使用弗洛伊德·沃歇爾演算法查詢任意兩個節點之間的最短路徑
C++ 有一種宏,它被定義為一段程式碼或期望值,並且會在使用者需要時重複使用。弗洛伊德·沃歇爾演算法是在給定的加權圖中找到所有頂點對之間最短路徑的過程。該演算法遵循動態規劃方法來找到最小權重圖。
讓我們藉助圖表瞭解什麼是弗洛伊德·沃歇爾演算法 -
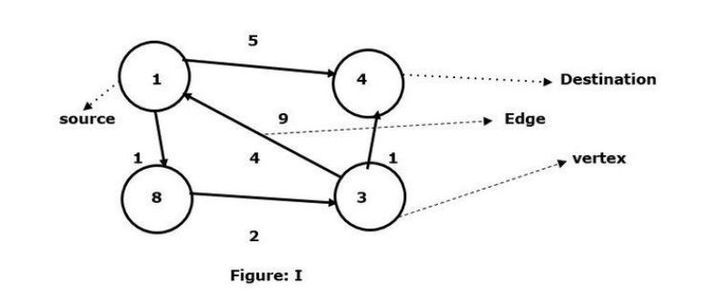
將頂點1作為源頂點,將頂點4作為目標頂點,並找到它們之間的最短路徑。
我們已經看到有兩條路徑可以連線到目標頂點 4。
1 -> 4 – 邊權重為 5
1 -> 8 -> 3 -> 4 – 邊權重 (1+2+1) 為 4。
在圖 I 中,我們看到兩個頂點之間連線的最小邊。因此,這裡頂點8和頂點3連線了頂點1到頂點4的路徑,邊的最小權重為4。另一方面,頂點1到頂點4之間有一條有向邊,邊的權重為5。
現在我們比較這兩個權重,即4和5。因此,這裡4是弗洛伊德·沃歇爾演算法意義上的圖的最小權重。
在本文中,我們將使用弗洛伊德·沃歇爾演算法解決任意兩個給定節點之間的最短路徑問題。
語法
程式中使用以下語法 -
data_type[][] array_name;
引數
data_type[][] - 使用者提到的資料型別。第一個陣列表示行,第二個陣列表示列。因此,這表示二維陣列。
array_name - 給陣列起的名字。
演算法
我們將從名為'iostream'的標頭檔案開始程式,並將宏位置定義為'INF'(無窮大),因為稍後它將遇到 2D 陣列矩陣和 if-else 語句。
接下來,我們建立名為'printPath'的全域性函式定義,並接受三個引數,即'parent[]'、'i'和'j',以驗證路徑是否存在。
然後我們開始主函式,並將值'4'儲存到變數'V'中,它表示頂點數。其次,將值以鄰接矩陣的形式儲存到'dist[V][V]'變數中。眾所周知,dist[i][j]表示定義從'i'到'j'的邊權重的二維矩陣,透過儲存鄰接矩陣來實現。
接下來,我們為'parent'變數初始化二維陣列,並具有大小[V][V]。
在此變數中,我們用於顯示每對頂點'i'和'j'相對於'parent[i][j]'。
透過使用兩個巢狀的 for 迴圈,我們將找到最短路徑。第一個 for 迴圈迭代矩陣中的行。繼續使用第二個 for 迴圈,它迭代矩陣中的列,然後我們將使用 if-else 語句檢查以下條件 -
if (dist[i][j] != INF && i != j){ parent[i][j] = i;}
在 if 語句中,我們使用'and' (&&)運算子來顯示兩個條件,如果這兩個條件都滿足,則'i'將儲存到'parent[i][j]'中,這驗證了路徑的存在。
else { parent[i][j] = -1;}
在 else 語句中,我們將'-1'初始化為'parent[i][j]',這驗證了路徑不存在。
現在我們從三個巢狀的for迴圈開始,並在 0 到 V-1 的範圍內應用 k 頂點,藉助此範圍,我們的最短距離和路徑將更新。在第三個巢狀迴圈內,我們使用以下條件,例如
if (dist[i][j] < dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]){
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
parent[i][j] = parent[k][j];
}
接下來,我們透過給出以下條件,列印所有頂點對的最短距離和路徑,例如
透過使用兩個巢狀的 for 迴圈,我們列印最短距離和路徑。
透過在第二個 for 迴圈下使用 if 語句,我們將檢查 dist[i][j] 是否等於無窮大。如果發現它為無窮大,則它將列印'INF',否則它將列印最短路徑。
最後,我們呼叫名為'printPath()'的函式以透過傳遞三個引數(即 parent[i]、i 和 j)來獲取最短路徑的值。
這裡 K 正在更新二維陣列矩陣中行和列的一部分,這驗證了新更新的最短路徑和距離。
示例
在此程式中,我們將使用弗洛伊德·沃歇爾演算法計算任意兩個節點之間的最短路徑。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define INF 1000000000 // Infinity
void printPath(int parent[], int i, int j) {
if (i == j)
cout << i << " ";
else if (parent[j] == -1)
cout << "No path exists";
else
{
printPath(parent, i, parent[j]);
cout << j << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
int V = 4;
// V represent number of vertices
int dist[V][V] = {{0, 2, INF, 4},
{6, 0, 5, 3},
{INF, 10, 0, 1},
{7, 9, 8, 0}};
// Represent the graph using adjacency matrix
