
- Swing 程式設計示例
- 示例 - 主頁
- 示例 - 環境設定
- 示例 - 邊框
- 示例 - 按鈕
- 示例 - 複選框
- 示例 - 組合框
- 示例 - 顏色選擇器
- 示例 - 對話方塊
- 示例 - 編輯器窗格
- 示例 - 檔案選擇器
- 示例 - 格式化文字欄位
- 示例 - 框架
- 示例 - 列表
- 示例 - 佈局
- 示例 - 選單
- 示例 - 密碼欄位
- 示例 - 進度條
- 示例 - 滾動窗格
- 示例 - 滑塊
- 示例 - 微調器
- 示例 - 表格
- 示例 - 工具欄
- 示例 - 樹形結構
- Swing 實用資源
- Swing - 快速指南
- Swing - 實用資源
- Swing - 討論
Swing 示例 - 使用 JEditorPane 顯示 HTML 網頁
以下示例展示瞭如何在基於 Swing 的應用程式中顯示 HTML 檔案的 HTML 內容。
我們正在使用以下 API。
JEditorPane − 建立一個編輯器框來顯示 HTML 內容。
jEditorPane.setPage(URL url) − 從傳遞的 URL 中獲取 HTML 並顯示。
示例
讓我們在 SwingTester.java 所在的當前目錄中建立一個 html 檔案 test.htm。
test.htm
<html>
<head>
<title>Swing Tester</title>
</head>
<body>
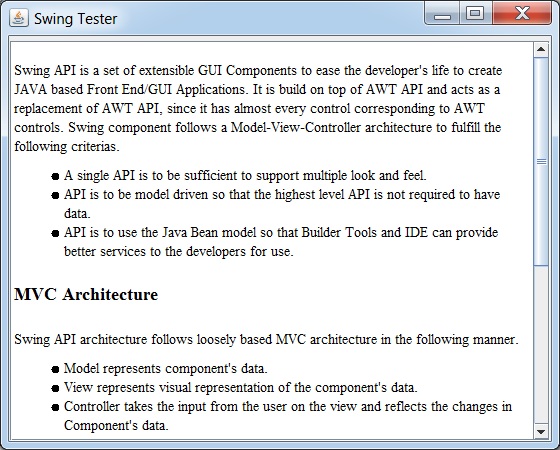
<p>Swing API is a set of extensible GUI Components
to ease the developer's life to create JAVA based Front End/GUI
Applications. It is build on top of AWT API and acts as a replacement of
AWT API, since it has almost every control corresponding to AWT controls.
Swing component follows a Model-View-Controller architecture to
fulfill the following criterias.</p>
<ul>
<li><p>A single API is to be sufficient to support multiple look and feel.</p></li>
<li><p>API is to be model driven so that the highest level API is not required to have data.</p></li>
<li><p>API is to use the Java Bean model so that Builder Tools and IDE can provide better services to the developers for use.</p></li>
</ul>
<h2>MVC Architecture</h2>
<p>Swing API architecture follows loosely based MVC architecture in the following manner.</p>
<ul>
<li><p>Model represents component's data.</p></li>
<li><p>View represents visual representation of the component's data.</p></li>
<li><p>Controller takes the input from the user on the view and reflects the changes in Component's data.</p></li>
<li><p>Swing component has Model as a seperate element, while the View and Controller part are clubbed in the User Interface elements. Because of which, Swing has a pluggable look-and-feel architecture.</p></li>
</ul>
<h2>Swing Features</h2>
<ul>
<li><p><b>Light Weight</b> − Swing components are independent of native Operating System's API as Swing API controls are rendered mostly using pure JAVA code instead of underlying operating system calls.</p></li>
<li><p><b>Rich Controls</b> − Swing provides a rich set of advanced controls like Tree, TabbedPane, slider, colorpicker, and table controls.</p></li>
<li><p><b>Highly Customizable</b> − Swing controls can be customized in a very easy way as visual apperance is independent of internal representation.</p></li>
<li><p><b>Pluggable look-and-feel</b> − SWING based GUI Application look and feel can be changed at run-time, based on available values.</p></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
SwingTester.htm
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.LayoutManager;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.swing.JEditorPane;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
public class SwingTester {
public static void main(String[] args) {
createWindow();
}
private static void createWindow() {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Swing Tester");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
createUI(frame);
frame.setSize(560, 450);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
private static void createUI(final JFrame frame){
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
LayoutManager layout = new FlowLayout();
panel.setLayout(layout);
JEditorPane jEditorPane = new JEditorPane();
jEditorPane.setEditable(false);
URL url= SwingTester.class.getResource("test.htm");
try {
jEditorPane.setPage(url);
} catch (IOException e) {
jEditorPane.setContentType("text/html");
jEditorPane.setText("<html>Page not found.</html>");
}
JScrollPane jScrollPane = new JScrollPane(jEditorPane);
jScrollPane.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(540,400));
panel.add(jScrollPane);
frame.getContentPane().add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
}
輸出
swingexamples_editorpanes.htm
廣告