Objects.requireNonNull(outputMap.get("age")).toString());
if (outputMap.containsKey("game"))
etGame.setText(Objects.requireNonNull(outputMap.get("game")).toString());
}
public void saveLocal(View view) {
String name = etName.getText().toString().trim();
String age = etAge.getText().toString().trim();
String game = etGame.getText().toString().trim();
if (name.isEmpty()) {
etName.setError("*required");
etName.requestFocus();
} else if (age.isEmpty()) {
etAge.setError("*required");
etAge.requestFocus();
} else if (game.isEmpty()) {
etGame.setError("*required");
etGame.requestFocus();
} else {
Map<String, Object> inputMap = new HashMap<>();
inputMap.put("name", name);
inputMap.put("age", age);
inputMap.put("game", game);
saveMap(inputMap);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Saved Locally!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
private void saveMap(Map<String, Object> inputMap) {
SharedPreferences pSharedPref = getApplicationContext().getSharedPreferences("MyVariables",
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
if (pSharedPref != null) {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(inputMap);
String jsonString = jsonObject.toString();
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = pSharedPref.edit();
editor.remove(mapKey).apply();
editor.putString(mapKey, jsonString);
editor.commit();
}
}
private Map<String, Object> loadMap() {
Map<String, Object> outputMap = new HashMap<>();
SharedPreferences pSharedPref = getApplicationContext().getSharedPreferences("MyVariables",
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
try {
if (pSharedPref != null) {
String jsonString = pSharedPref.getString(mapKey, (new JSONObject()).toString());
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(jsonString);
Iterator<String> keysItr = jsonObject.keys();
while (keysItr.hasNext()) {
String key = keysItr.next();
outputMap.put(key, jsonObject.get(key));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return outputMap;
}
}步驟 4 − 將以下程式碼新增到 androidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="app.com.sample"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name=".MainActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
讓我們嘗試執行您的應用程式。我假設您已將您的實際 Android 移動裝置連線到您的計算機。要從 Android Studio 執行應用程式,請開啟您的一個專案活動檔案,然後單擊執行 ![]() 工具欄中的圖示。選擇您的移動裝置作為選項,然後檢查您的移動裝置,它將顯示您的預設螢幕 –
工具欄中的圖示。選擇您的移動裝置作為選項,然後檢查您的移動裝置,它將顯示您的預設螢幕 –
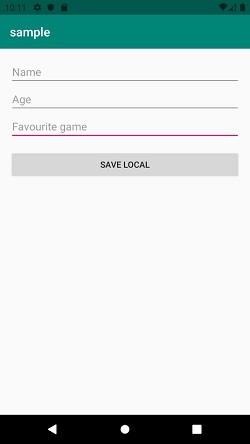
點選 這裡 下載專案程式碼。

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP