
- Groovy 教程
- Groovy - 首頁
- Groovy - 概述
- Groovy - 環境配置
- Groovy - 基本語法
- Groovy - 資料型別
- Groovy - 變數
- Groovy - 運算子
- Groovy - 迴圈
- Groovy - 條件判斷
- Groovy - 方法
- Groovy - 檔案 I/O
- Groovy - 可選值
- Groovy - 數字
- Groovy - 字串
- Groovy - 範圍
- Groovy - 列表
- Groovy - 對映
- Groovy - 日期和時間
- Groovy - 正則表示式
- Groovy - 異常處理
- Groovy - 面向物件程式設計
- Groovy - 泛型
- Groovy - 特性
- Groovy - 閉包
- Groovy - 註解
- Groovy - XML
- Groovy - JMX
- Groovy - JSON
- Groovy - DSL
- Groovy - 資料庫
- Groovy - 構造器
- Groovy - 命令列
- Groovy - 單元測試
- Groovy - 模板引擎
- Groovy - 元物件程式設計
- Groovy 有用資源
- Groovy - 快速指南
- Groovy - 有用資源
- Groovy - 討論
Groovy - 異常處理
任何程式語言都需要異常處理來處理執行時錯誤,以便維護應用程式的正常流程。
異常通常會中斷應用程式的正常流程,這就是為什麼我們需要在應用程式中使用異常處理的原因。
異常大致分為以下幾類:
檢查異常 - 擴充套件 Throwable 類但不包括 RuntimeException 和 Error 的類被稱為檢查異常,例如 IOException、SQLException 等。檢查異常在編譯時進行檢查。
一個典型的例子是 FileNotFoundException。假設您的應用程式中有以下程式碼從 E 盤讀取檔案。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("E://file.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
}
}
如果 E 盤中不存在該檔案 (file.txt),則會引發以下異常。
捕獲到:java.io.FileNotFoundException: E:\file.txt (系統找不到指定的檔案)。
java.io.FileNotFoundException: E:\file.txt (系統找不到指定的檔案)。
未檢查異常 - 擴充套件 RuntimeException 的類被稱為未檢查異常,例如 ArithmeticException、NullPointerException、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 等。未檢查異常不在編譯時檢查,而是在執行時檢查。
一個典型的例子是 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,它發生在您嘗試訪問陣列索引超出陣列長度時。以下是一個此類錯誤的典型示例。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
}
}
執行上述程式碼時,將引發以下異常。
捕獲到:java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5
錯誤 - 錯誤是不可恢復的,例如 OutOfMemoryError、VirtualMachineError、AssertionError 等。
這些是程式無法從中恢復的錯誤,並將導致程式崩潰。
下圖顯示了 Groovy 中異常的繼承結構。它完全基於 Java 中定義的繼承結構。
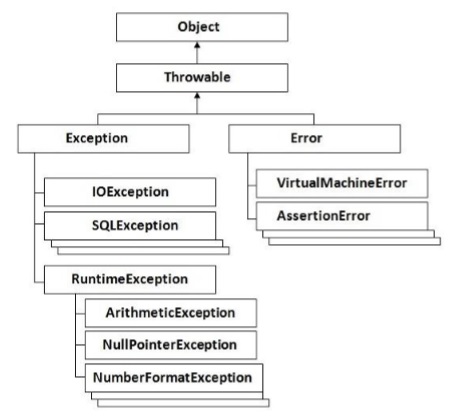
捕獲異常
方法使用try和catch關鍵字的組合來捕獲異常。try/catch 塊放置在可能生成異常的程式碼周圍。
try {
//Protected code
} catch(ExceptionName e1) {
//Catch block
}
所有可能引發異常的程式碼都放在受保護的程式碼塊中。
在 catch 塊中,您可以編寫自定義程式碼來處理異常,以便應用程式可以從異常中恢復。
讓我們來看一個與上面類似的例子,訪問陣列的索引值大於陣列大小。但是這次讓我們將程式碼包裝在 try/catch 塊中。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
try {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
} catch(Exception ex) {
println("Catching the exception");
}
println("Let's move on after the exception");
}
}
執行上述程式時,我們將得到以下結果:
Catching the exception Let's move on after the exception
從上面的程式碼中,我們將有問題的程式碼包裝在 try 塊中。在 catch 塊中,我們只是捕獲異常並輸出一條訊息,指出發生了異常。
多個 catch 塊
可以使用多個 catch 塊來處理多種型別的異常。對於每個 catch 塊,根據引發的異常型別,您可以編寫相應的程式碼來處理它。
讓我們修改上面的程式碼來專門捕獲 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。以下是用程式碼片段。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
try {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
println("Catching the Array out of Bounds exception");
}catch(Exception ex) {
println("Catching the exception");
}
println("Let's move on after the exception");
}
}
執行上述程式時,我們將得到以下結果:
Catching the Aray out of Bounds exception Let's move on after the exception
從上面的程式碼可以看出,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException catch 塊首先被捕獲,因為它滿足異常的條件。
finally 塊
finally塊跟在 try 塊或 catch 塊之後。finally 塊的程式碼始終執行,無論是否發生異常。
使用 finally 塊允許您執行任何您想要執行的清理型別的語句,無論受保護的程式碼中發生什麼情況。此塊的語法如下所示。
try {
//Protected code
} catch(ExceptionType1 e1) {
//Catch block
} catch(ExceptionType2 e2) {
//Catch block
} catch(ExceptionType3 e3) {
//Catch block
} finally {
//The finally block always executes.
}
讓我們修改上面的程式碼並新增 finally 程式碼塊。以下是用程式碼片段。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
try {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
println("Catching the Array out of Bounds exception");
}catch(Exception ex) {
println("Catching the exception");
} finally {
println("The final block");
}
println("Let's move on after the exception");
}
}
執行上述程式時,我們將得到以下結果:
Catching the Array out of Bounds exception The final block Let's move on after the exception
以下是 Groovy 中可用的異常方法:
public String getMessage()
返回關於發生的異常的詳細訊息。此訊息在 Throwable 建構函式中初始化。
public Throwable getCause()
返回異常的原因,以 Throwable 物件表示。
public String toString()
返回類名與 getMessage() 結果的連線。
public void printStackTrace()
將 toString() 的結果以及堆疊跟蹤列印到 System.err(錯誤輸出流)。
public StackTraceElement [] getStackTrace()
返回一個包含堆疊跟蹤中每個元素的陣列。索引為 0 的元素表示呼叫堆疊的頂部,陣列中的最後一個元素表示呼叫堆疊底部的函式。
public Throwable fillInStackTrace()
使用當前堆疊跟蹤填充此 Throwable 物件的堆疊跟蹤,新增到堆疊跟蹤中的任何先前資訊。
示例
以下是使用上面一些方法的程式碼示例:
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
try {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
println(ex.toString());
println(ex.getMessage());
println(ex.getStackTrace());
} catch(Exception ex) {
println("Catching the exception");
}finally {
println("The final block");
}
println("Let's move on after the exception");
}
}
執行上述程式時,我們將得到以下結果:
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5 5 [org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.dgmimpl.arrays.IntegerArrayPutAtMetaMethod$MyPojoMetaMet hodSite.call(IntegerArrayPutAtMetaMethod.java:75), org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.callsite.CallSiteArray.defaultCall(CallSiteArray.java:48) , org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.callsite.AbstractCallSite.call(AbstractCallSite.java:113) , org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.callsite.AbstractCallSite.call(AbstractCallSite.java:133) , Example.main(Sample:8), sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method), sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57), sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) , java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606), org.codehaus.groovy.reflection.CachedMethod.invoke(CachedMethod.java:93), groovy.lang.MetaMethod.doMethodInvoke(MetaMethod.java:325), groovy.lang.MetaClassImpl.invokeStaticMethod(MetaClassImpl.java:1443), org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.InvokerHelper.invokeMethod(InvokerHelper.java:893), groovy.lang.GroovyShell.runScriptOrMainOrTestOrRunnable(GroovyShell.java:287), groovy.lang.GroovyShell.run(GroovyShell.java:524), groovy.lang.GroovyShell.run(GroovyShell.java:513), groovy.ui.GroovyMain.processOnce(GroovyMain.java:652), groovy.ui.GroovyMain.run(GroovyMain.java:384), groovy.ui.GroovyMain.process(GroovyMain.java:370), groovy.ui.GroovyMain.processArgs(GroovyMain.java:129), groovy.ui.GroovyMain.main(GroovyMain.java:109), sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method), sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57), sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) , java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606), org.codehaus.groovy.tools.GroovyStarter.rootLoader(GroovyStarter.java:109), org.codehaus.groovy.tools.GroovyStarter.main(GroovyStarter.java:131), sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method), sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57), sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) , java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606), com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:144)] The final block Let's move on after the exception