C++ 中二叉樹中半節點的計數(迭代和遞迴)
給定一棵二叉樹,任務是使用迭代和遞迴方法計算二叉樹中可用半節點的數量。半節點是指只有一個子節點,另一個子節點為空的節點。請注意,在半節點中,我們不考慮葉節點。
二叉樹是一種用於資料儲存的特殊資料結構。二叉樹有一個特殊條件,即每個節點最多可以有兩個子節點。二叉樹兼具有序陣列和連結串列的優點,搜尋速度與排序陣列一樣快,插入或刪除操作速度與連結串列一樣快。非葉節點也稱為父節點,因為它們具有超過 0 個子節點且少於 2 個子節點。
二叉樹的結構如下所示:

例如
輸入-
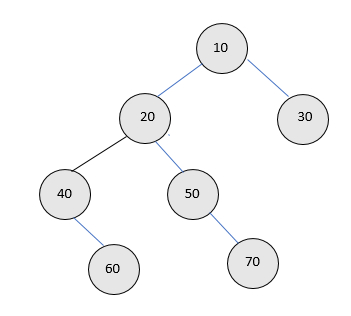
輸出 - 計數為 2
說明 - 在給定的樹中,有 2 個節點,即 40 和 50 恰好有一個子節點或半節點,其他節點可能有兩個子節點或沒有子節點。
迭代
下面程式中使用的方法如下
建立一個節點結構,包含資料部分、左指標和右指標。
建立一個函式,將節點插入到二叉樹中。
建立一個函式來計算半節點。
在函式內部,檢查 IF !node 則返回,因為樹中沒有節點。
宣告一個臨時變數 count 來儲存半節點的數量
建立一個佇列型別變數,例如 qu
將節點推入佇列,例如 qu.push(node)
迴圈 while !qu.empty()
建立一個臨時變數,例如 Node 型別的 temp,並將其初始化為 queue.front()
使用 qu.pop() 彈出元素
檢查 IF (!temp-> leftAND temp-> right) OR (temp->left AND !temp->right) 則將 count 加 1
檢查 IF (temp->left != NULL) 則執行 qu.push(temp->left)
返回計數
列印結果。
示例
// Program to count half nodes in a Binary Tree
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
// Function to get the count of half Nodes
int halfcount(struct Node* node){
// If tree is empty
if (!node)
return 0;
int result = 0; // Initialize count of half nodes
// Do level order traversal starting from root
queue<Node *> myqueue;
myqueue.push(node);
while (!myqueue.empty()){
struct Node *temp = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
if ((!temp->left && temp->right) || (temp->left && !temp->right)){
result++;
}
if (temp->left != NULL){
myqueue.push(temp->left);
}
if (temp->right != NULL){
myqueue.push(temp->right);
}
}
return result;
}
/* To allocate new Node with the given data and NULL left
and right pointers. */
struct Node* newNode(int data){
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main(void){
struct Node *root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(20);
root->right = newNode(30);
root->left->left = newNode(40);
root->left->right = newNode(50);
root->left->left->right = newNode(60);
root->left->right->right = newNode(70);
cout <<"count is: "<<halfcount(root);
return 0;
}輸出
如果我們執行以上程式碼,我們將得到以下輸出:
count is: 2
遞迴
下面程式中使用的方法如下
建立一個節點結構,包含資料部分、左指標和右指標。
建立一個函式,將節點插入到二叉樹中。
建立一個函式來計算半節點。
在函式內部,檢查 IF !node 則返回,因為樹中沒有節點。
宣告一個臨時變數 count 來儲存半節點的數量
檢查 IF (root -> left = NULL AND root->right != NULL) OR (root -> left != NULL AND root->right == NULL) 則將 count 加 1
設定 count = count + 遞迴呼叫此函式(root->left) + 遞迴呼叫此函式(root->right)
返回計數
列印結果。
示例
// Recursive program to count half nodes
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A binary tree Node has data, pointer to left
// child and a pointer to right child
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
int halfcount(struct Node* root){
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int result = 0;
if ((root->left == NULL && root->right != NULL) || (root->left != NULL && root->right ==
NULL)){
result++;
}
result += (halfcount(root->left) + halfcount(root->right));
return result;
}
/* to allocate a new Node with the given data and NULL left
and right pointers. */
struct Node* newNode(int data){
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main(){
struct Node *root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(20);
root->right = newNode(30);
root->left->left = newNode(40);
root->left->right = newNode(50);
root->left->left->right = newNode(60);
root->left->right->right = newNode(70);
cout <<"count is: "<<halfcount(root);
return 0;
}輸出
如果我們執行以上程式碼,我們將得到以下輸出:
count is: 2


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP