在 C 程式設計中,什麼是靜態記憶體分配?
記憶體可以按照以下兩種方式分配 −
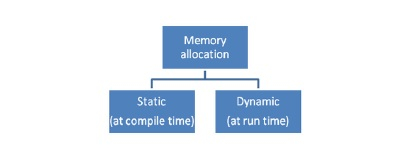
靜態記憶體分配
靜態變數在一個已分配空間塊中定義,且大小固定。一旦分配,就永遠不能釋放。
記憶體為程式中宣告的變數分配。
可使用“&”運算子獲取地址,並可以將其分配給指標。
記憶體是在編譯時分配的。
它使用棧來維護記憶體的靜態分配。
在這種分配中,一旦分配了記憶體,記憶體大小就無法更改。
它的效率較低。
在執行程式之前就決定變數的最終大小,這將稱為靜態記憶體分配。它也稱為編譯時記憶體分配。
我們不能更改在編譯時分配的變數的大小。
示例 1
靜態記憶體分配通常用於陣列。讓我們看一個關於陣列的示例程式 −
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int a[5] = {10,20,30,40,50};
int i;
printf (“Elements of the array are”);
for ( i=0; i<5; i++)
printf (“%d, a[i]);
}輸出
Elements of the array are 1020304050
示例 2
讓我們考慮另一個示例,計算陣列中所有元素的總和和乘積 −
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
//Declaring the array - run time//
int array[5]={10,20,30,40,50};
int i,sum=0,product=1;
//Reading elements into the array//
//For loop//
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
//Calculating sum and product, printing output//
sum=sum+array[i];
product=product*array[i];
}
//Displaying sum and product//
printf("Sum of elements in the array is : %d
",sum);
printf("Product of elements in the array is : %d
",product);
}輸出
Sum of elements in the array is : 150 Product of elements in the array is : 12000000

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統
關係型資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP