
- LISP 教程
- LISP - 首頁
- LISP - 概述
- LISP - 環境
- LISP - 程式結構
- LISP - 基本語法
- LISP - 資料型別
- LISP - 宏
- LISP - 變數
- LISP - 常量
- LISP - 運算子
- LISP - 決策
- LISP - 迴圈
- LISP - 函式
- LISP - 謂詞
- LISP - 數字
- LISP - 字元
- LISP - 陣列
- LISP - 字串
- LISP - 序列
- LISP - 列表
- LISP - 符號
- LISP - 向量
- LISP - 集合
- LISP - 樹
- LISP - 雜湊表
- LISP - 輸入 & 輸出
- LISP - 檔案 I/O
- LISP - 結構體
- LISP - 包
- LISP - 錯誤處理
- LISP - CLOS
- LISP 有用資源
- Lisp - 快速指南
- Lisp - 有用資源
- Lisp - 討論
Lisp - 陣列
LISP 允許您使用make-array函式定義一維或多維陣列。陣列可以儲存任何 LISP 物件作為其元素。
所有陣列都由連續的記憶體位置組成。最低地址對應於第一個元素,最高地址對應於最後一個元素。
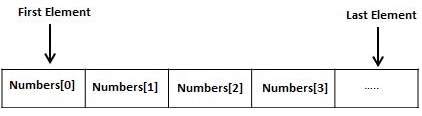
陣列的維度數稱為其秩。
在 LISP 中,陣列元素由一系列非負整數索引指定。序列的長度必須等於陣列的秩。索引從零開始。
例如,要建立一個包含 10 個單元的陣列,名為 my-array,我們可以這樣寫:
(setf my-array (make-array '(10)))
aref 函式允許訪問單元的內容。它接受兩個引數:陣列的名稱和索引值。
例如,要訪問第十個單元的內容,我們可以這樣寫:
(aref my-array 9)
示例
建立一個名為 main.lisp 的新原始碼檔案,並在其中輸入以下程式碼。
main.lisp
; create an empty array of size 10 and print it (write (setf my-array (make-array '(10)))) ; terminate printing (terpri) ; set value at each index of the array (setf (aref my-array 0) 25) (setf (aref my-array 1) 23) (setf (aref my-array 2) 45) (setf (aref my-array 3) 10) (setf (aref my-array 4) 20) (setf (aref my-array 5) 17) (setf (aref my-array 6) 25) (setf (aref my-array 7) 19) (setf (aref my-array 8) 67) (setf (aref my-array 9) 30) ; print the updated array (write my-array)
輸出
執行程式碼時,它返回以下結果:
#(NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL) #(25 23 45 10 20 17 25 19 67 30)
示例
讓我們建立一個 3x3 陣列。
更新名為 main.lisp 的原始碼檔案,並在其中輸入以下程式碼。
main.lisp
; create an array of 3 x 3 (setf x (make-array '(3 3) ; initialize the array :initial-contents '((0 1 2 ) (3 4 5) (6 7 8))) ) ; print the array (write x)
輸出
執行程式碼時,它返回以下結果:
#2A((0 1 2) (3 4 5) (6 7 8))
示例
更新名為 main.lisp 的原始碼檔案,並在其中輸入以下程式碼。
main.lisp
; assign a an array of 4 x 3
(setq a (make-array '(4 3)))
; loop 4 times
(dotimes (i 4)
; loop 3 times
(dotimes (j 3)
; set the values at a index i, j
(setf (aref a i j) (list i 'x j '= (* i j)))
)
)
; loop 4 times
(dotimes (i 4)
; loop 3 times
(dotimes (j 3)
; print values of array
(print (aref a i j))
)
)
輸出
執行程式碼時,它返回以下結果:
(0 X 0 = 0) (0 X 1 = 0) (0 X 2 = 0) (1 X 0 = 0) (1 X 1 = 1) (1 X 2 = 2) (2 X 0 = 0) (2 X 1 = 2) (2 X 2 = 4) (3 X 0 = 0) (3 X 1 = 3) (3 X 2 = 6)
make-array 函式的完整語法
make-array 函式接受許多其他引數。讓我們看一下此函式的完整語法:
make-array dimensions :element-type :initial-element :initial-contents :adjustable :fill-pointer :displaced-to :displaced-index-offset
除了dimensions引數外,所有其他引數都是關鍵字。下表提供了引數的簡要說明。
| 序號 | 引數 & 說明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | dimensions 它給出陣列的維度。對於一維陣列,它是一個數字;對於多維陣列,它是一個列表。 |
| 2 | :element-type 它是型別說明符,預設值為 T,即任何型別 |
| 3 | :initial-element 初始元素值。它將建立一個所有元素都初始化為特定值的陣列。 |
| 4 | :initial-content 作為物件的初始內容。 |
| 5 | :adjustable 它有助於建立一個可調整大小(或可調整)的向量,其底層記憶體可以調整大小。該引數是一個布林值,指示陣列是否可調整,預設值為 NIL。 |
| 6 | :fill-pointer 它跟蹤可調整大小向量中實際儲存的元素數量。 |