// Apply the Floyd Warshall algorithm to find the shortest paths
int parent[V][V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
if (dist[i][j] != INF && i != j)
parent[i][j] = i;
else
parent[i][j] = -1;
}
}
// update the path and distance using the k vertex range from 0 to V-1.
for (int k = 0; k < V; k++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
if (dist[i][j] > dist[i][k] + dist[k][j])
{
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
parent[i][j] = parent[k][j];
}
}
}
}
// Print shortest distances and paths between all pairs of vertices
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
cout << "The Shortest distance between " << i << " and " << j << " is ";
if (dist[i][j] == INF)
cout << "INF ";
else
cout << dist[i][j] << " ";
cout << "and the shortest path is:- ";
printPath(parent[i], i, j);
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
輸出
The Shortest distance between 0 and 0 is 0 and the shortest path is:- 0 The Shortest distance between 0 and 1 is 2 and the shortest path is:- 0 1 The Shortest distance between 0 and 2 is 7 and the shortest path is:- 0 1 2 The Shortest distance between 0 and 3 is 4 and the shortest path is:- 0 3 The Shortest distance between 1 and 0 is 6 and the shortest path is:- 1 0 The Shortest distance between 1 and 1 is 0 and the shortest path is:- 1 The Shortest distance between 1 and 2 is 5 and the shortest path is:- 1 2 The Shortest distance between 1 and 3 is 3 and the shortest path is:- 1 3 The Shortest distance between 2 and 0 is 8 and the shortest path is:- 2 3 0 The Shortest distance between 2 and 1 is 10 and the shortest path is:- 2 1 The Shortest distance between 2 and 2 is 0 and the shortest path is:- 2 The Shortest distance between 2 and 3 is 1 and the shortest path is:- 2 3 The Shortest distance between 3 and 0 is 7 and the shortest path is:- 3 0 The Shortest distance between 3 and 1 is 9 and the shortest path is:- 3 1 The Shortest distance between 3 and 2 is 8 and the shortest path is:- 3 2 The Shortest distance between 3 and 3 is 0 and the shortest path is:- 3
結論
我們學習了使用弗洛伊德·沃歇爾演算法查詢任意兩個節點之間最短路徑的概念。我們使用鄰接矩陣作為程式的輸入,在其中找到最短路徑和距離。除此之外,為了更新路徑和距離,我們使用 k 頂點來更新行和列。在我們的日常生活中,我們在 Google 地圖上搜索從一個源到目的地的最短路線或路徑。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP