
- Python PostgreSQL 教程
- Python PostgreSQL - 首頁
- Python PostgreSQL - 簡介
- Python PostgreSQL - 資料庫連線
- Python PostgreSQL - 建立資料庫
- Python PostgreSQL - 建立表
- Python PostgreSQL - 插入資料
- Python PostgreSQL - 查詢資料
- Python PostgreSQL - WHERE 子句
- Python PostgreSQL - ORDER BY 子句
- Python PostgreSQL - 更新表
- Python PostgreSQL - 刪除資料
- Python PostgreSQL - 刪除表
- Python PostgreSQL - LIMIT 子句
- Python PostgreSQL - JOIN 子句
- Python PostgreSQL - 遊標物件
- Python PostgreSQL 有用資源
- Python PostgreSQL 快速指南
- Python PostgreSQL - 有用資源
- Python PostgreSQL - 討論
Python PostgreSQL 快速指南
Python PostgreSQL - 簡介
PostgreSQL 是一個功能強大的開源物件關係資料庫系統。它擁有超過 15 年的活躍開發階段,並且擁有經過驗證的架構,使其贏得了可靠性、資料完整性和正確性的良好聲譽。
要使用 Python 與 PostgreSQL 通訊,您需要安裝 psycopg,這是一個為 Python 程式設計提供的介面卡,當前版本為 psycog2。
psycopg2 的編寫目標是體積小、速度快且穩定。它可以透過 PIP(Python 的包管理器)獲得。
使用 PIP 安裝 Psycog2
首先,確保 Python 和 PIP 已正確安裝在您的系統中,並且 PIP 已更新到最新版本。
要升級 PIP,請開啟命令提示符並執行以下命令:
C:\Users\Tutorialspoint>python -m pip install --upgrade pip
Collecting pip
Using cached
https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/8d/07/f7d7ced2f97ca3098c16565efbe6b15fafcba53e8d9bdb431e09140514b0/pip-19.2.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Installing collected packages: pip
Found existing installation: pip 19.0.3
Uninstalling pip-19.0.3:
Successfully uninstalled pip-19.0.3
Successfully installed pip-19.2.2
然後,以管理員身份開啟命令提示符並執行 pip install psycopg2-binary 命令,如下所示:
C:\WINDOWS\system32>pip install psycopg2-binary Collecting psycopg2-binary Using cached https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/80/79/d0d13ce4c2f1addf4786f4a2ded802c2df66ddf3c1b1a982ed8d4cb9fc6d/psycopg2_binary-2.8.3-cp37-cp37m-win32.whl Installing collected packages: psycopg2-binary Successfully installed psycopg2-binary-2.8.3
驗證
要驗證安裝,請建立一個包含以下行的 Python 指令碼示例。
import mysql.connector
如果安裝成功,當您執行它時,您不應該得到任何錯誤:
D:\Python_PostgreSQL>import psycopg2 D:\Python_PostgreSQL>
Python PostgreSQL - 資料庫連線
PostgreSQL 提供了自己的 shell 來執行查詢。要建立與 PostgreSQL 資料庫的連線,請確保您已在系統中正確安裝它。開啟 PostgreSQL shell 提示符並傳遞伺服器、資料庫、使用者名稱和密碼等詳細資訊。如果您提供的所有詳細資訊都正確,則會與 PostgreSQL 資料庫建立連線。
傳遞詳細資訊時,您可以使用 shell 建議的預設伺服器、資料庫、埠和使用者名稱。
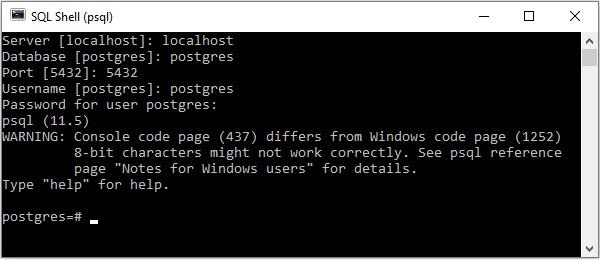
使用 Python 建立連線
psycopg2 的 connection 類表示/處理連線的例項。您可以使用 connect() 函式建立新的連線。它接受基本的連線引數,例如 dbname、user、password、host、port,並返回一個連線物件。使用此函式,您可以建立與 PostgreSQL 的連線。
示例
以下 Python 程式碼演示瞭如何連線到現有資料庫。如果資料庫不存在,則會建立它,最後返回一個數據庫物件。PostgreSQL 的預設資料庫名稱為 postrgre。因此,我們將其作為資料庫名稱提供。
import psycopg2
#establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="postgres", user='postgres', password='password',
host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Executing an MYSQL function using the execute() method
cursor.execute("select version()")
#Fetch a single row using fetchone() method.
data = cursor.fetchone()
print("Connection established to: ",data)
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
Connection established to: (
'PostgreSQL 11.5, compiled by Visual C++ build 1914, 64-bit',
)
輸出
Connection established to: ( 'PostgreSQL 11.5, compiled by Visual C++ build 1914, 64-bit', )
Python PostgreSQL - 建立資料庫
您可以使用 CREATE DATABASE 語句在 PostgreSQL 中建立資料庫。您可以在 PostgreSQL shell 提示符下執行此語句,並在命令後指定要建立的資料庫的名稱。
語法
以下是 CREATE DATABASE 語句的語法。
CREATE DATABASE dbname;
示例
以下語句在 PostgreSQL 中建立一個名為 testdb 的資料庫。
postgres=# CREATE DATABASE testdb; CREATE DATABASE
您可以使用 \l 命令列出 PostgreSQL 中的資料庫。如果您驗證資料庫列表,您可以找到如下所示的新建立的資料庫:
postgres=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype |
-----------+----------+----------+----------------------------+-------------+
mydb | postgres | UTF8 | English_United States.1252 | ........... |
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | English_United States.1252 | ........... |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | English_United States.1252 | ........... |
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | English_United States.1252 | ........... |
testdb | postgres | UTF8 | English_United States.1252 | ........... |
(5 rows)
您還可以使用 createdb 命令(SQL 語句 CREATE DATABASE 的包裝器)從命令提示符在 PostgreSQL 中建立資料庫。
C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\11\bin> createdb -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres sampledb Password:
使用 Python 建立資料庫
psycopg2 的 cursor 類提供了各種方法來執行各種 PostgreSQL 命令、獲取記錄和複製資料。您可以使用 Connection 類的 cursor() 方法建立遊標物件。
此類的 execute() 方法接受 PostgreSQL 查詢作為引數並執行它。
因此,要在 PostgreSQL 中建立資料庫,請使用此方法執行 CREATE DATABASE 查詢。
示例
以下 Python 示例在 PostgreSQL 資料庫中建立一個名為 mydb 的資料庫。
import psycopg2
#establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="postgres", user='postgres', password='password',
host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
conn.autocommit = True
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Preparing query to create a database
sql = '''CREATE database mydb''';
#Creating a database
cursor.execute(sql)
print("Database created successfully........")
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
Database created successfully........
Python PostgreSQL - 建立表
您可以使用 CREATE TABLE 語句在 PostgreSQL 資料庫中建立一個新表。在執行此操作時,您需要指定表名、列名及其資料型別。
語法
以下是 PostgreSQL 中 CREATE TABLE 語句的語法。
CREATE TABLE table_name( column1 datatype, column2 datatype, column3 datatype, ..... columnN datatype, );
示例
以下示例在 PostgreSQL 中建立一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表。
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age INT, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255)); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
您可以使用 \dt 命令獲取 PostgreSQL 資料庫中表的列表。建立表後,如果您驗證表列表,您可以在其中觀察到新建立的表,如下所示:
postgres=# \dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------+-------+----------
public | cricketers | table | postgres
(1 row)
postgres=#
同樣,您可以使用 \d 獲取已建立表的描述,如下所示:
postgres=# \d cricketers
Table "public.cricketers"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default
----------------+------------------------+-----------+----------+---------
first_name | character varying(255) | | |
last_name | character varying(255) | | |
age | integer | | |
place_of_birth | character varying(255) | | |
country | character varying(255) | | |
postgres=#
使用 Python 建立表
要使用 python 建立表,您需要使用 pyscopg2 的 Cursor 的 execute() 方法執行 CREATE TABLE 語句。
示例
以下 Python 示例建立一個名為 employee 的表。
import psycopg2
#Establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Doping EMPLOYEE table if already exists.
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")
#Creating table as per requirement
sql ='''CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE(
FIRST_NAME CHAR(20) NOT NULL,
LAST_NAME CHAR(20),
AGE INT,
SEX CHAR(1),
INCOME FLOAT)'''
cursor.execute(sql)
print("Table created successfully........")
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
Table created successfully........
Python PostgreSQL - 插入資料
您可以使用 INSERT INTO 語句將記錄插入 PostgreSQL 中的現有表中。在執行此操作時,您需要指定表名以及其中列的值。
語法
以下是 INSERT 語句的推薦語法:
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME (column1, column2, column3,...columnN) VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...valueN);
其中,column1、column2、column3... 是表的列名,value1、value2、value3... 是您需要插入表中的值。
示例
假設我們使用 CREATE TABLE 語句建立了一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表,如下所示:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age INT, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255) ); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
以下 PostgreSQL 語句在上面建立的表中插入一行:
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS
(First_Name, Last_Name, Age, Place_Of_Birth, Country) values
('Shikhar', 'Dhawan', 33, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=#
在使用 INSERT INTO 語句插入記錄時,如果您跳過任何列名,則會插入記錄,並在您跳過的列處留下空位。
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS
(First_Name, Last_Name, Country) values('Jonathan', 'Trott', 'SouthAfrica');
INSERT 0 1
如果傳遞的值的順序與表中各自列名的順序相同,您也可以在不指定列名的情況下將記錄插入表中。
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Kumara', 'Sangakkara', 41, 'Matale', 'Srilanka');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Virat', 'Kohli', 30, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Rohit', 'Sharma', 32, 'Nagpur', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=#
將記錄插入表後,您可以使用 SELECT 語句驗證其內容,如下所示:
postgres=# SELECT * from CRICKETERS; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+------------- Shikhar | Dhawan | 33 | Delhi | India Jonathan | Trott | | | SouthAfrica Kumara | Sangakkara | 41 | Matale | Srilanka Virat | Kohli | 30 | Delhi | India Rohit | Sharma | 32 | Nagpur | India (5 rows)
使用 Python 插入資料
psycopg2 的 cursor 類提供了一個名為 execute() 的方法。此方法接受查詢作為引數並執行它。
因此,要使用 python 在 PostgreSQL 中將資料插入表中:
匯入 psycopg2 包。
使用 connect() 方法建立一個連線物件,將使用者名稱、密碼、主機(可選,預設為 localhost)和資料庫(可選)作為引數傳遞給它。
透過將 false 作為值設定為 autocommit 屬性來關閉自動提交模式。
psycopg2 庫的 Connection 類的 cursor() 方法返回一個遊標物件。使用此方法建立一個遊標物件。
然後,透過將其作為引數傳遞給 execute() 方法來執行 INSERT 語句。
示例
以下 Python 程式在 PostgreSQL 資料庫中建立一個名為 EMPLOYEE 的表,並使用 execute() 方法將記錄插入其中:
import psycopg2
#Establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
#Setting auto commit false
conn.autocommit = True
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Preparing SQL queries to INSERT a record into the database.
cursor.execute('''INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE(FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME)
VALUES ('Ramya', 'Rama priya', 27, 'F', 9000)''')
cursor.execute('''INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE(FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME)
VALUES ('Vinay', 'Battacharya', 20, 'M', 6000)''')
cursor.execute('''INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE(FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME)
VALUES ('Sharukh', 'Sheik', 25, 'M', 8300)''')
cursor.execute('''INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE(FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME)
VALUES ('Sarmista', 'Sharma', 26, 'F', 10000)''')
cursor.execute('''INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE(FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME)
VALUES ('Tripthi', 'Mishra', 24, 'F', 6000)''')
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
print("Records inserted........")
# Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
Records inserted........
Python PostgreSQL - 查詢資料
您可以使用 SELECT 語句檢索 PostgreSQL 中現有表的內容。在此語句中,您需要指定表名,它會以表格格式返回其內容,這稱為結果集。
語法
以下是 PostgreSQL 中 SELECT 語句的語法:
SELECT column1, column2, columnN FROM table_name;
示例
假設我們使用以下查詢建立了一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age int, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255) ); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
如果我們使用 INSERT 語句在其中插入了 5 條記錄,如下所示:
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Shikhar', 'Dhawan', 33, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Jonathan', 'Trott', 38, 'CapeTown', 'SouthAfrica');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Kumara', 'Sangakkara', 41, 'Matale', 'Srilanka');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Virat', 'Kohli', 30, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Rohit', 'Sharma', 32, 'Nagpur', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
以下 SELECT 查詢從 CRICKETERS 表中檢索 FIRST_NAME、LAST_NAME 和 COUNTRY 列的值。
postgres=# SELECT FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, COUNTRY FROM CRICKETERS; first_name | last_name | country ------------+------------+------------- Shikhar | Dhawan | India Jonathan | Trott | SouthAfrica Kumara | Sangakkara | Srilanka Virat | Kohli | India Rohit | Sharma | India (5 rows)
如果要檢索每個記錄的所有列,則需要將列名替換為“\*”,如下所示:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+------------- Shikhar | Dhawan | 33 | Delhi | India Jonathan | Trott | 38 | CapeTown | SouthAfrica Kumara | Sangakkara | 41 | Matale | Srilanka Virat | Kohli | 30 | Delhi | India Rohit | Sharma | 32 | Nagpur | India (5 rows) postgres=#
使用 Python 檢索資料
在任何資料庫上執行讀取操作意味著從資料庫中獲取一些有用的資訊。您可以使用 psycopg2 提供的 fetch() 方法從 PostgreSQL 中獲取資料。
Cursor 類提供了三個方法,即 fetchall()、fetchmany() 和 fetchone(),其中:
fetchall() 方法檢索查詢結果集中的所有行,並將其作為元組列表返回。(如果我們在檢索幾行後執行此操作,它將返回其餘行)。
fetchone() 方法獲取查詢結果中的下一行,並將其作為元組返回。
注意 - 結果集是在使用遊標物件查詢表時返回的物件。
示例
以下 Python 程式連線到 PostgreSQL 的名為 mydb 的資料庫,並從名為 EMPLOYEE 的表中檢索所有記錄。
import psycopg2
#establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
#Setting auto commit false
conn.autocommit = True
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Retrieving data
cursor.execute('''SELECT * from EMPLOYEE''')
#Fetching 1st row from the table
result = cursor.fetchone();
print(result)
#Fetching 1st row from the table
result = cursor.fetchall();
print(result)
#Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
('Ramya', 'Rama priya', 27, 'F', 9000.0)
[
('Vinay', 'Battacharya', 20, 'M', 6000.0),
('Sharukh', 'Sheik', 25, 'M', 8300.0),
('Sarmista', 'Sharma', 26, 'F', 10000.0),
('Tripthi', 'Mishra', 24, 'F', 6000.0)
]
Python PostgreSQL - WHERE 子句
在執行 SELECT、UPDATE 或 DELETE 操作時,您可以使用 WHERE 子句指定條件來過濾記錄。操作將對滿足給定條件的記錄執行。
語法
以下是 PostgreSQL 中 WHERE 子句的語法:
SELECT column1, column2, columnN FROM table_name WHERE [search_condition]
您可以使用比較運算子或邏輯運算子指定 search_condition。例如 >、<、=、LIKE、NOT 等。以下示例將使此概念更加清晰。
示例
假設我們使用以下查詢建立了一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age int, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255) ); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
如果我們使用 INSERT 語句在其中插入了 5 條記錄,如下所示:
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Shikhar', 'Dhawan', 33, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Jonathan', 'Trott', 38, 'CapeTown', 'SouthAfrica');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Kumara', 'Sangakkara', 41, 'Matale', 'Srilanka');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Virat', 'Kohli', 30, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Rohit', 'Sharma', 32, 'Nagpur', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
以下 SELECT 語句檢索年齡大於 35 的記錄:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS WHERE AGE > 35; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+------------- Jonathan | Trott | 38 | CapeTown | SouthAfrica Kumara | Sangakkara | 41 | Matale | Srilanka (2 rows) postgres=#
使用 Python 的 WHERE 子句
要使用 python 程式從表中獲取特定記錄,請執行帶有 WHERE 子句的 SELECT 語句,並將其作為引數傳遞給 execute() 方法。
示例
以下 python 示例演示了使用 python 的 WHERE 命令。
import psycopg2
#establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
#Setting auto commit false
conn.autocommit = True
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Doping EMPLOYEE table if already exists.
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")
sql = '''CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE(
FIRST_NAME CHAR(20) NOT NULL,
LAST_NAME CHAR(20),
AGE INT,
SEX CHAR(1),
INCOME FLOAT)'''
cursor.execute(sql)
#Populating the table
insert_stmt = "INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE
(FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)"
data = [('Krishna', 'Sharma', 19, 'M', 2000), ('Raj', 'Kandukuri', 20, 'M', 7000),
('Ramya', 'Ramapriya', 25, 'M', 5000),('Mac', 'Mohan', 26, 'M', 2000)]
cursor.executemany(insert_stmt, data)
#Retrieving specific records using the where clause
cursor.execute("SELECT * from EMPLOYEE WHERE AGE <23")
print(cursor.fetchall())
#Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
[('Krishna', 'Sharma', 19, 'M', 2000.0), ('Raj', 'Kandukuri', 20, 'M', 7000.0)]
Python PostgreSQL - ORDER BY 子句
通常,如果您嘗試從表中檢索資料,您將按插入它們的相同順序獲取記錄。
在檢索表的記錄時,可以使用 ORDER BY 子句根據所需的列對結果記錄進行升序或降序排序。
語法
以下是 PostgreSQL 中 ORDER BY 子句的語法。
SELECT column-list FROM table_name [WHERE condition] [ORDER BY column1, column2, .. columnN] [ASC | DESC];
示例
假設我們使用以下查詢建立了一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age int, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255) ); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
如果我們使用 INSERT 語句在其中插入了 5 條記錄,如下所示:
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Shikhar', 'Dhawan', 33, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Jonathan', 'Trott', 38, 'CapeTown', 'SouthAfrica');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Kumara', 'Sangakkara', 41, 'Matale', 'Srilanka');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Virat', 'Kohli', 30, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Rohit', 'Sharma', 32, 'Nagpur', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
以下 SELECT 語句按年齡的升序檢索 CRICKETERS 表的行:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS ORDER BY AGE; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+------------- Virat | Kohli | 30 | Delhi | India Rohit | Sharma | 32 | Nagpur | India Shikhar | Dhawan | 33 | Delhi | India Jonathan | Trott | 38 | CapeTown | SouthAfrica Kumara | Sangakkara | 41 | Matale | Srilanka (5 rows)es:
您可以使用多個列對錶的記錄進行排序。以下 SELECT 語句根據年齡和 FIRST_NAME 列對 CRICKETERS 表的記錄進行排序。
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS ORDER BY AGE, FIRST_NAME; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+------------- Virat | Kohli | 30 | Delhi | India Rohit | Sharma | 32 | Nagpur | India Shikhar | Dhawan | 33 | Delhi | India Jonathan | Trott | 38 | CapeTown | SouthAfrica Kumara | Sangakkara | 41 | Matale | Srilanka (5 rows)
預設情況下,ORDER BY 子句按升序對錶的記錄進行排序。您可以使用 DESC 將結果按降序排列,如下所示:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS ORDER BY AGE DESC; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+------------- Kumara | Sangakkara | 41 | Matale | Srilanka Jonathan | Trott | 38 | CapeTown | SouthAfrica Shikhar | Dhawan | 33 | Delhi | India Rohit | Sharma | 32 | Nagpur | India Virat | Kohli | 30 | Delhi | India (5 rows)
使用 Python 的 ORDER BY 子句
要以特定順序檢索表的內容,請在遊標物件上呼叫 execute() 方法,並將 SELECT 語句以及 ORDER BY 子句作為引數傳遞給它。
示例
在下面的示例中,我們正在建立一個名為 name 和 Employee 的表,對其進行填充,並使用 ORDER BY 子句按年齡(升序)檢索其記錄。
import psycopg2
#establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
#Setting auto commit false
conn.autocommit = True
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Doping EMPLOYEE table if already exists.
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")
#Creating a table
sql = '''CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE(
FIRST_NAME CHAR(20) NOT NULL,
LAST_NAME CHAR(20),
AGE INT, SEX CHAR(1),
INCOME INT,
CONTACT INT)'''
cursor.execute(sql)
#Populating the table
insert_stmt = "INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE
(FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, AGE, SEX, INCOME, CONTACT) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)"
data = [('Krishna', 'Sharma', 26, 'M', 2000, 101),
('Raj', 'Kandukuri', 20, 'M', 7000, 102),
('Ramya', 'Ramapriya', 29, 'F', 5000, 103),
('Mac', 'Mohan', 26, 'M', 2000, 104)]
cursor.executemany(insert_stmt, data)
conn.commit()
#Retrieving specific records using the ORDER BY clause
cursor.execute("SELECT * from EMPLOYEE ORDER BY AGE")
print(cursor.fetchall())
#Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
[('Sharukh', 'Sheik', 25, 'M', 8300.0), ('Sarmista', 'Sharma', 26, 'F', 10000.0)]
Python PostgreSQL - 更新表
您可以使用 UPDATE 語句修改 PostgreSQL 中現有表中記錄的內容。要更新特定行,您需要與之一起使用 WHERE 子句。
語法
以下是 PostgreSQL 中 UPDATE 語句的語法:
UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2...., columnN = valueN WHERE [condition];
示例
假設我們使用以下查詢建立了一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age int, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255) ); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
如果我們使用 INSERT 語句在其中插入了 5 條記錄,如下所示:
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Shikhar', 'Dhawan', 33, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Jonathan', 'Trott', 38, 'CapeTown', 'SouthAfrica');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Kumara', 'Sangakkara', 41, 'Matale', 'Srilanka');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Virat', 'Kohli', 30, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values('Rohit', 'Sharma', 32, 'Nagpur', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
以下語句修改了名為 Shikhar 的板球運動員的年齡:
postgres=# UPDATE CRICKETERS SET AGE = 45 WHERE FIRST_NAME = 'Shikhar' ; UPDATE 1 postgres=#
如果您檢索 FIRST_NAME 為 Shikhar 的記錄,您會觀察到年齡值已更改為 45:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS WHERE FIRST_NAME = 'Shikhar'; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+-----------+-----+----------------+--------- Shikhar | Dhawan | 45 | Delhi | India (1 row) postgres=#
如果您沒有使用 WHERE 子句,則所有記錄的值都將更新。以下 UPDATE 語句將 CRICKETERS 表中所有記錄的年齡增加 1:
postgres=# UPDATE CRICKETERS SET AGE = AGE+1; UPDATE 5
如果您使用 SELECT 命令檢索表的內容,您可以看到更新後的值,如下所示:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+------------- Jonathan | Trott | 39 | CapeTown | SouthAfrica Kumara | Sangakkara | 42 | Matale | Srilanka Virat | Kohli | 31 | Delhi | India Rohit | Sharma | 33 | Nagpur | India Shikhar | Dhawan | 46 | Delhi | India (5 rows)
使用 Python 更新記錄
psycopg2 的 cursor 類提供了一個名為 execute() 的方法。此方法接受查詢作為引數並執行它。
因此,要使用 python 在 PostgreSQL 中將資料插入表中:
匯入 psycopg2 包。
使用 connect() 方法建立一個連線物件,將使用者名稱、密碼、主機(可選,預設為 localhost)和資料庫(可選)作為引數傳遞給它。
透過將 false 作為值設定為 autocommit 屬性來關閉自動提交模式。
psycopg2 庫的 Connection 類的 cursor() 方法返回一個遊標物件。使用此方法建立一個遊標物件。
然後,透過將其作為引數傳遞給 execute() 方法來執行 UPDATE 語句。
示例
以下 Python 程式碼更新 Employee 表的內容並檢索結果:
import psycopg2
#establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect (
database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
#Setting auto commit false
conn.autocommit = True
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Fetching all the rows before the update
print("Contents of the Employee table: ")
sql = '''SELECT * from EMPLOYEE'''
cursor.execute(sql)
print(cursor.fetchall())
#Updating the records
sql = "UPDATE EMPLOYEE SET AGE = AGE + 1 WHERE SEX = 'M'"
cursor.execute(sql)
print("Table updated...... ")
#Fetching all the rows after the update
print("Contents of the Employee table after the update operation: ")
sql = '''SELECT * from EMPLOYEE'''
cursor.execute(sql)
print(cursor.fetchall())
#Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
Contents of the Employee table:
[
('Ramya', 'Rama priya', 27, 'F', 9000.0),
('Vinay', 'Battacharya', 20, 'M', 6000.0),
('Sharukh', 'Sheik', 25, 'M', 8300.0),
('Sarmista', 'Sharma', 26, 'F', 10000.0),
('Tripthi', 'Mishra', 24, 'F', 6000.0)
]
Table updated......
Contents of the Employee table after the update operation:
[
('Ramya', 'Rama priya', 27, 'F', 9000.0),
('Sarmista', 'Sharma', 26, 'F', 10000.0),
('Tripthi', 'Mishra', 24, 'F', 6000.0),
('Vinay', 'Battacharya', 21, 'M', 6000.0),
('Sharukh', 'Sheik', 26, 'M', 8300.0)
]
Python PostgreSQL - 刪除資料
您可以使用 PostgreSQL 資料庫的 DELETE FROM 語句刪除現有表中的記錄。要刪除特定記錄,您需要與之一起使用 WHERE 子句。
語法
以下是 PostgreSQL 中 DELETE 查詢的語法:
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE Clause]
示例
假設我們使用以下查詢建立了一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age int, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255) ); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
如果我們使用 INSERT 語句在其中插入了 5 條記錄,如下所示:
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Shikhar', 'Dhawan', 33, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Jonathan', 'Trott', 38, 'CapeTown', 'SouthAfrica');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Kumara', 'Sangakkara', 41, 'Matale', 'Srilanka');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Virat', 'Kohli', 30, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Rohit', 'Sharma', 32, 'Nagpur', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
以下語句刪除姓氏為 'Sangakkara' 的板球運動員的記錄。
postgres=# DELETE FROM CRICKETERS WHERE LAST_NAME = 'Sangakkara'; DELETE 1
如果您使用 SELECT 語句檢索表的內容,您只能看到 4 條記錄,因為我們已刪除了一條。
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+-----------+-----+----------------+------------- Jonathan | Trott | 39 | CapeTown | SouthAfrica Virat | Kohli | 31 | Delhi | India Rohit | Sharma | 33 | Nagpur | India Shikhar | Dhawan | 46 | Delhi | India (4 rows)
如果您在沒有 WHERE 子句的情況下執行 DELETE FROM 語句,則將刪除指定表中的所有記錄。
postgres=# DELETE FROM CRICKETERS; DELETE 4
由於您已刪除所有記錄,因此如果您嘗試使用 SELECT 語句檢索 CRICKETERS 表的內容,您將獲得一個空的結果集,如下所示:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+-----------+-----+----------------+--------- (0 rows)
使用 Python 刪除資料
psycopg2 的 cursor 類提供了一個名為 execute() 的方法。此方法接受查詢作為引數並執行它。
因此,要使用 python 在 PostgreSQL 中將資料插入表中:
匯入 psycopg2 包。
使用 connect() 方法建立連線物件,並將使用者名稱、密碼、主機(可選,預設為 localhost)和資料庫(可選)作為引數傳遞給它。
透過將 false 作為值設定為屬性 autocommit 來關閉自動提交模式。
psycopg2 庫的 Connection 類的 cursor() 方法返回一個遊標物件。使用此方法建立一個遊標物件。
然後,透過將其作為引數傳遞給 execute() 方法來執行 DELETE 語句。
示例
以下 Python 程式碼刪除 EMPLOYEE 表中年齡值大於 25 的記錄:
import psycopg2
#establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432'
)
#Setting auto commit false
conn.autocommit = True
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Retrieving contents of the table
print("Contents of the table: ")
cursor.execute('''SELECT * from EMPLOYEE''')
print(cursor.fetchall())
#Deleting records
cursor.execute('''DELETE FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE AGE > 25''')
#Retrieving data after delete
print("Contents of the table after delete operation ")
cursor.execute("SELECT * from EMPLOYEE")
print(cursor.fetchall())
#Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
Contents of the table:
[
('Ramya', 'Rama priya', 27, 'F', 9000.0),
('Sarmista', 'Sharma', 26, 'F', 10000.0),
('Tripthi', 'Mishra', 24, 'F', 6000.0),
('Vinay', 'Battacharya', 21, 'M', 6000.0),
('Sharukh', 'Sheik', 26, 'M', 8300.0)
]
Contents of the table after delete operation:
[
('Tripthi', 'Mishra', 24, 'F', 6000.0),
('Vinay', 'Battacharya', 21, 'M', 6000.0)
]
Python PostgreSQL - 刪除表
您可以使用 DROP TABLE 語句從 PostgreSQL 資料庫中刪除表。
語法
以下是 PostgreSQL 中 DROP TABLE 語句的語法:
DROP TABLE table_name;
示例
假設我們使用以下查詢建立了兩個名為 CRICKETERS 和 EMPLOYEES 的表:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age int, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255) ); CREATE TABLE postgres=# postgres=# CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE( FIRST_NAME CHAR(20) NOT NULL, LAST_NAME CHAR(20), AGE INT, SEX CHAR(1), INCOME FLOAT ); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
現在,如果您使用“\dt”命令驗證表列表,您可以看到上面建立的表,如下所示:
postgres=# \dt;
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------+-------+----------
public | cricketers | table | postgres
public | employee | table | postgres
(2 rows)
postgres=#
以下語句從資料庫中刪除名為 Employee 的表:
postgres=# DROP table employee; DROP TABLE
由於您已刪除 Employee 表,因此如果您再次檢索表列表,您只會看到其中一個表。
postgres=# \dt;
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------+-------+----------
public | cricketers | table | postgres
(1 row)
postgres=#
如果您嘗試再次刪除 Employee 表,由於您已將其刪除,您將收到一條錯誤訊息,提示“表不存在”,如下所示:
postgres=# DROP table employee; ERROR: table "employee" does not exist postgres=#
要解決此問題,您可以將 IF EXISTS 子句與 DELTE 語句一起使用。如果表存在,則刪除它,否則跳過 DLETE 操作。
postgres=# DROP table IF EXISTS employee; NOTICE: table "employee" does not exist, skipping DROP TABLE postgres=#
使用 Python 刪除整個表
您可以根據需要使用 DROP 語句刪除表。但在刪除任何現有表時,您需要非常小心,因為刪除表後將無法恢復丟失的資料。
import psycopg2
#establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432')
#Setting auto commit false
conn.autocommit = True
#Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
#Doping EMPLOYEE table if already exists
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE emp")
print("Table dropped... ")
#Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
#Closing the connection
conn.close()
輸出
#Table dropped...
Python PostgreSQL - LIMIT 子句
在執行 PostgreSQL SELECT 語句時,您可以使用 LIMIT 子句限制其結果中的記錄數。
語法
以下是 PostgreSQL 中 LMIT 子句的語法:
SELECT column1, column2, columnN FROM table_name LIMIT [no of rows]
示例
假設我們使用以下查詢建立了一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS ( First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age int, Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255) ); CREATE TABLE postgres=#
如果我們使用 INSERT 語句在其中插入了 5 條記錄,如下所示:
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Shikhar', 'Dhawan', 33, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Jonathan', 'Trott', 38, 'CapeTown', 'SouthAfrica');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Kumara', 'Sangakkara', 41, 'Matale', 'Srilanka');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Virat', 'Kohli', 30, 'Delhi', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Rohit', 'Sharma', 32, 'Nagpur', 'India');
INSERT 0 1
以下語句使用 LIMIT 子句檢索 Cricketers 表的前 3 條記錄:
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS LIMIT 3; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+------------- Shikhar | Dhawan | 33 | Delhi | India Jonathan | Trott | 38 | CapeTown | SouthAfrica Kumara | Sangakkara | 41 | Matale | Srilanka (3 rows)
如果您想從特定記錄(偏移量)開始獲取記錄,您可以使用 OFFSET 子句與 LIMIT 一起執行此操作。
postgres=# SELECT * FROM CRICKETERS LIMIT 3 OFFSET 2; first_name | last_name | age | place_of_birth | country ------------+------------+-----+----------------+---------- Kumara | Sangakkara | 41 | Matale | Srilanka Virat | Kohli | 30 | Delhi | India Rohit | Sharma | 32 | Nagpur | India (3 rows) postgres=#
使用 Python 的 Limit 子句
以下 Python 示例檢索名為 EMPLOYEE 的表的內容,將結果中的記錄數限制為 2:
import psycopg2 #establishing the connection conn = psycopg2.connect( database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432' ) #Setting auto commit false conn.autocommit = True #Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method cursor = conn.cursor() #Retrieving single row sql = '''SELECT * from EMPLOYEE LIMIT 2 OFFSET 2''' #Executing the query cursor.execute(sql) #Fetching the data result = cursor.fetchall(); print(result) #Commit your changes in the database conn.commit() #Closing the connection conn.close()
輸出
[('Sharukh', 'Sheik', 25, 'M', 8300.0), ('Sarmista', 'Sharma', 26, 'F', 10000.0)]
Python PostgreSQL - JOIN 子句
當您將資料分成兩個表時,您可以使用連線從這兩個表中獲取組合記錄。
示例
假設我們建立了一個名為 CRICKETERS 的表,並在其中插入了 5 條記錄,如下所示:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE CRICKETERS (
First_Name VARCHAR(255), Last_Name VARCHAR(255), Age int,
Place_Of_Birth VARCHAR(255), Country VARCHAR(255)
);
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Shikhar', 'Dhawan', 33, 'Delhi', 'India');
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Jonathan', 'Trott', 38, 'CapeTown', 'SouthAfrica');
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Kumara', 'Sangakkara', 41, 'Matale', 'Srilanka');
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Virat', 'Kohli', 30, 'Delhi', 'India');
postgres=# insert into CRICKETERS values ('Rohit', 'Sharma', 32, 'Nagpur', 'India');
並且,如果我們建立了另一個名為 OdiStats 的表並在其中插入了 5 條記錄,如下所示:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE ODIStats (
First_Name VARCHAR(255), Matches INT, Runs INT, AVG FLOAT,
Centuries INT, HalfCenturies INT
);
postgres=# insert into OdiStats values ('Shikhar', 133, 5518, 44.5, 17, 27);
postgres=# insert into OdiStats values ('Jonathan', 68, 2819, 51.25, 4, 22);
postgres=# insert into OdiStats values ('Kumara', 404, 14234, 41.99, 25, 93);
postgres=# insert into OdiStats values ('Virat', 239, 11520, 60.31, 43, 54);
postgres=# insert into OdiStats values ('Rohit', 218, 8686, 48.53, 24, 42);
以下語句檢索這兩個表中值的組合資料:
postgres=# SELECT Cricketers.First_Name, Cricketers.Last_Name, Cricketers.Country, OdiStats.matches, OdiStats.runs, OdiStats.centuries, OdiStats.halfcenturies from Cricketers INNER JOIN OdiStats ON Cricketers.First_Name = OdiStats.First_Name; first_name | last_name | country | matches | runs | centuries | halfcenturies ------------+------------+-------------+---------+-------+-----------+--------------- Shikhar | Dhawan | India | 133 | 5518 | 17 | 27 Jonathan | Trott | SouthAfrica | 68 | 2819 | 4 | 22 Kumara | Sangakkara | Srilanka | 404 | 14234 | 25 | 93 Virat | Kohli | India | 239 | 11520 | 43 | 54 Rohit | Sharma | India | 218 | 8686 | 24 | 42 (5 rows) postgres=#
使用 Python 連線
當您將資料分成兩個表時,您可以使用連線從這兩個表中獲取組合記錄。
示例
以下 Python 程式演示了 JOIN 子句的使用:
import psycopg2 #establishing the connection conn = psycopg2.connect( database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432' ) #Setting auto commit false conn.autocommit = True #Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method cursor = conn.cursor() #Retrieving single row sql = '''SELECT * from EMP INNER JOIN CONTACT ON EMP.CONTACT = CONTACT.ID''' #Executing the query cursor.execute(sql) #Fetching 1st row from the table result = cursor.fetchall(); print(result) #Commit your changes in the database conn.commit() #Closing the connection conn.close()
輸出
[
('Ramya', 'Rama priya', 27, 'F', 9000.0, 101, 101, 'Krishna@mymail.com', 'Hyderabad'),
('Vinay', 'Battacharya', 20, 'M', 6000.0, 102, 102, 'Raja@mymail.com', 'Vishakhapatnam'),
('Sharukh', 'Sheik', 25, 'M', 8300.0, 103, 103, 'Krishna@mymail.com ', 'Pune'),
('Sarmista', 'Sharma', 26, 'F', 10000.0, 104, 104, 'Raja@mymail.com', 'Mumbai')
]
Python PostgreSQL - 遊標物件
psycopg 庫的 Cursor 類提供方法,可以使用 python 程式碼在資料庫中執行 PostgreSQL 命令。
使用其方法,您可以執行 SQL 語句、從結果集中獲取資料、呼叫過程。
您可以使用 Connection 物件/類的 cursor() 方法建立 Cursor 物件。
示例
import psycopg2 #establishing the connection conn = psycopg2.connect( database="mydb", user='postgres', password='password', host='127.0.0.1', port= '5432' ) #Setting auto commit false conn.autocommit = True #Creating a cursor object using the cursor() method cursor = conn.cursor()
方法
以下是 Cursor 類/物件提供的各種方法。
| 序號 | 方法和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
callproc() 此方法用於呼叫 PostgreSQL 資料庫中現有的過程。 |
| 2 |
close() 此方法用於關閉當前遊標物件。 |
| 3 |
executemany() 此方法接受一系列引數列表。準備一個 MySQL 查詢並使用所有引數執行它。 |
| 4 |
execute() 此方法接受 MySQL 查詢作為引數並執行給定的查詢。 |
| 5 |
fetchall() 此方法檢索查詢結果集中的所有行,並將它們作為元組列表返回。(如果我們在檢索幾行後執行此操作,它將返回其餘的行) |
| 6 |
fetchone() 此方法獲取查詢結果中的下一行,並將其作為元組返回。 |
| 7 |
fetchmany() 此方法類似於 fetchone(),但它檢索查詢結果集中的下一組行,而不是單個行。 |
屬性
以下是 Cursor 類的屬性。
| 序號 | 屬性和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
description 這是一個只讀屬性,它返回包含結果集中列描述的列表。 |
| 2 |
lastrowid 這是一個只讀屬性,如果表中存在任何自動遞增列,則返回在上次 INSERT 或 UPDATE 操作中為此列生成的值。 |
| 3 |
rowcount 在 SELECT 和 UPDATE 操作的情況下,這將返回返回/更新的行數。 |
| 4 |
closed 此屬性指定遊標是否已關閉,如果是,則返回 true,否則返回 false。 |
| 5 |
connection 這將返回對建立此遊標所使用的連線物件的引用。 |
| 6 |
name 此屬性返回遊標的名稱。 |
| 7 |
scrollable 此屬性指定特定遊標是否可滾動。 |