- Java BeanUtils 教程
- Java BeanUtils - 首頁
- Java BeanUtils - 概述
- 動態 Bean (DynaBeans)
- 背景
- 基本 DynaBeans
- ResultSetDynaClass
- RowSetDynaClass
- WrapDynaBean
- 延遲 DynaBeans
- 資料型別轉換
- 背景
- BeanUtils 和 ConvertUtils
- 建立自定義轉換器
- 區域感知轉換
- 實用工具物件和類
- 實用工具物件和類
Java BeanUtils - 基本屬性訪問
描述
您可以透過以下方式訪問基本屬性
簡單屬性
索引屬性
對映屬性
簡單屬性
您可以使用以下 API 簽名獲取和設定**簡單**屬性值
PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(Object, String)
PropertyUtils.setSimpleProperty(Object, String, Object)
引數
**Object**: 它是一個 Bean 物件,指定要提取的 Bean 屬性。
**String**: 它是一個字串名稱,指定要提取的屬性的名稱。
索引屬性
您可以使用兩種方法建立**索引**屬性;第一種方法是將下標構建到屬性名稱中,第二種方法是在單獨的引數中定義下標以呼叫該方法。
可以使用以下方法獲取和設定索引屬性
PropertyUtils.getIndexedProperty(Object, String)
PropertyUtils.getIndexedProperty(Object, String, int)
PropertyUtils.setIndexedProperty(Object, String, Object)
PropertyUtils.setIndexedProperty(Object, String, int, Object)
引數
**Object**: 它是一個 Bean 物件,指定要提取的 Bean 屬性。
**String**: 它是一個字串名稱,指定要提取的屬性的名稱。
**int**: 它設定屬性值的索引。
**Object**: 它指定索引屬性元素的值。
對映屬性
您可以使用以下 API 簽名獲取和設定**對映**屬性值。如果您有任何額外的引數,則可以使用括號 ("(" 和 ")") 而不是方括號。
PropertyUtils.getMappedProperty(Object, String)
PropertyUtils.getMappedProperty(Object, String, String)
PropertyUtils.setMappedProperty(Object, String, Object)
PropertyUtils.setMappedProperty(Object, String, String, Object)
引數
**Object**: 它是一個 Bean 物件,指定要提取的 Bean 屬性。
**String**: 它是應為對映屬性設定的屬性值的名稱。
**String**: 它定義要設定的屬性值的鍵。
**Object**: 它指定要設定的屬性的值。
示例
以下示例演示了在 beanUtils 中使用上述屬性
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BeanUtilsPropertyDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
// Creating the bean and allows to access getter and setter properties
MyBean myBean = new MyBean();
// Setting the properties on the myBean
PropertyUtils.setSimpleProperty(myBean, "stringProp", "Hello!This is a string");
PropertyUtils.setSimpleProperty(myBean, "floatProp", new Float(25.20));
// Getting the simple properties
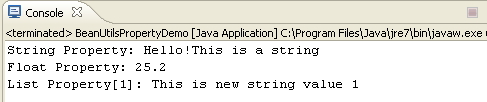
System.out.println("String Property: " + PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(myBean, "stringProp"));
System.out.println("Float Property: " + PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(myBean, "floatProp"));
// Here we will create a list for the indexed property
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("String value 0");
list.add("String value 1");
myBean.setListProp(list);
// get and set this indexed property
PropertyUtils.setIndexedProperty(myBean, "listProp[1]", "This is new string value 1");
System.out.println("List Property[1]: " + PropertyUtils.getIndexedProperty(myBean, "listProp[1]"));
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
現在,我們將建立一個名為 *MyBean.java* 的 Bean 類
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MyBean {
private String stringProp;
private float floatProp;
//indexed property
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private List listProp = new ArrayList();
public void setStringProp(String stringProp) { this.stringProp = stringProp; }
public String getStringProp() { return this.stringProp; }
public void setFloatProp(float floatProp) { this.floatProp = floatProp; }
public float getFloatProp() { return this.floatProp; }
public void setListProp(List<?> listProp) { this.listProp = listProp; }
public List<?> getListProp() { return this.listProp; }
}
輸出
讓我們執行以下步驟來檢視上述程式碼的工作方式
將上述第一段程式碼儲存為 *BeanUtilsPropertyDemo.java*。
現在使用“執行”選項或 Ctrl+F11 執行程式碼,並顯示如下輸出。