| 7 | :displaced-to 它有助於建立一個與指定陣列共享其內容的置換陣列或共享陣列。兩個陣列都應具有相同的元素型別。:displaced-to 選項不能與 :initial-element 或 :initial-contents 選項一起使用。此引數預設為 nil。 |
| 8 | :displaced-index-offset 它給出建立的共享陣列的索引偏移量。 |
示例
更新名為 main.lisp 的原始碼檔案,並在其中輸入以下程式碼。
main.lisp
; set myarray as an array
(setq myarray (make-array '(3 2 3)
; set the contents of the array
:initial-contents
'(((a b c) (1 2 3))
((d e f) (4 5 6))
((g h i) (7 8 9))
))
)
; set array2 using myarray as one dimensional array
(setq array2 (make-array 4 :displaced-to myarray :displaced-index-offset 2))
; print myarray
(write myarray)
; terminate printing
(terpri)
; print array2
(write array2)
輸出
執行程式碼時,它返回以下結果:
#3A(((A B C) (1 2 3)) ((D E F) (4 5 6)) ((G H I) (7 8 9))) #(C 1 2 3)
如果置換陣列是二維的:
main.lisp
; set myarray as an array
(setq myarray (make-array '(3 2 3)
; set the contents of the array
:initial-contents
'(((a b c) (1 2 3))
((d e f) (4 5 6))
((g h i) (7 8 9))
))
)
; set array2 using myarray as two dimensional array
(setq array2 (make-array '(3 2) :displaced-to myarray :displaced-index-offset 2))
; print myarray
(write myarray)
; terminate printing
(terpri)
; print array2
(write array2)
輸出
執行程式碼時,它返回以下結果:
#3A(((A B C) (1 2 3)) ((D E F) (4 5 6)) ((G H I) (7 8 9))) #2A((C 1) (2 3) (D E))
讓我們將置換索引偏移量更改為 5:
main.lisp
; set myarray as an array
(setq myarray (make-array '(3 2 3)
; set the contents of the array
:initial-contents
'(((a b c) (1 2 3))
((d e f) (4 5 6))
((g h i) (7 8 9))
))
)
; set array2 using myarray as two dimensional array with offset 5
(setq array2 (make-array '(3 2) :displaced-to myarray :displaced-index-offset 5))
; print myarray
(write myarray)
; terminate printing
(terpri)
; print array2
(write array2)
輸出
執行程式碼時,它返回以下結果:
#3A(((A B C) (1 2 3)) ((D E F) (4 5 6)) ((G H I) (7 8 9))) #2A((3 D) (E F) (4 5))
示例
更新名為 main.lisp 的原始碼檔案,並在其中輸入以下程式碼。
main.lisp
;a one dimensional array with 5 elements, ;initail value 5 (write (make-array 5 :initial-element 5)) (terpri) ;two dimensional array, with initial element a (write (make-array '(2 3) :initial-element 'a)) (terpri) ;an array of capacity 14, but fill pointer 5, is 5 (write(length (make-array 14 :fill-pointer 5))) (terpri) ;however its length is 14 (write (array-dimensions (make-array 14 :fill-pointer 5))) (terpri) ; a bit array with all initial elements set to 1 (write(make-array 10 :element-type 'bit :initial-element 1)) (terpri) ; a character array with all initial elements set to a ; is a string actually (write(make-array 10 :element-type 'character :initial-element #\a)) (terpri) ; a two dimensional array with initial values a (setq myarray (make-array '(2 2) :initial-element 'a :adjustable t)) (write myarray) (terpri) ;readjusting the array (adjust-array myarray '(1 3) :initial-element 'b) (write myarray)
輸出
執行程式碼時,它返回以下結果:
#(5 5 5 5 5) #2A((A A A) (A A A)) 5 (14) #*1111111111 "aaaaaaaaaa" #2A((A A) (A A)) #2A((A A B))