如何使用 TensorFlow 實現邏輯迴歸?
TensorFlow 是 Google 提供的一個機器學習框架。它是一個開源框架,與 Python 結合使用以實現演算法、深度學習應用程式等等。它用於研究和生產目的。它具有最佳化技術,有助於快速執行復雜的數學運算。這是因為它使用了 NumPy 和多維陣列。
多維陣列也稱為“張量”。該框架支援使用深度神經網路。它具有高度可擴充套件性,並附帶許多流行的資料集。它使用 GPU 計算並自動管理資源。
可以使用以下程式碼行在 Windows 上安裝“tensorflow”包:
pip install tensorflow
張量是 TensorFlow 中使用的一種資料結構。它有助於連線資料流圖中的邊。此資料流圖稱為“資料流圖”。張量只不過是多維陣列或列表。
MNIST 資料集包含手寫數字,其中 60000 個用於訓練模型,10000 個用於測試訓練後的模型。這些數字已進行大小歸一化和居中處理,以適應固定大小的影像。
以下是一個示例:
示例
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
num_classes = 10
num_features = 784
learning_rate = 0.01
training_steps = 1000
batch_size = 256
display_step = 50
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = np.array(x_train, np.float32), np.array(x_test, np.float32)
x_train, x_test = x_train.reshape([-1, num_features]), x_test.reshape([−1, num_features])
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255., x_test / 255.
train_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
train_data = train_data.repeat().shuffle(5000).batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)
A = tf.Variable(tf.ones([num_features, num_classes]), name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_classes]), name="bias")
def logistic_reg(x):
return tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, A) + b)
def cross_entropy(y_pred, y_true):
y_true = tf.one_hot(y_true, depth=num_classes)
y_pred = tf.clip_by_value(y_pred, 1e−9, 1.)
return tf.reduce_mean(−tf.reduce_sum(y_true * tf.math.log(y_pred),1))
def accuracy_val(y_pred, y_true):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pred, 1), tf.cast(y_true, tf.int64))
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
optimizer = tf.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate)
def run_optimization(x, y):
with tf.GradientTape() as g:
pred = logistic_reg(x)
loss = cross_entropy(pred, y)
gradients = g.gradient(loss, [A, b])
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, [A, b]))
for step, (batch_x, batch_y) in enumerate(train_data.take(training_steps), 1):
run_optimization(batch_x, batch_y)
if step % display_step == 0:
pred = logistic_regression(batch_x)
loss = cross_entropy(pred, batch_y)
acc = accuracy_val(pred, batch_y)
print("step: %i, loss: %f, accuracy: %f" % (step, loss, acc))
pred = logistic_reg(x_test)
print("Test accuracy is : %f" % accuracy_val(pred, y_test))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n_images = 4
test_images = x_test[:n_images]
predictions = logistic_reg(test_images)
for i in range(n_images):
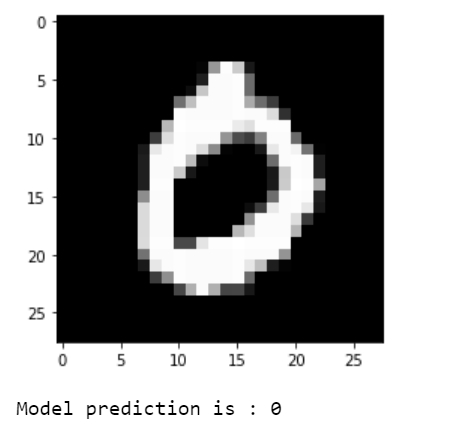
plt.imshow(np.reshape(test_images[i], [28, 28]), cmap='gray')
plt.show()
print("Model prediction is : %i" % np.argmax(predictions.numpy()[i]))輸出
step: 50, loss: 2.301992, accuracy: 0.132812 step: 100, loss: 2.301754, accuracy: 0.125000 step: 150, loss: 2.303200, accuracy: 0.117188 step: 200, loss: 2.302409, accuracy: 0.117188 step: 250, loss: 2.303324, accuracy: 0.101562 step: 300, loss: 2.301391, accuracy: 0.113281 step: 350, loss: 2.299984, accuracy: 0.140625 step: 400, loss: 2.303896, accuracy: 0.093750 step: 450, loss: 2.303662, accuracy: 0.093750 step: 500, loss: 2.297976, accuracy: 0.148438 step: 550, loss: 2.300465, accuracy: 0.121094 step: 600, loss: 2.299437, accuracy: 0.140625 step: 650, loss: 2.299458, accuracy: 0.128906 step: 700, loss: 2.302172, accuracy: 0.117188 step: 750, loss: 2.306451, accuracy: 0.101562 step: 800, loss: 2.303451, accuracy: 0.109375 step: 850, loss: 2.303128, accuracy: 0.132812 step: 900, loss: 2.307874, accuracy: 0.089844 step: 950, loss: 2.309694, accuracy: 0.082031 step: 1000, loss: 2.302263, accuracy: 0.097656 Test accuracy is : 0.869700
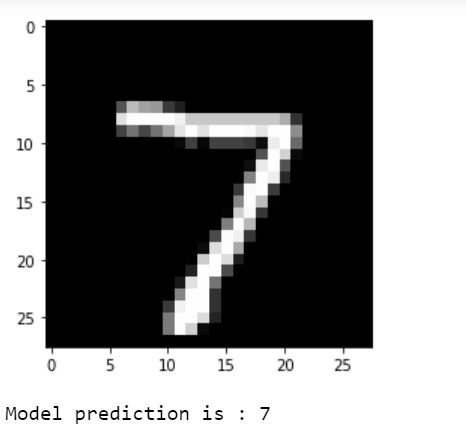
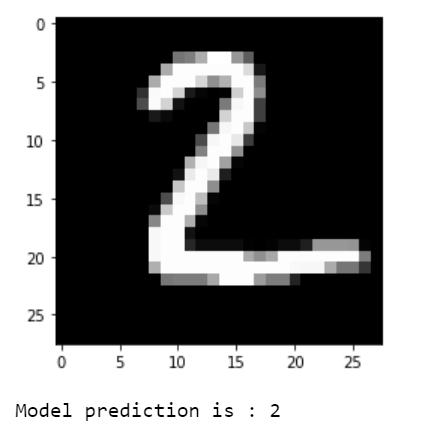
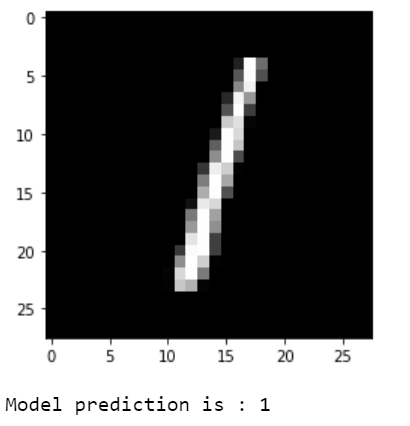
解釋
匯入併為所需的包設定別名。
定義 MNIST 資料集的學習引數。
從源載入 MNIST 資料集。
將資料集拆分為訓練資料集和測試資料集。資料集中的影像被展平為具有 28 x 28 = 784 個特徵的一維向量。
影像值被歸一化到 [0,1] 而不是 [0,255]。
定義了一個名為“logistic_reg”的函式,該函式給出輸入資料的 softmax 值。它將 logits 歸一化為機率分佈。
定義交叉熵損失函式,它將標籤編碼為獨熱向量。預測值被格式化以減少 log(0) 錯誤。
需要計算準確性指標,因此定義了一個函式。
定義隨機梯度下降最佳化器。
定義了一個用於最佳化的函式,該函式計算梯度並更新權重和偏差的值。
對資料進行指定步數的訓練。
在驗證集上測試構建的模型。
視覺化預測結果。

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係型資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP