用 C++ 統計二叉樹中二叉搜尋樹的數量
給定一個二叉樹作為輸入。目標是在其中找到作為子樹存在的二叉搜尋樹 (BST) 的數量。BST 是一棵二叉樹,其左子節點小於根節點,右子節點大於根節點。
例如
輸入
輸入值建立後的樹如下所示:

輸出
Count the Number of Binary Search Trees present in a Binary Tree are: 2
解釋
我們得到一個整數陣列,用於形成一棵二叉樹,我們將檢查其中是否存在二叉搜尋樹。每個根節點都表示二叉搜尋樹,所以在給定的二叉樹中,我們可以看到不存在其他二叉搜尋樹,因此計數為 2,這是二叉樹中葉節點的總數。
輸入
輸入值建立後的樹如下所示:
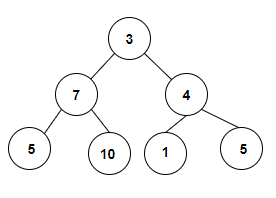
輸出
Count the Number of Binary Search Trees present in a Binary Tree are: 6
解釋
我們得到一個整數陣列,用於形成一棵二叉樹,我們將檢查其中是否存在二叉搜尋樹。每個根節點都表示二叉搜尋樹,所以在給定的二叉樹中,我們可以看到有 4 個葉節點和兩個形成 BST 的子樹,因此計數為 6。
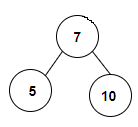
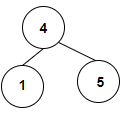
下面程式中使用的方法如下:
在這種方法中,我們將找到節點 N 左子樹中節點的最大值,並檢查它是否小於 N。此外,我們還將在節點 N 的右子樹中找到最小值,並檢查它是否大於 N。如果為真,則它是一個 BST。自下而上遍歷二叉樹並檢查上述條件,並遞增 BST 的計數。
每個 `node_data` 節點包含的資訊包括:存在的 BST 數量、該樹中的最大值、最小值、如果該子樹是 BST 則為 true 的布林值。
函式 `BST_present(struct tree_node* parent)` 查詢以 `parent` 為根的二叉樹中存在的 BST 的數量。
如果 `parent` 為 NULL,則返回 `{0, min, max, true}`,其中 `min` 為 INT_MIN,`max` 為 INT_MAX。
如果左子節點和右子節點都為 NULL,則返回 `{1, parent->data, parent->data, true}`。
設定 `node_data Left = BST_present(parent->left);` 和 `node_data Right = BST_present(parent->right);`
取節點 n1 並設定 `n1.lowest = min(parent->data, (min(Left.lowest, Right.lowest)))` 為其右子樹中的最小值。
設定 `n1.highest = max(parent->data, (max(Left.highest, Right.highest)));` 為其左子樹中的最大值。
如果 `(Left.check && Right.check && parent->data > Left.highest && parent->data < Right.lowest)` 返回 true,則設定 `n1.check = true`,因為它是一個 BST。
將 BST 的計數增加為 `n1.total_bst = 1 + Left.total_bst + Right.total_bst;`
否則,設定 `n1.check = false`,並將計數設定為 `n1.total_bst = Left.total_bst + Right.total_bst;`。
最後返回 n1。
示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct tree_node{
struct tree_node* left;
struct tree_node* right;
int data;
tree_node(int data){
this−>data = data;
this−>left = NULL;
this−>right = NULL;
}
};
struct node_data{
int total_bst;
int highest, lowest;
bool check;
};
node_data BST_present(struct tree_node* parent){
if(parent == NULL){
int max = INT_MAX;
int min = INT_MIN;
return { 0, min, max, true };
}
if(parent−>left == NULL){
if(parent−>right == NULL){
return { 1, parent−>data, parent−>data, true };
}
}
node_data Left = BST_present(parent−>left);
node_data Right = BST_present(parent−>right);
node_data n1;
n1.lowest = min(parent−>data, (min(Left.lowest, Right.lowest)));
n1.highest = max(parent−>data, (max(Left.highest, Right.highest)));
if(Left.check && Right.check && parent−>data > Left.highest && parent−>data < Right.lowest){
n1.check = true;
n1.total_bst = 1 + Left.total_bst + Right.total_bst;
} else{
n1.check = false;
n1.total_bst = Left.total_bst + Right.total_bst;
}
return n1;
}
int main(){
struct tree_node* root = new tree_node(3);
root−>left = new tree_node(7);
root−>right = new tree_node(4);
root−>left−>left = new tree_node(5);
root−>right−>right = new tree_node(1);
root−>left−>left−>left = new tree_node(10);
cout<<"Count the Number of Binary Search Trees present in a Binary Tree are: "<<BST_present(root).total_bst;
return 0;
}輸出
如果我們執行以上程式碼,它將生成以下輸出:
Count the Number of Binary Search Trees present in a Binary Tree are: 2


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP