
- JPA 教程
- JPA - 首頁
- JPA - 簡介
- JPA - 架構
- JPA - ORM 元件
- JPA - 安裝
- JPA - 實體管理器
- JPA - JPQL
- JPA - 高階對映
- JPA - 實體關係
- JPA - Criteria API
- JPA 有用資源
- JPA - 快速指南
- JPA - 有用資源
JPA - 實體關係
本章將引導您瞭解實體之間的關係。通常,資料庫中表之間的關係更有效。這裡實體類被視為關係表(JPA 的概念),因此實體類之間的關係如下:
- @ManyToOne 關係
- @OneToMany 關係
- @OneToOne 關係
- @ManyToMany 關係
@ManyToOne 關係
實體之間的多對一關係:其中一個實體(列或列集)被引用到另一個實體(列或列集),該實體包含唯一值。在關係資料庫中,這些關係是透過使用表之間的外部索引鍵/主鍵來實現的。
讓我們考慮一下員工和部門實體之間關係的示例。以單向方式,即從員工到部門,適用多對一關係。這意味著每個員工記錄都包含一個部門 ID,該 ID 應該是部門表中的主鍵。此處,在員工表中,部門 ID 是外部索引鍵。
該圖解釋了多對一關係如下:
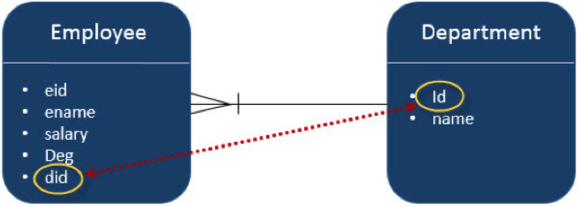
在 Eclipse IDE 中建立一個名為 **JPA_Eclipselink_MTO** 的 JPA 專案。該專案的所有模組如下所示:
建立實體
按照上面給出的圖建立實體。在 **src** 包下建立一個名為 **‘com.tutorialspoin.eclipselink.entity’** 的包。在給定的包下建立一個名為 **Department.java** 的類。Department 實體類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue( strategy=GenerationType.AUTO )
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName( ){
return name;
}
public void setName( String deptName ){
this.name = deptName;
}
}
在此關係中建立第二個實體 - 在 **‘com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity’** 包下建立一個名為 **Employee.java** 的 Employee 實體類。Employee 實體類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
@Entity
public class Employee{
@Id
@GeneratedValue( strategy= GenerationType.AUTO )
private int eid;
private String ename;
private double salary;
private String deg;
@ManyToOne
private Department department;
public Employee(int eid, String ename, double salary, String deg) {
super( );
this.eid = eid;
this.ename = ename;
this.salary = salary;
this.deg = deg;
}
public Employee( ) {
super();
}
public int getEid( ) {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getEname( ) {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public double getSalary( ) {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getDeg( ) {
return deg;
}
public void setDeg(String deg) {
this.deg = deg;
}
public Department getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
}
persistence.xml
persistence.xml 檔案是配置資料庫和註冊實體類所必需的。
在建立 JPA 專案時,persistence.xml 檔案將由 Eclipse IDE 建立。配置細節是使用者指定的。persistence.xml 檔案如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<persistence version = "2.0"
xmlns = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd">
<persistence-unit name = "Eclipselink_JPA" transaction-type = "RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<class>com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Employee</class>
<class>com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Department</class>
<properties>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value = "jdbc:mysql://:3306/jpadb"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value = "root"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value="root"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name = "eclipselink.logging.level" value = "FINE"/>
<property name = "eclipselink.ddl-generation" value = "create-tables"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
服務類
此模組包含服務類,這些類使用屬性初始化實現關係部分。在 **src** 包下建立一個名為 **‘com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.service’** 的包。在給定的包下建立一個名為 **ManyToOne.java** 的 DAO 類。DAO 類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspointeclipselink.service;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.persistence.Persistence;
import com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Department;
import com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Employee;
public class ManyToOne {
public static void main( String[ ] args ) {
EntityManagerFactory emfactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory( "Eclipselink_JPA" );
EntityManager entitymanager = emfactory.createEntityManager( );
entitymanager.getTransaction( ).begin( );
//Create Department Entity
Department department = new Department();
department.setName("Development");
//Store Department
entitymanager.persist(department);
//Create Employee1 Entity
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setEname("Satish");
employee1.setSalary(45000.0);
employee1.setDeg("Technical Writer");
employee1.setDepartment(department);
//Create Employee2 Entity
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setEname("Krishna");
employee2.setSalary(45000.0);
employee2.setDeg("Technical Writer");
employee2.setDepartment(department);
//Create Employee3 Entity
Employee employee3 = new Employee();
employee3.setEname("Masthanvali");
employee3.setSalary(50000.0);
employee3.setDeg("Technical Writer");
employee3.setDepartment(department);
//Store Employees
entitymanager.persist(employee1);
entitymanager.persist(employee2);
entitymanager.persist(employee3);
entitymanager.getTransaction().commit();
entitymanager.close();
emfactory.close();
}
}
編譯並執行上述程式後,您將在 Eclipse IDE 的控制檯面板中收到通知。對於輸出,請檢查 MySQL Workbench。在此示例中,建立了兩個表。
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,部門表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from department; Id Name 101 Development
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,員工表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from employee; Eid Deg Ename Salary Department_Id 102 Technical Writer Satish 45000 101 103 Technical Writer Krishna 45000 101 104 Technical Writer Masthan Wali 50000 101
在上表中,Deparment_Id 是來自部門表的外部索引鍵(引用欄位)。
@OneToMany 關係
在此關係中,一個實體的每一行都引用另一個實體中的許多子記錄。重要的是,子記錄不能有多個父記錄。在一個表 A 和表 B 之間的一對多關係中,表 A 中的每一行都連結到表 B 中的 0、1 或多行。
讓我們考慮上面的例子。如果 **Employee** 和 **Department** 以反向單向方式存在,則關係為多對一關係。在 Eclipse IDE 中建立一個名為 **JPA_Eclipselink_OTM** 的 JPA 專案。該專案的所有模組如下所示:
建立實體
按照上面給出的圖建立實體。在 **src** 包下建立一個名為 **‘com.tutorialspoin.eclipselink.entity’** 的包。在給定的包下建立一個名為 **Department.java** 的類。Department 實體類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
@Entity
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue( strategy=GenerationType.AUTO )
private int id;
private String name;
@OneToMany( targetEntity=Employee.class )
private List employeelist;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName( ) {
return name;
}
public void setName( String deptName ) {
this.name = deptName;
}
public List getEmployeelist() {
return employeelist;
}
public void setEmployeelist(List employeelist) {
this.employeelist = employeelist;
}
}
在此關係中建立第二個實體 - 在 **‘com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity’** 包下建立一個名為 **Employee.java** 的 Employee 實體類。Employee 實體類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue( strategy= GenerationType.AUTO )
private int eid;
private String ename;
private double salary;
private String deg;
public Employee(int eid, String ename, double salary, String deg) {
super( );
this.eid = eid;
this.ename = ename;
this.salary = salary;
this.deg = deg;
}
public Employee( ) {
super();
}
public int getEid( ) {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getEname( ) {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public double getSalary( ) {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getDeg( ) {
return deg;
}
public void setDeg(String deg) {
this.deg = deg;
}
}
persistence.xml
在建立 JPA 專案時,persistence.xml 檔案將由 Eclipse IDE 建立。配置細節是使用者指定的。persistence.xml 檔案如下所示:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<persistence version = "2.0" xmlns = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd">
<persistence-unit name = "Eclipselink_JPA" transaction-type = "RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<class>com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Employee</class>
<class>com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Department</class>
<properties>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value = "jdbc:mysql://:3306/jpadb"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value = "root"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value = "root"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name = "eclipselink.logging.level" value = "FINE"/>
<property name = "eclipselink.ddl-generation" value = "create-tables"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
服務類
此模組包含服務類,這些類使用屬性初始化實現關係部分。在 **src** 包下建立一個名為 **‘com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.service’** 的包。在給定的包下建立一個名為 **OneToMany.java** 的 DAO 類。DAO 類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspointeclipselink.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.persistence.Persistence;
import com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Department;
import com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Employee;
public class OneToMany {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emfactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory( "Eclipselink_JPA" );
EntityManager entitymanager = emfactory.createEntityManager( );
entitymanager.getTransaction( ).begin( );
//Create Employee1 Entity
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setEname("Satish");
employee1.setSalary(45000.0);
employee1.setDeg("Technical Writer");
//Create Employee2 Entity
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setEname("Krishna");
employee2.setSalary(45000.0);
employee2.setDeg("Technical Writer");
//Create Employee3 Entity
Employee employee3 = new Employee();
employee3.setEname("Masthanvali");
employee3.setSalary(50000.0);
employee3.setDeg("Technical Writer");
//Store Employee
entitymanager.persist(employee1);
entitymanager.persist(employee2);
entitymanager.persist(employee3);
//Create Employeelist
List<Employee> emplist = new ArrayList();
emplist.add(employee1);
emplist.add(employee2);
emplist.add(employee3);
//Create Department Entity
Department department = new Department();
department.setName("Development");
department.setEmployeelist(emplist);
//Store Department
entitymanager.persist(department);
entitymanager.getTransaction().commit();
entitymanager.close();
emfactory.close();
}
}
編譯並執行上述程式後,您將在 Eclipse IDE 的控制檯面板中收到通知。對於輸出,請檢查 MySQL Workbench,如下所示。在此專案中建立了三個表。
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,department_employee 表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from department_Id; Department_Id Employee_Eid 254 251 254 252 254 253
在上表中,deparment_id 和 employee_id 欄位是來自部門表和員工表的外部索引鍵(引用欄位)。
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,部門表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from department; Id Name 254 Development
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,員工表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from employee; Eid Deg Ename Salary 251 Technical Writer Satish 45000 252 Technical Writer Krishna 45000 253 Technical Writer Masthanvali 50000
@OneToOne 關係
在一對一關係中,一個專案只能屬於另一個專案。這意味著一個實體的每一行都只引用另一個實體的一行。
讓我們考慮上面的例子。**Employee** 和 **Department** 以反向單向方式存在,則關係為一對一關係。這意味著每個員工只屬於一個部門。在 Eclipse IDE 中建立一個名為 **JPA_Eclipselink_OTO** 的 JPA 專案。該專案的所有模組如下所示:
建立實體
按照上面給出的圖建立實體。在 **src** 包下建立一個名為 **‘com.tutorialspoin.eclipselink.entity’** 的包。在給定的包下建立一個名為 **Department.java** 的類。Department 實體類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue( strategy=GenerationType.AUTO )
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName( ) {
return name;
}
public void setName( String deptName ) {
this.name = deptName;
}
}
在此關係中建立第二個實體 - 在 **‘com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity’** 包下建立一個名為 **Employee.java** 的 Employee 實體類。Employee 實體類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
@Entity
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue( strategy= GenerationType.AUTO )
private int eid;
private String ename;
private double salary;
private String deg;
@OneToOne
private Department department;
public Employee(int eid, String ename, double salary, String deg) {
super( );
this.eid = eid;
this.ename = ename;
this.salary = salary;
this.deg = deg;
}
public Employee( ) {
super();
}
public int getEid( ) {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getEname( ) {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public double getSalary( ) {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getDeg( ) {
return deg;
}
public void setDeg(String deg) {
this.deg = deg;
}
public Department getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
}
persistence.xml
在建立 JPA 專案時,persistence.xml 檔案將由 Eclipse IDE 建立。配置細節是使用者指定的。persistence.xml 檔案如下所示:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<persistence version = "2.0" xmlns = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd">
<persistence-unit name = "Eclipselink_JPA" transaction-type = "RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<class>com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Employee</class>
<class>com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Department</class>
<properties>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value = "jdbc:mysql://:3306/jpadb"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value = "root"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value = "root"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name = "eclipselink.logging.level" value = "FINE"/>
<property name = "eclipselink.ddl-generation" value = "create-tables"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
服務類
此模組包含服務類,這些類使用屬性初始化實現關係部分。在 **src** 包下建立一個名為 **‘com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.service’** 的包。在給定的包下建立一個名為 **OneToOne.java** 的 DAO 類。DAO 類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspointeclipselink.service;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.persistence.Persistence;
import com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Department;
import com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Employee;
public class OneToOne {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emfactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory( "Eclipselink_JPA" );
EntityManager entitymanager = emfactory.createEntityManager( );
entitymanager.getTransaction( ).begin( );
//Create Department Entity
Department department = new Department();
department.setName("Development");
//Store Department
entitymanager.persist(department);
//Create Employee Entity
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setEname("Satish");
employee.setSalary(45000.0);
employee.setDeg("Technical Writer");
employee.setDepartment(department);
//Store Employee
entitymanager.persist(employee);
entitymanager.getTransaction().commit();
entitymanager.close();
emfactory.close();
}
}
編譯並執行上述程式後,您將在 Eclipse IDE 的控制檯面板中收到通知。對於輸出,請檢查 MySQL Workbench,如下所示。在上面的示例中,建立了兩個表。
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,department 表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from department Id Name 301 Development
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,employee 表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from employee Eid Deg Ename Salary Department_id 302 Technical Writer Satish 45000 301
@ManyToMany 關係
多對多關係是指一個實體的一行或多行與另一個實體的多行相關聯。
讓我們考慮一下班級和教師實體之間關係的示例。在雙向方式下,班級和教師都具有多對一關係。這意味著每個班級的記錄都被教師集(教師 ID)引用,這些 ID 應該是教師表中的主鍵,並存儲在 Teacher_Class 表中,反之亦然。此處,Teachers_Class 表包含兩個外部索引鍵欄位。在 Eclipse IDE 中建立一個名為 **JPA_Eclipselink_MTM** 的 JPA 專案。該專案的所有模組如下所示:
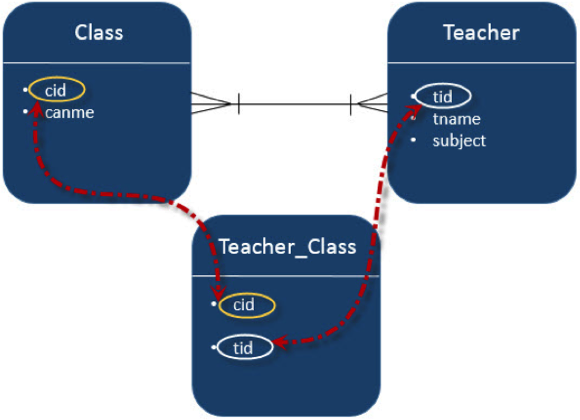
建立實體
按照上面給出的圖建立實體。在 **src** 包下建立一個名為 **‘com.tutorialspoin.eclipselink.entity’** 的包。在給定的包下建立一個名為 **Clas.java** 的類。Department 實體類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
@Entity
public class Clas {
@Id
@GeneratedValue( strategy = GenerationType.AUTO )
private int cid;
private String cname;
@ManyToMany(targetEntity=Teacher.class)
private Set teacherSet;
public Clas(){
super();
}
public Clas(int cid, String cname, Set teacherSet) {
super();
this.cid = cid;
this.cname = cname;
this.teacherSet = teacherSet;
}
public int getCid(){
return cid;
}
public void setCid(int cid) {
this.cid = cid;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public Set getTeacherSet() {
return teacherSet;
}
public void setTeacherSet(Set teacherSet) {
this.teacherSet = teacherSet;
}
}
在此關係中建立第二個實體 - 在 **‘com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity’** 包下建立一個名為 **Teacher.java** 的 Employee 實體類。Employee 實體類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
@Entity
public class Teacher {
@Id
@GeneratedValue( strategy = GenerationType.AUTO )
private int tid;
private String tname;
private String subject;
@ManyToMany(targetEntity = Clas.class)
private Set clasSet;
public Teacher(){
super();
}
public Teacher(int tid, String tname, String subject, Set clasSet) {
super();
this.tid = tid;
this.tname = tname;
this.subject = subject;
this.clasSet = clasSet;
}
public int getTid() {
return tid;
}
public void setTid(int tid) {
this.tid = tid;
}
public String getTname() {
return tname;
}
public void setTname(String tname) {
this.tname = tname;
}
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public Set getClasSet() {
return clasSet;
}
public void setClasSet(Set clasSet) {
this.clasSet = clasSet;
}
}
persistence.xml
在建立 JPA 專案時,persistence.xml 檔案將由 Eclipse IDE 建立。配置細節是使用者指定的。persistence.xml 檔案如下所示:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<persistence version = "2.0" xmlns = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd">
<persistence-unit name = "Eclipselink_JPA" transaction-type = "RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<class>com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Employee</class>
<class>com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Department</class>
<properties>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value = "jdbc:mysql://:3306/jpadb"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value = "root"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value = "root"/>
<property name = "javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name = "eclipselink.logging.level" value = "FINE"/>
<property name = "eclipselink.ddl-generation" value = "create-tables"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
服務類
此模組包含服務類,這些類使用屬性初始化實現關係部分。在 **src** 包下建立一個名為 **‘com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.service’** 的包。在給定的包下建立一個名為 **ManyToMany.java** 的 DAO 類。DAO 類如下所示:
package com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.service;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.persistence.Persistence;
import com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Clas;
import com.tutorialspoint.eclipselink.entity.Teacher;
public class ManyToMany {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emfactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory( "Eclipselink_JPA" );
EntityManager entitymanager = emfactory.createEntityManager( );
entitymanager.getTransaction( ).begin( );
//Create Clas Entity
Clas clas1 = new Clas(0, "1st", null);
Clas clas2 = new Clas(0, "2nd", null);
Clas clas3 = new Clas(0, "3rd", null);
//Store Clas
entitymanager.persist(clas1);
entitymanager.persist(clas2);
entitymanager.persist(clas3);
//Create Clas Set1
Set<Clas> classSet1 = new HashSet();
classSet1.add(clas1);
classSet1.add(clas2);
classSet1.add(clas3);
//Create Clas Set2
Set<Clas> classSet2 = new HashSet();
classSet2.add(clas3);
classSet2.add(clas1);
classSet2.add(clas2);
//Create Clas Set3
Set<Clas> classSet3 = new HashSet();
classSet3.add(clas2);
classSet3.add(clas3);
classSet3.add(clas1);
//Create Teacher Entity
Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher(0, "Satish","Java",classSet1);
Teacher teacher2 = new Teacher(0, "Krishna","Adv Java",classSet2);
Teacher teacher3 = new Teacher(0, "Masthanvali","DB2",classSet3);
//Store Teacher
entitymanager.persist(teacher1);
entitymanager.persist(teacher2);
entitymanager.persist(teacher3);
entitymanager.getTransaction( ).commit( );
entitymanager.close( );
emfactory.close( );
}
}
編譯並執行上述程式後,您將在 Eclipse IDE 的控制檯面板中收到通知。對於輸出,請檢查 MySQL Workbench,如下所示。在此示例專案中,建立了三個表。
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,teacher_clas 表的表格格式結果如下所示。
Select * form teacher_clas; Teacher _tid Classet_cid 354 351 355 351 356 351 354 352 355 352 356 352 354 353 355 353 356 353
在上表中,teacher_tid 是來自教師表的外部索引鍵,classet_cid 是來自班級表的外部索引鍵。因此,不同的教師被分配到不同的班級。
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,教師表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from teacher; Tid Subject Tname 354 Java Satish 355 Adv Java Krishna 356 DB2 Masthanvali
在 MySQL 介面中傳遞以下查詢,clas 表的表格格式結果如下所示:
Select * from clas; cid Cname 351 1st 352 2nd 353 3rd